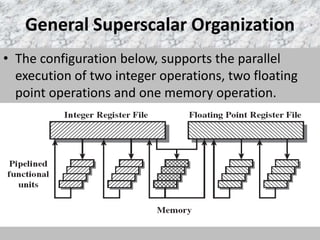
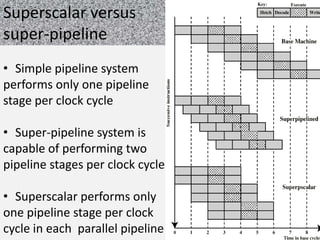
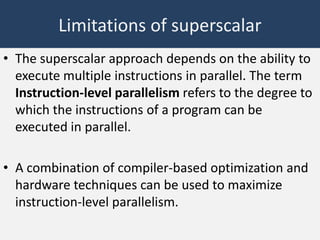
This document discusses superscalar and super pipeline approaches to improving processor performance. Superscalar processors execute multiple independent instructions in parallel using multiple pipelines. Super pipelines break pipeline stages into smaller stages to reduce clock period and increase instruction throughput. While superscalar utilizes multiple parallel pipelines, super pipelines perform multiple stages per clock cycle in each pipeline. Super pipelines benefit from higher parallelism but also increase potential stalls from dependencies. Both approaches aim to maximize parallel instruction execution but face limitations from true data and other dependencies.