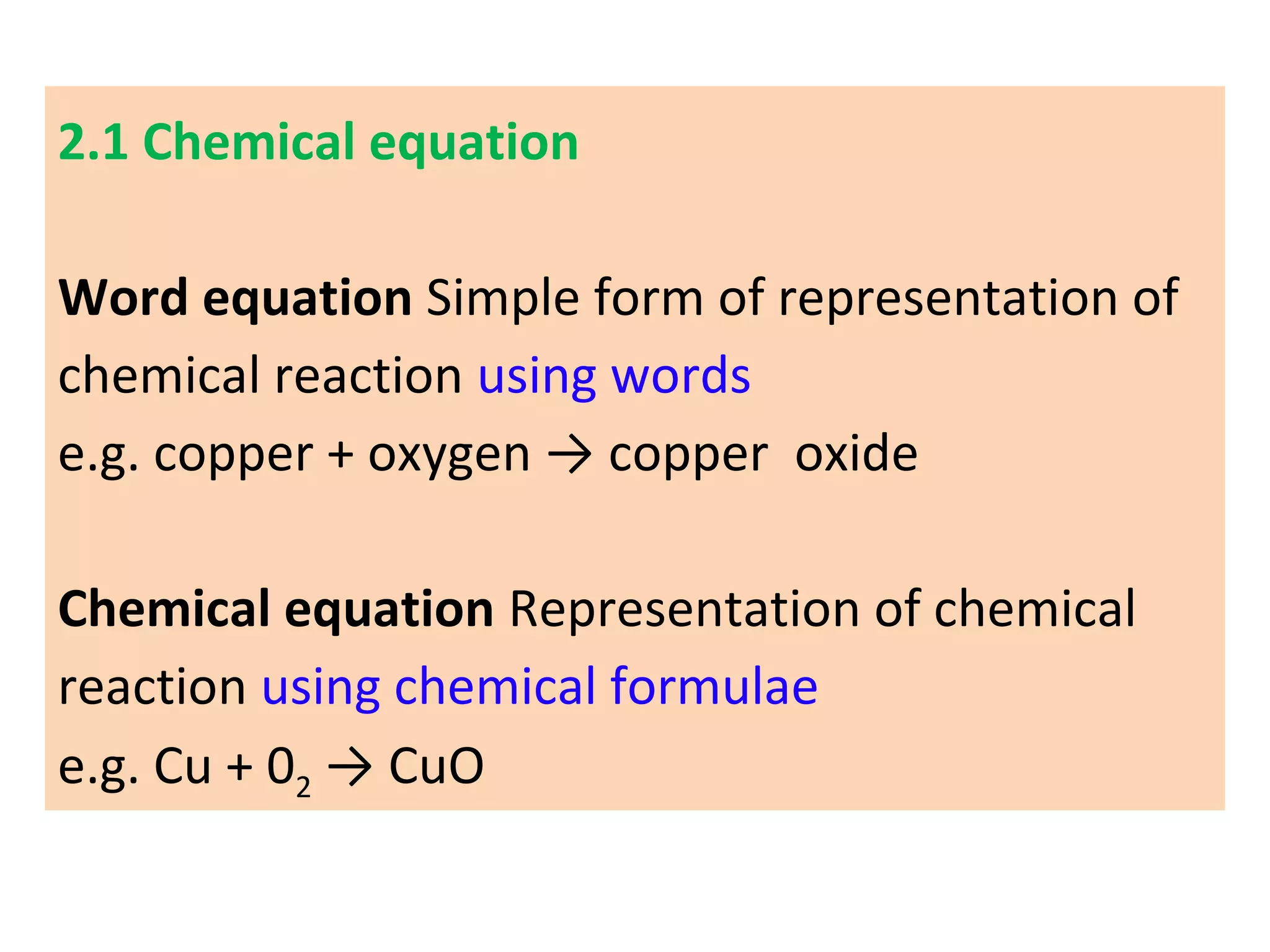
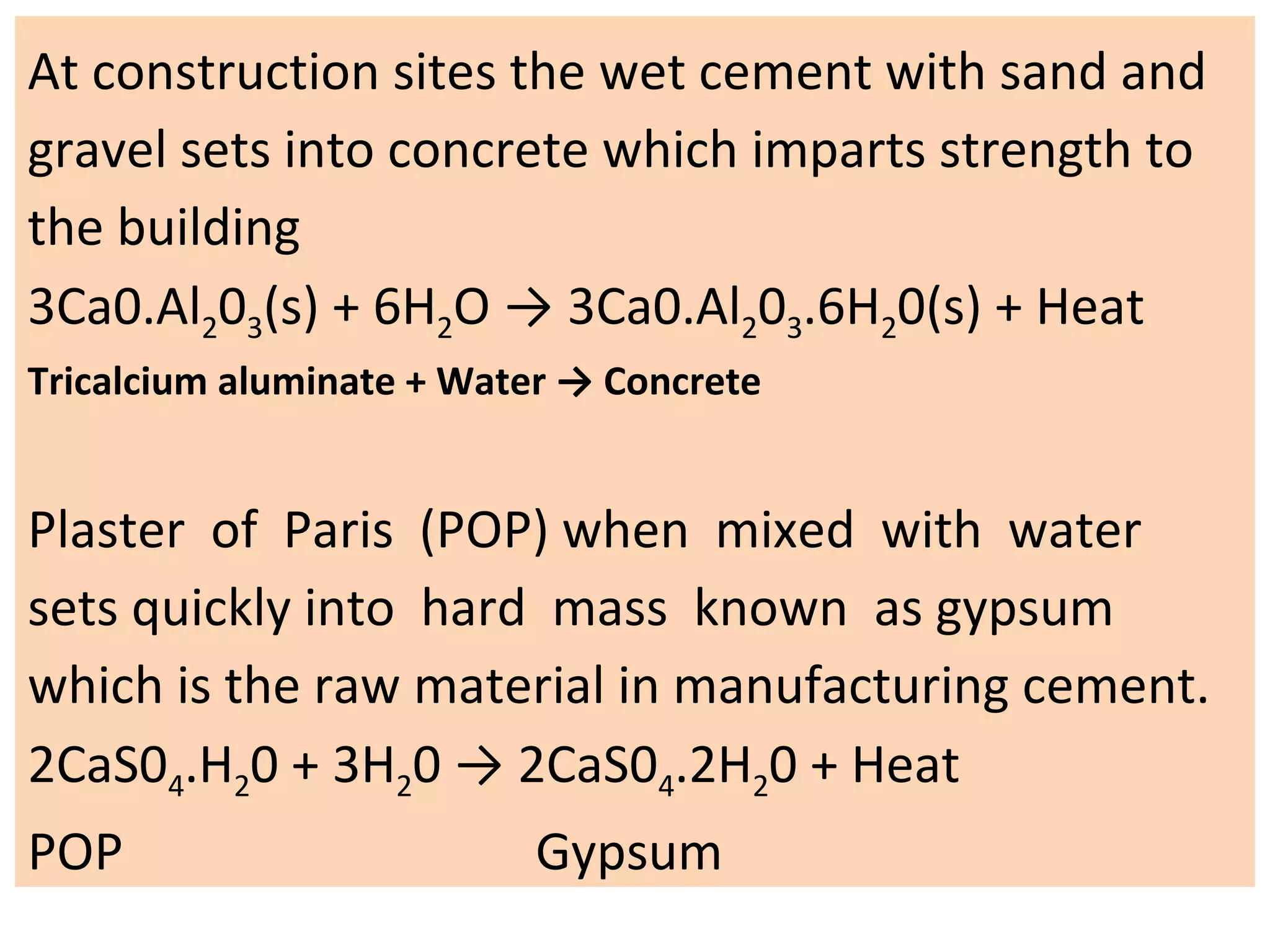
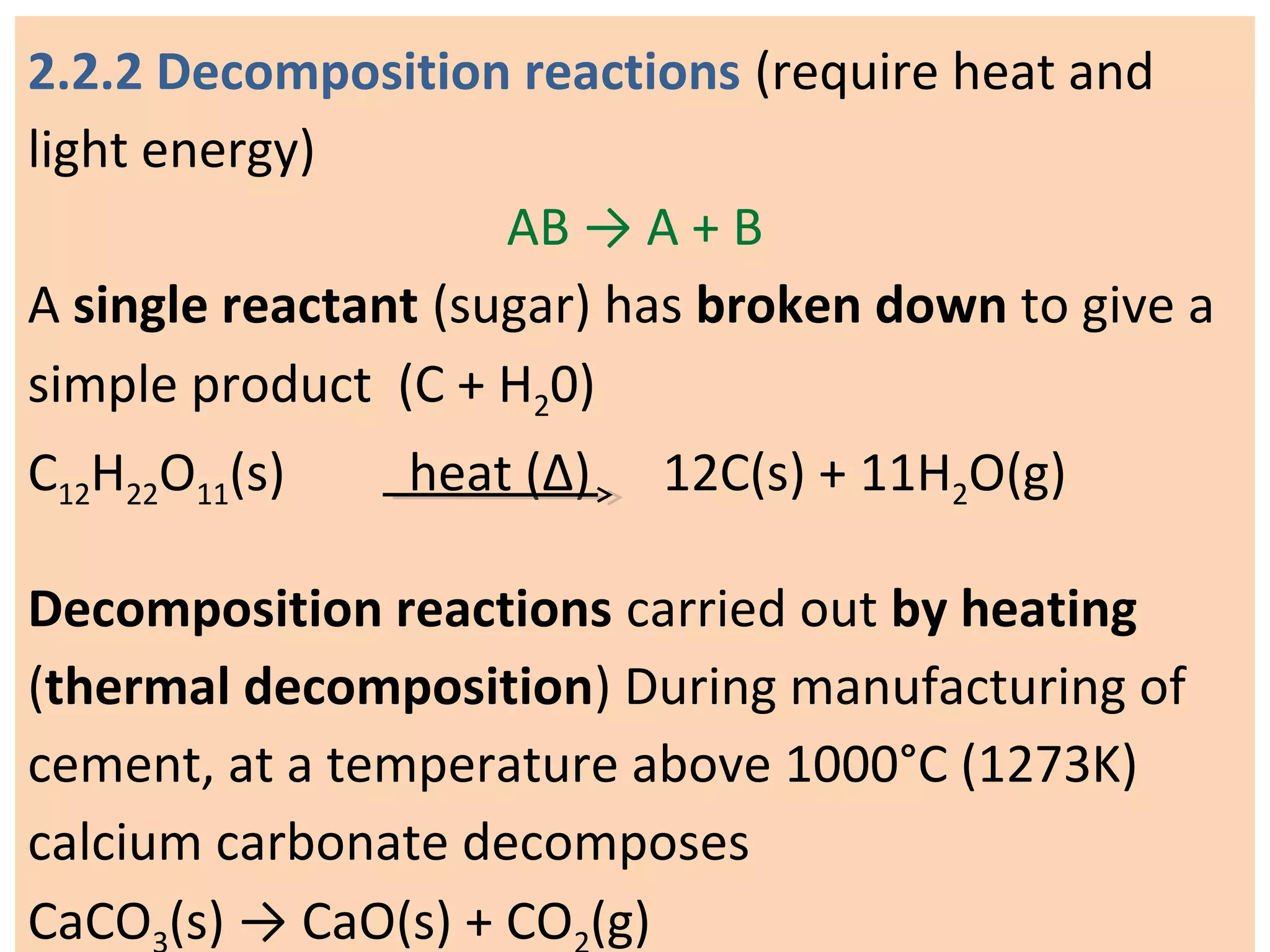
