Embed presentation
Downloaded 31 times
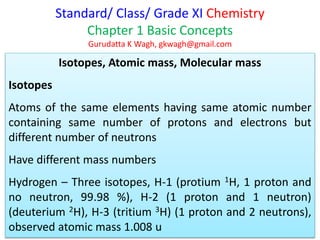


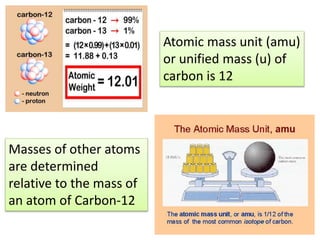



This document discusses isotopes, atomic mass, and molecular mass. It defines isotopes as atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons. Atomic mass is determined relative to carbon-12, which is assigned a mass of 12 atomic mass units. Molecular mass is calculated as the sum of the atomic masses of each atom in the molecular formula. It represents the mass of one molecule relative to 1/12 the mass of one carbon-12 atom.





