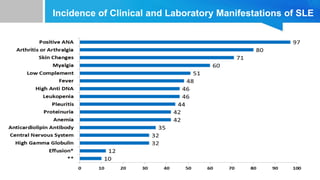
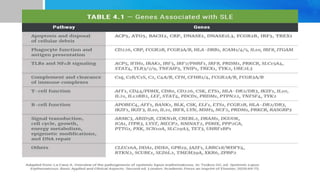
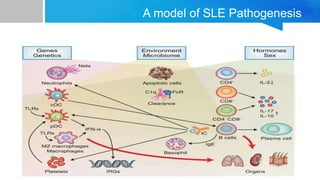
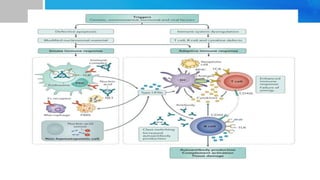
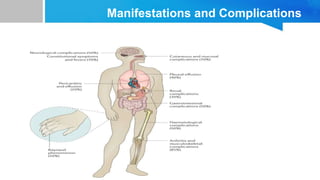
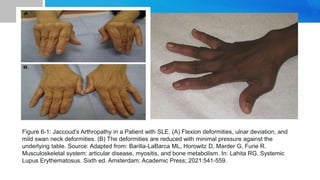
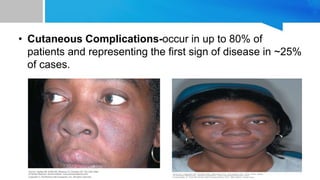
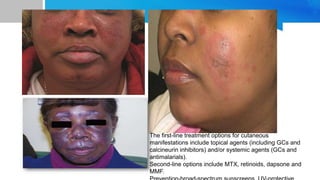
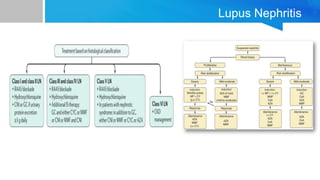
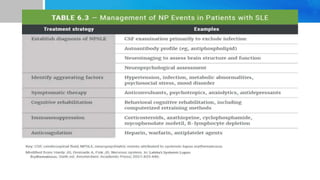
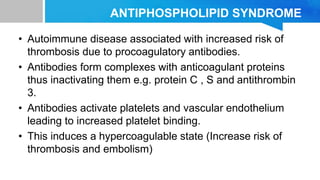
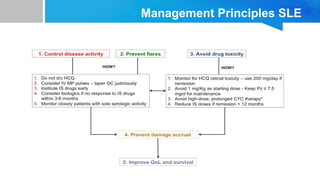
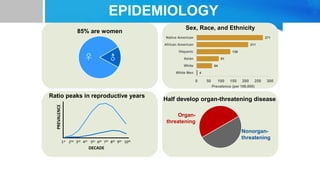
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by autoantibodies directed against self-antigens. It can affect many different organs and tissues in the body. Kelsey, a 23-year-old woman, presented with fatigue, joint pain, and a rash. Laboratory tests showed positive ANA, anti-DNA, low complement levels, meeting criteria for SLE. SLE results from genetic and environmental factors interacting to cause immune system dysregulation and loss of self-tolerance. It commonly affects the skin, joints, kidneys, and cardiovascular and pulmonary systems. Timely diagnosis and treatment can help prevent organ damage and disease complications.







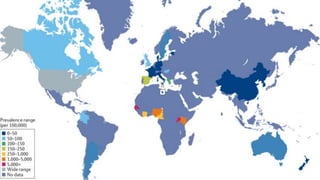
![Global and regional prevalence and incidence of systemic lupus
erythematosus in low-and-middle income countries: a systematic
review and meta-analysis- July 2022
The highest estimates of incidence and prevalence of SLE were in
Brazil [8.7(95% CI 6.3–11.7)/100 000 persons and in Kenya 3000
[95% 1800–5600]/100 000 persons, respectively. The lowest
incidences of SLE were reported in Ukraine (0.3 (95% CI 0.0–1.8)/100
000 people, and the lowest prevalence was in India 3.2 (95% CI 0–
6.86)/100,000 persons.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/systemiclupuserythematosuspresentation-240212194501-d93c72eb/85/SYSTEMIC-LUPUS-ERYTHEMATOSUS-PRESENTATION-pptx-8-320.jpg)


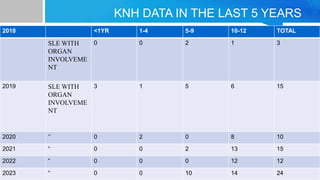

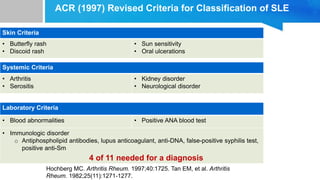

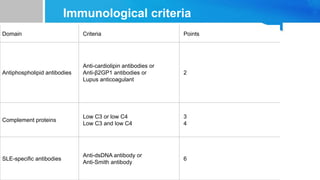
![2019 EULAR/ACR criteria2
Domain Criteria Points
Constitutional Fever 2
Hematologic
Leukopenia
Thrombocytopenia
Autoimmune hemolysis
3
4
4
Neuropsychiatric
Delirium
Psychosis
Seizure
2
3
5
Mucocutaneous
Non-scarring alopecia
Oral ulcers
Subacute cutaneous or discoid
lupus
Acute cutaneous lupus
2
2
4
6
Serosal
Pleural or pericardial effusion
Acute pericarditis
5
6
Musculoskeletal Joint involvement 6
Renal
Proteinuria > 0.5 g/24 h
Renal biopsy class II or V lupus
nephritis
Renal biopsy class III or IV lupus
nephritis
4
8
10
The European League Against
Rheumatism
(EULAR)/American College of
Rheumatology (ACR)
classification criteria for SLE
were developed to improve
detection of early or new-onset
SLE as well as improve the
sensitivity and
specificity compared
with previous criteria [1].
Patients with a score of 10 or
more points are classified as
having SLE. With a positive
ANA as an entry level](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/systemiclupuserythematosuspresentation-240212194501-d93c72eb/85/SYSTEMIC-LUPUS-ERYTHEMATOSUS-PRESENTATION-pptx-17-320.jpg)