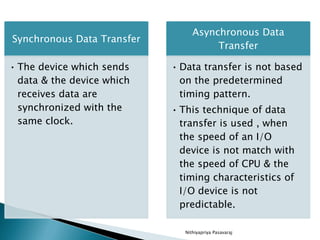
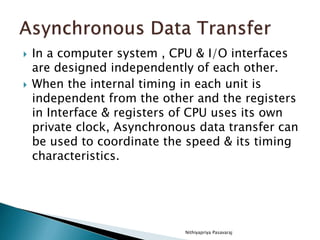
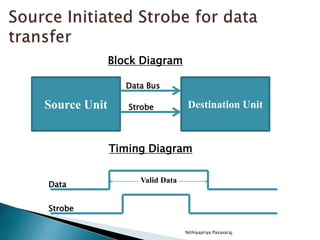
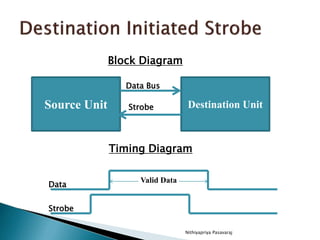
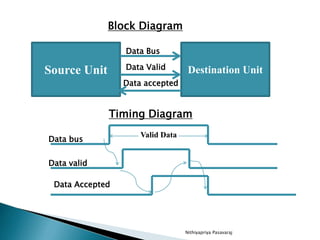
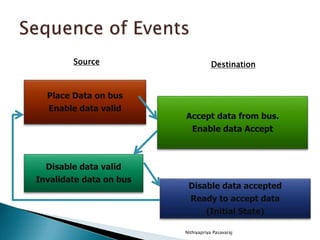
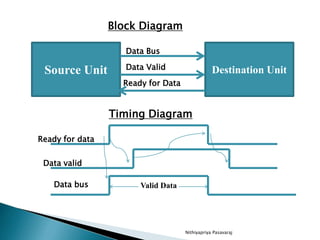
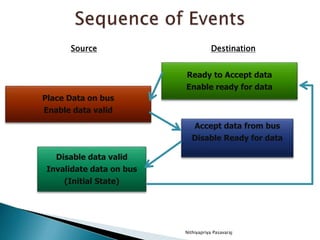
This document discusses asynchronous data transfer between independent units. It describes two methods for asynchronous transfer - strobe control and handshaking. Strobe control uses a single control line to time each transfer, while handshaking introduces a second control signal to provide confirmation between units. Specifically, it details the handshaking process, which involves control signals like "data valid" and "data accepted" or "ready for data" to coordinate placing data on the bus and accepting data between a source and destination unit.