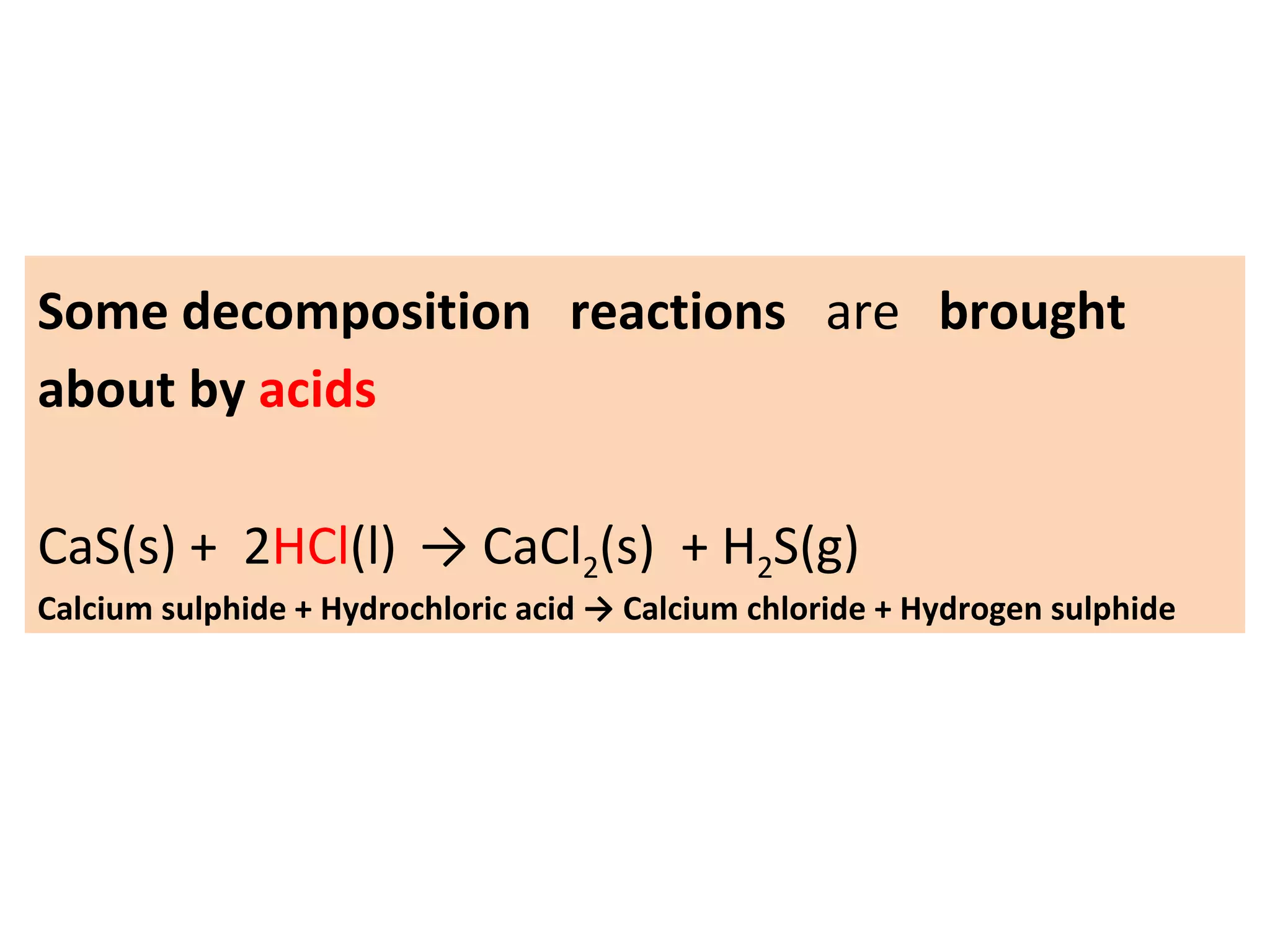
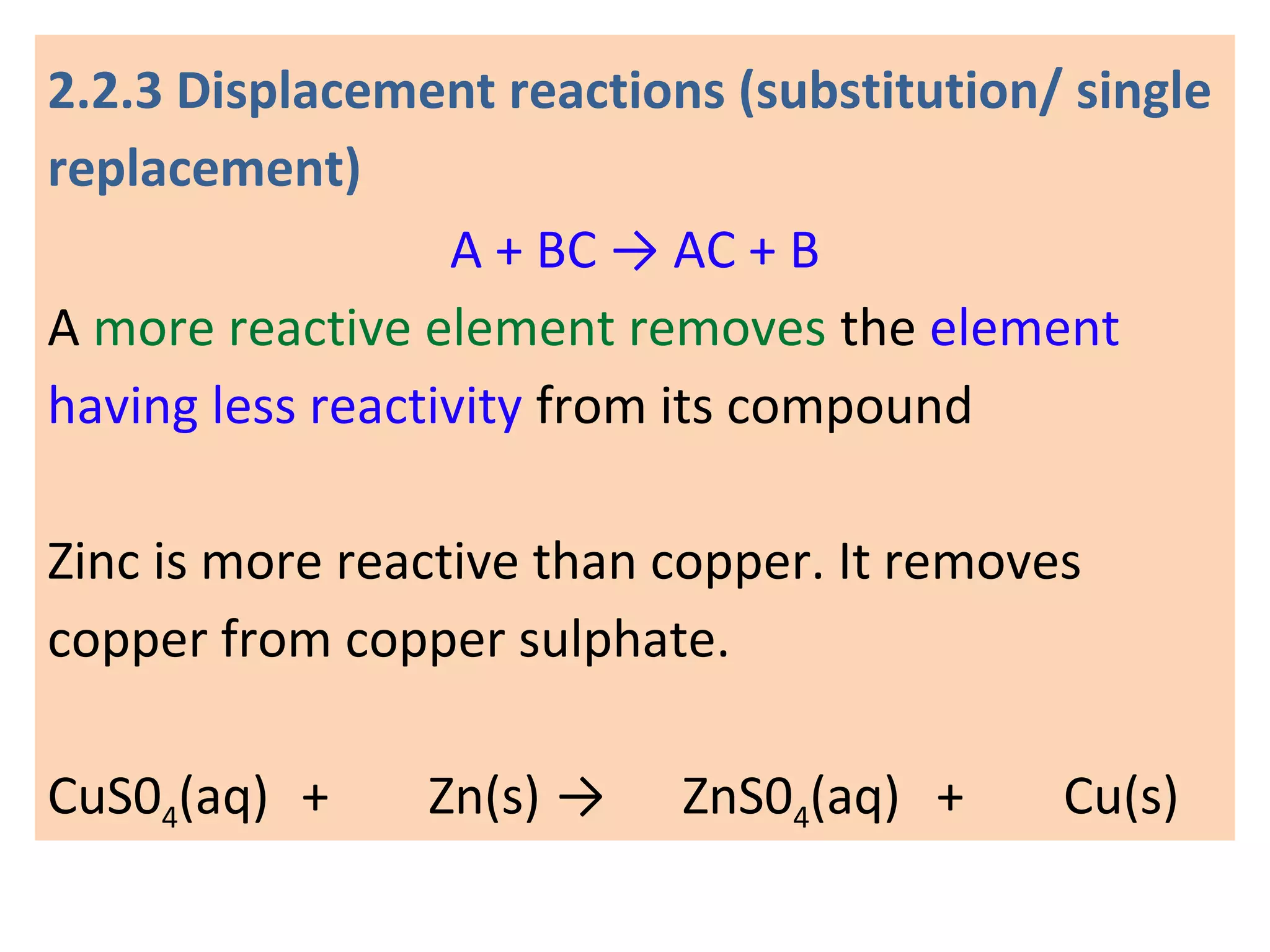
This document provides an overview of key topics in