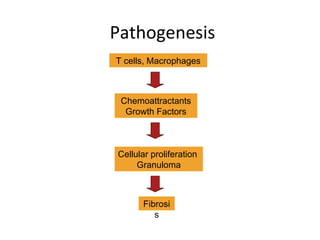
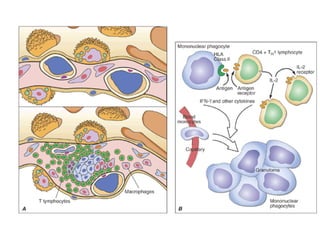
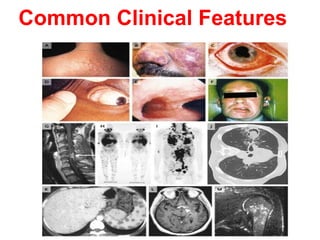
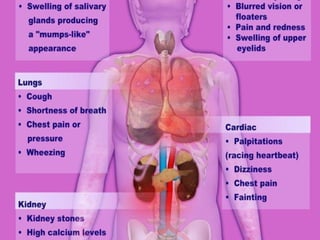
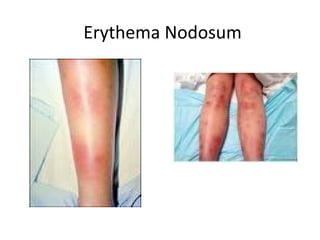
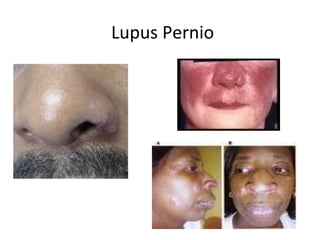
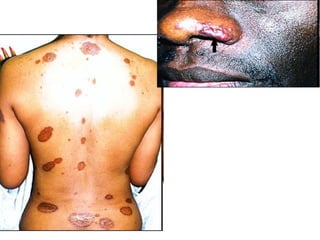
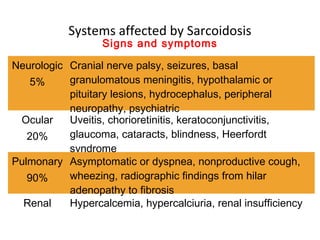
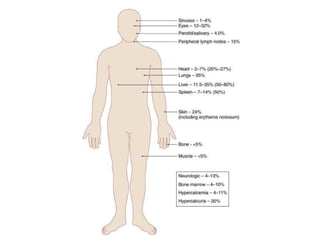
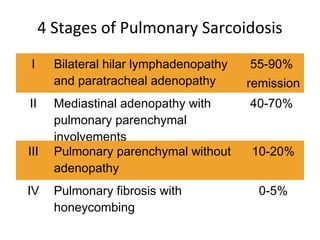
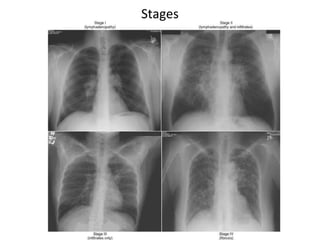
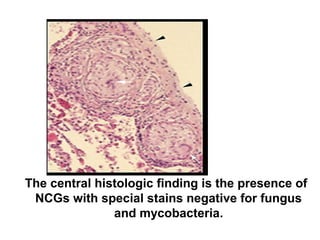
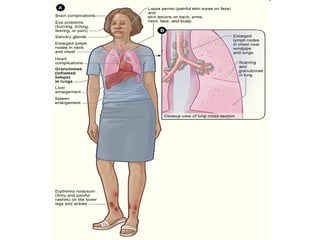
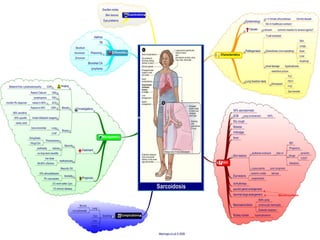
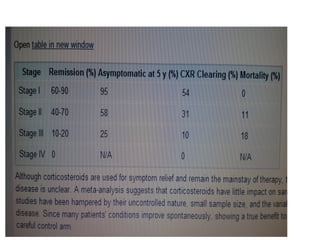
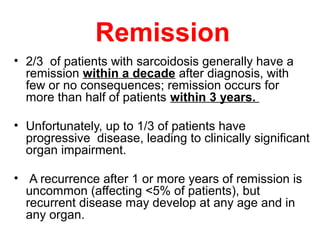
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem disorder characterized by noncaseating granulomas in affected tissues. It most commonly involves the lungs but can affect other organs. The cause is unknown but genetic and environmental factors are thought to play a role. Diagnosis is made through biopsy showing granulomas and excluding other causes. Treatment involves corticosteroids for organ involvement. Prognosis is generally good with remission occurring within 3 years for over half of patients.