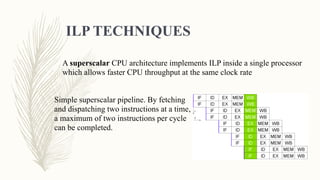
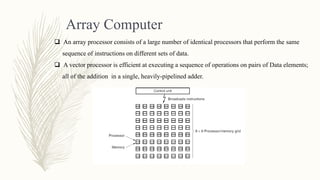
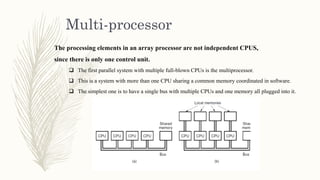
This document discusses parallelism and its goals of increasing computational speed and throughput. It describes two types of parallelism: instruction level parallelism and processor level parallelism. Instruction level parallelism techniques include pipelining and superscalar processing to allow multiple instructions to execute simultaneously. Processor level parallelism involves multiple independent processors working concurrently through approaches like array computers and multi-processors.