chemical reactions covered in Standard 10 Chapter 2, including:
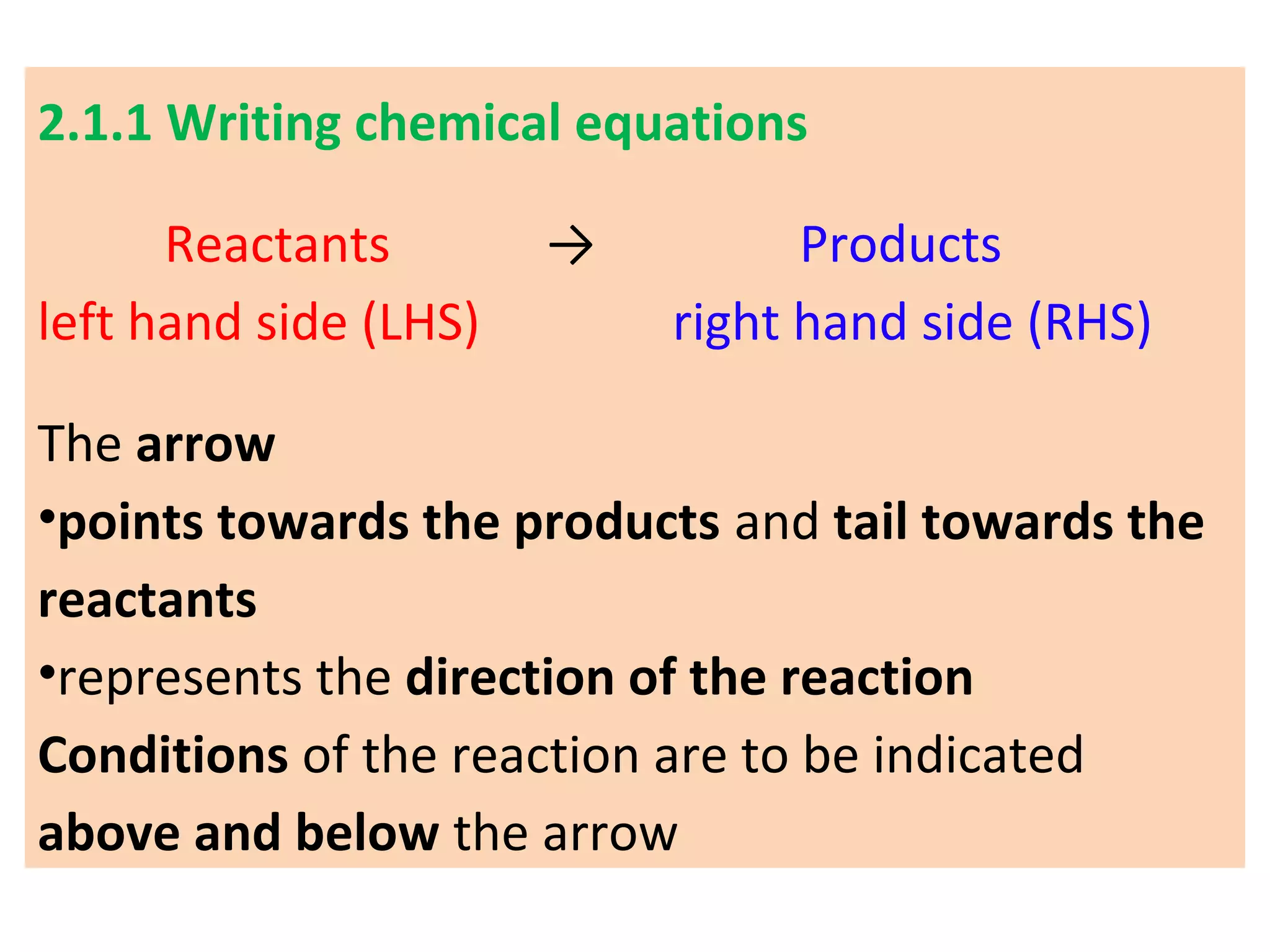
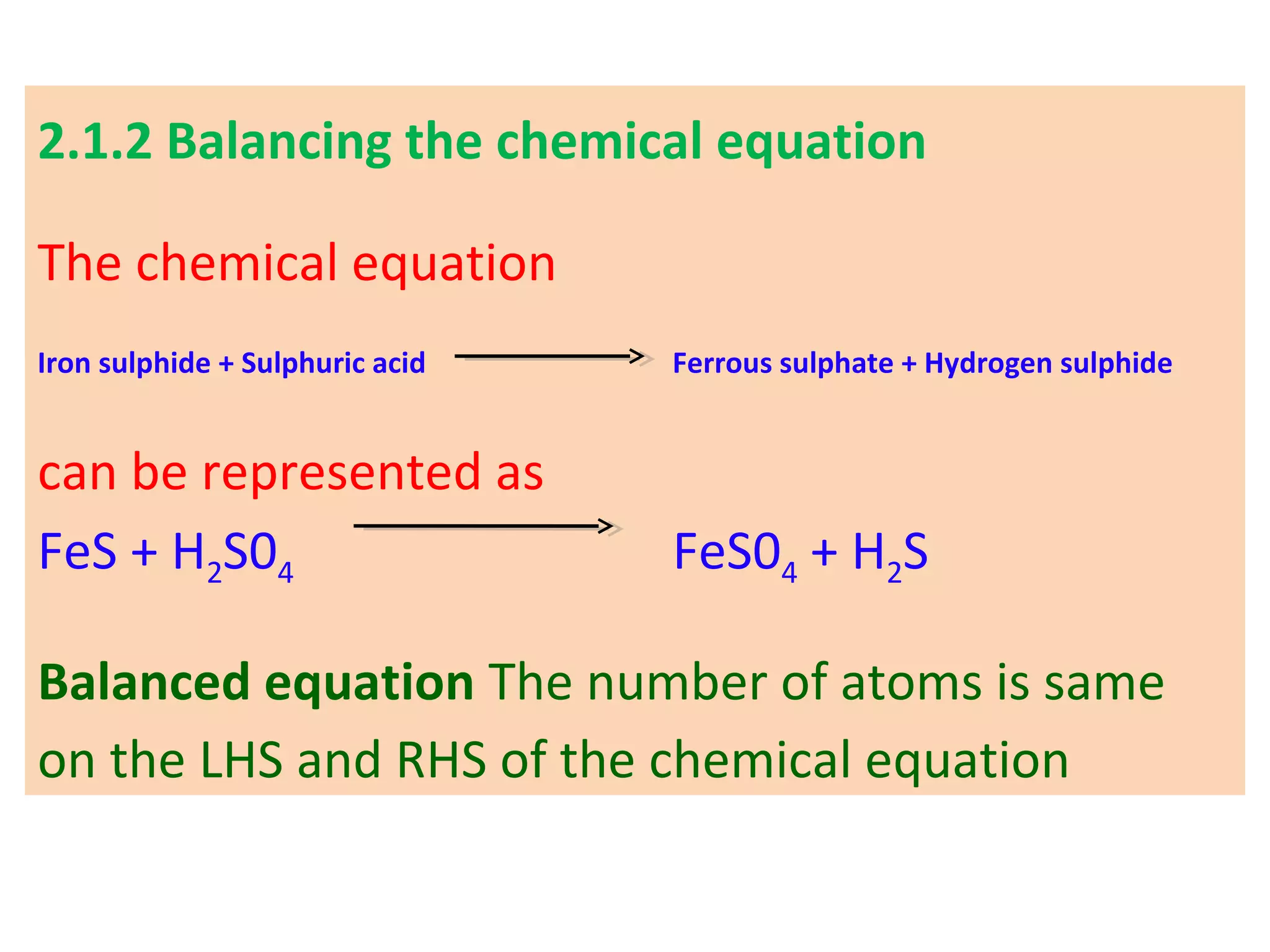
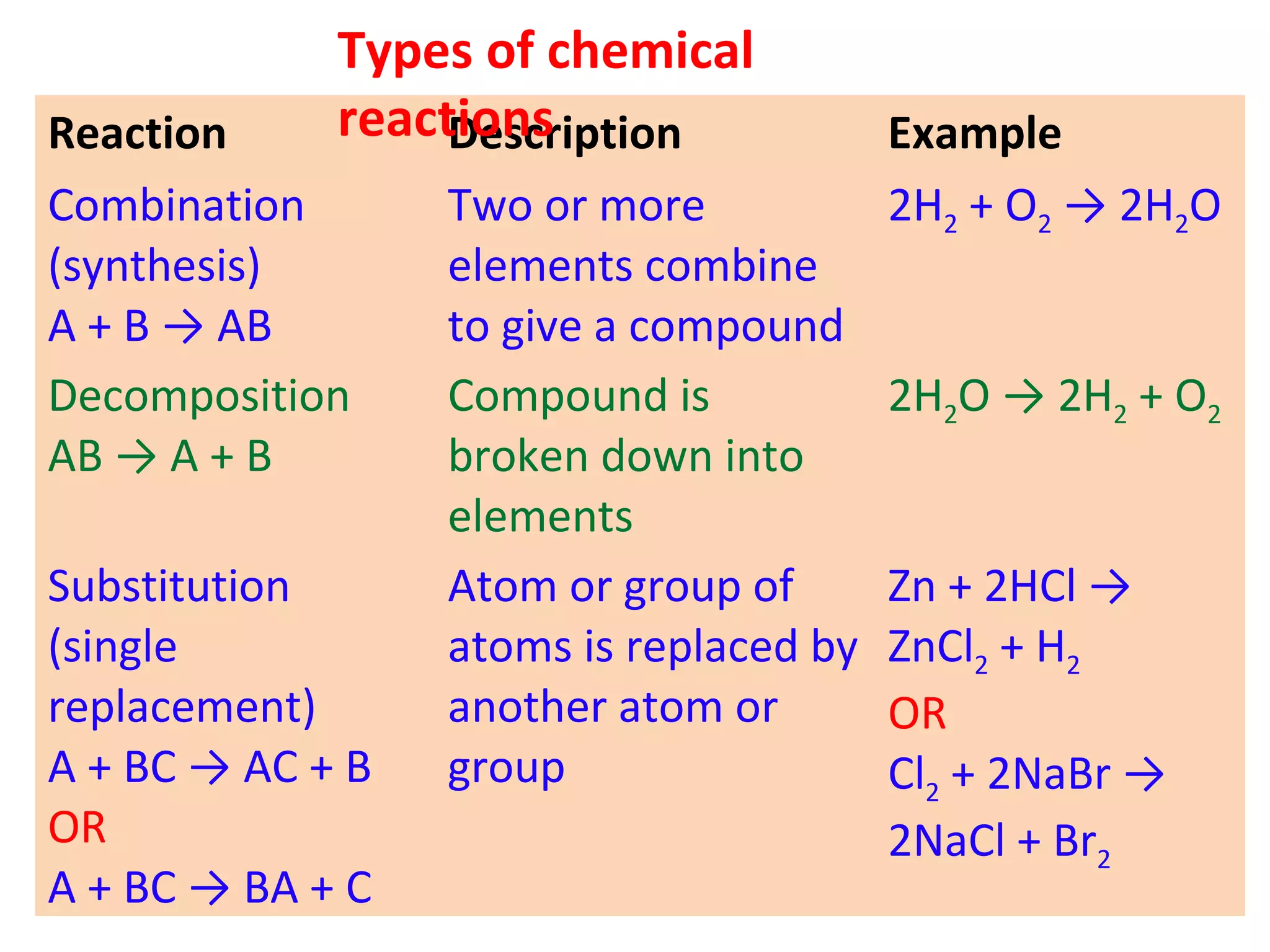
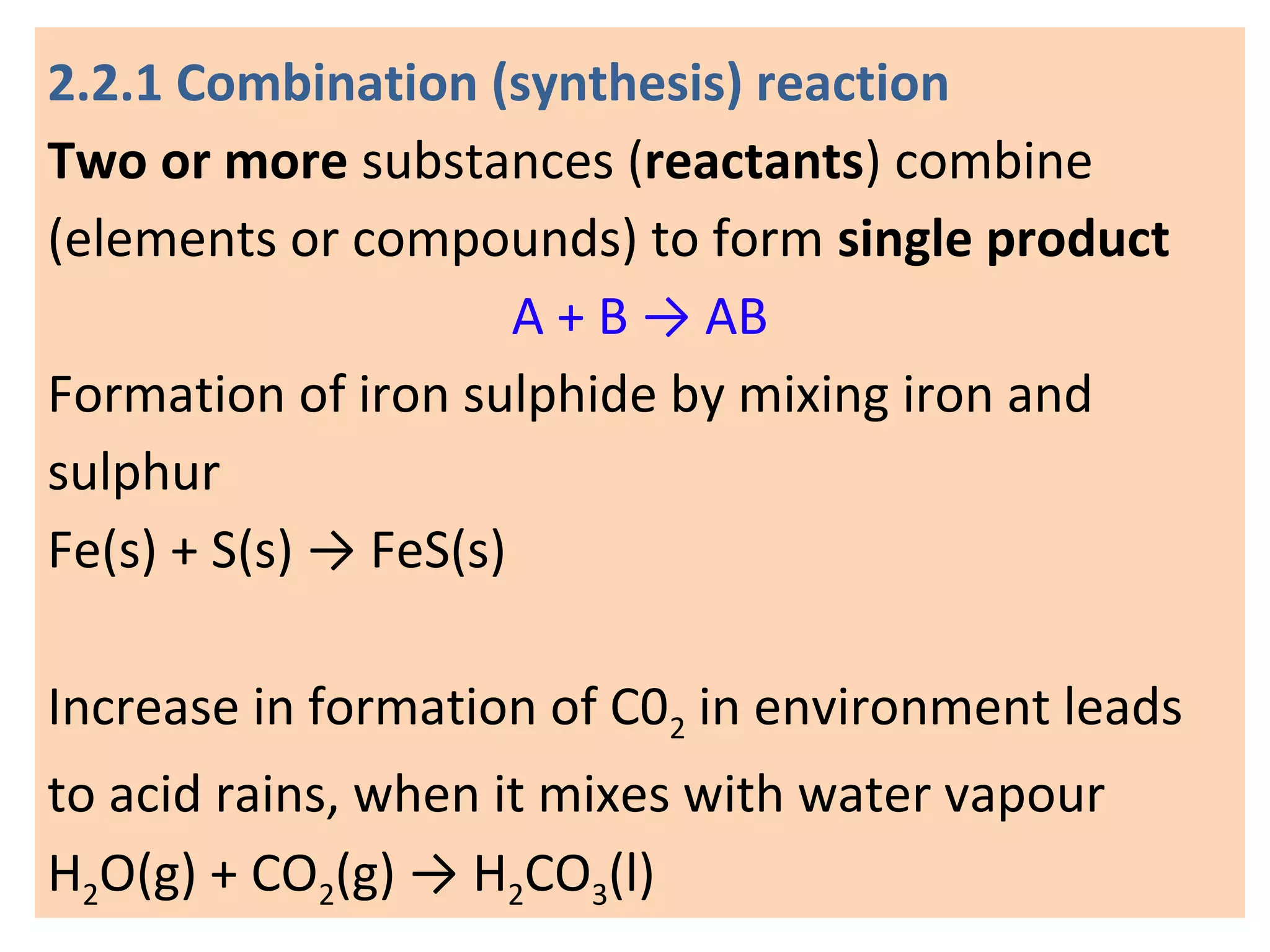
1. Writing and balancing chemical equations, and the main types of chemical reactions - combination, decomposition, displacement, and double displacement.
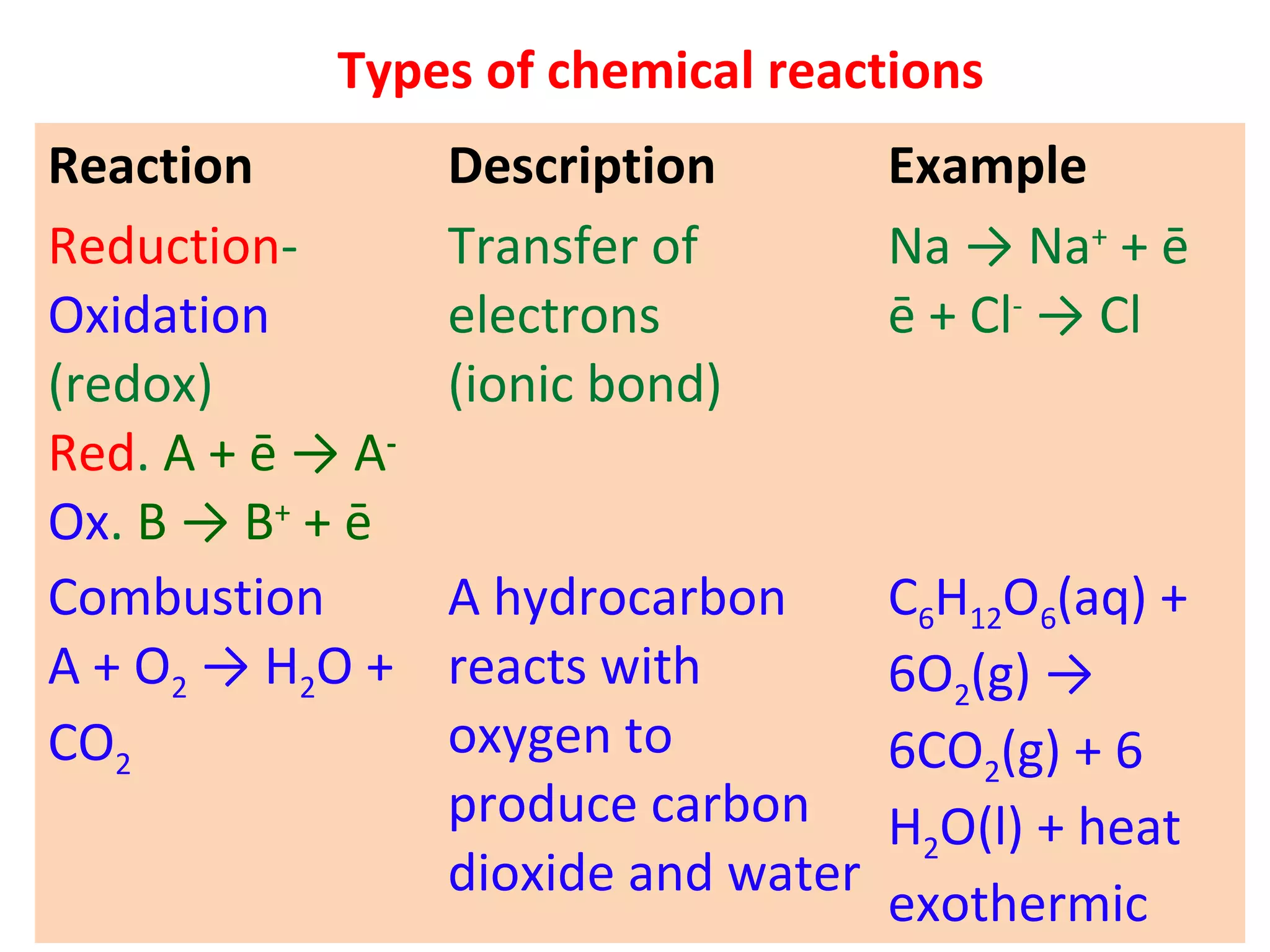
2. Oxidation and reduction reactions, and examples like corrosion.
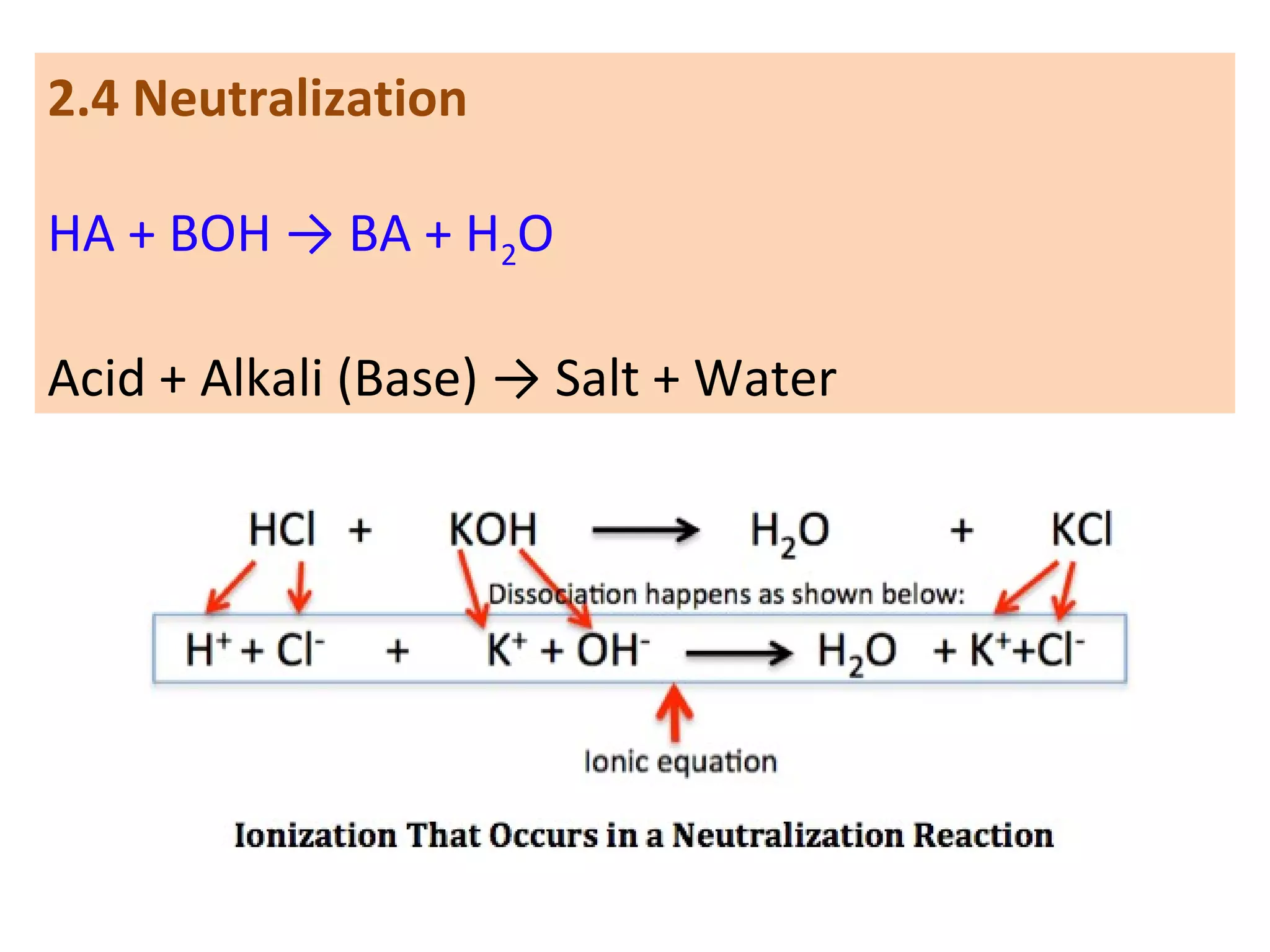
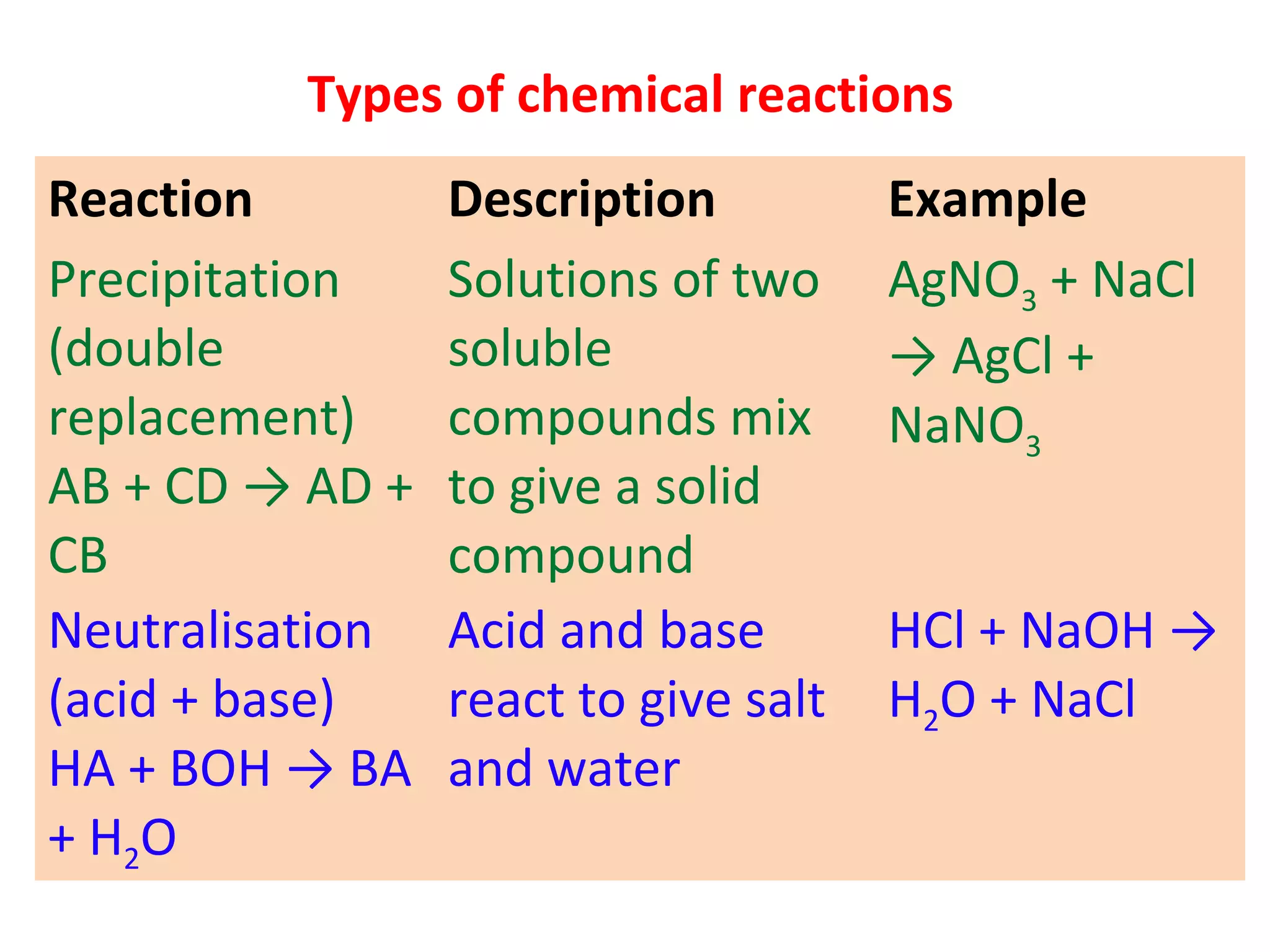
3. Neutralization reactions between acids and bases.
It defines important concepts like reactants, products, oxidation, reduction, and provides examples for different reaction types. Steps for balancing chemical equations are also summarized.











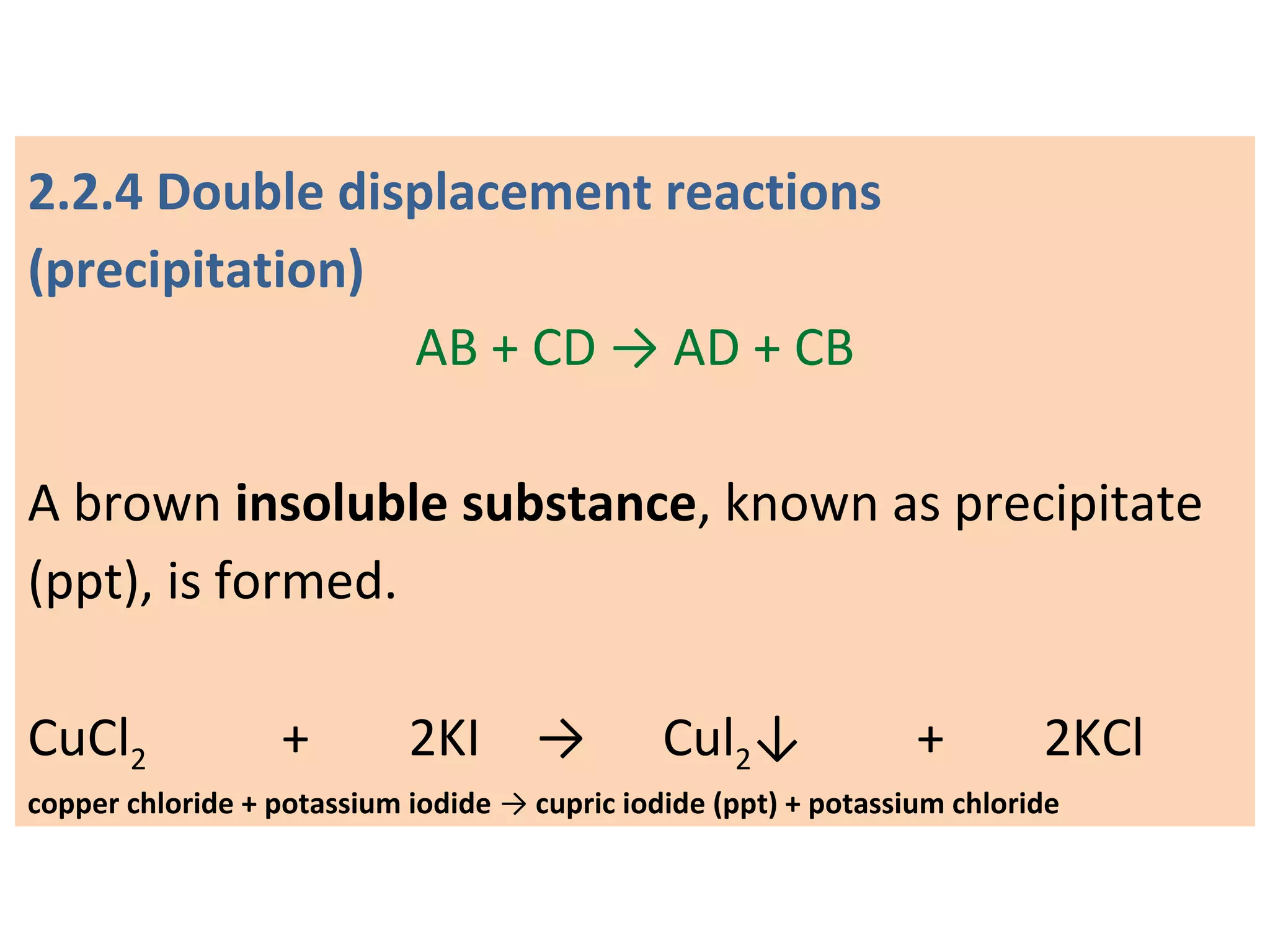
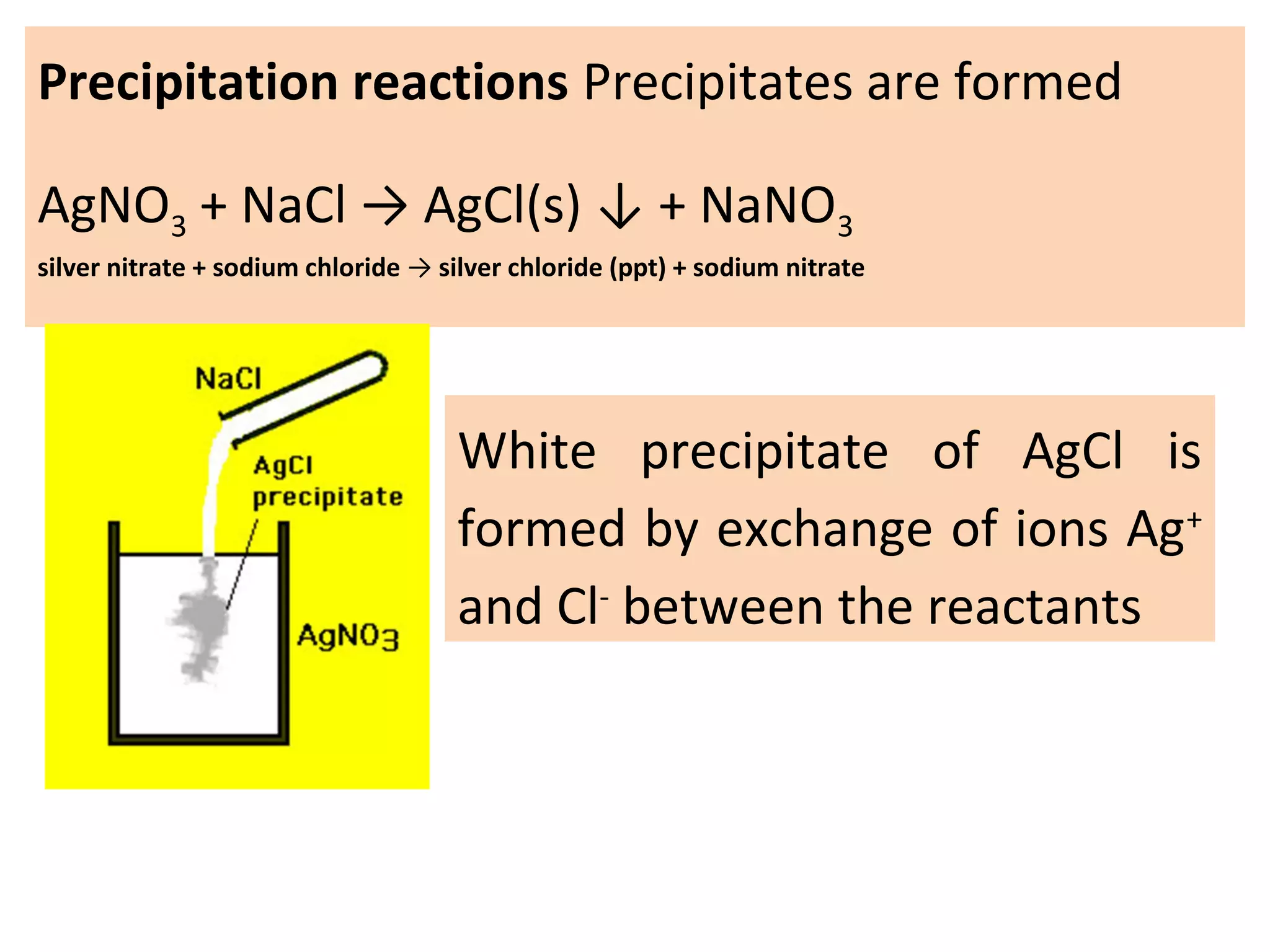


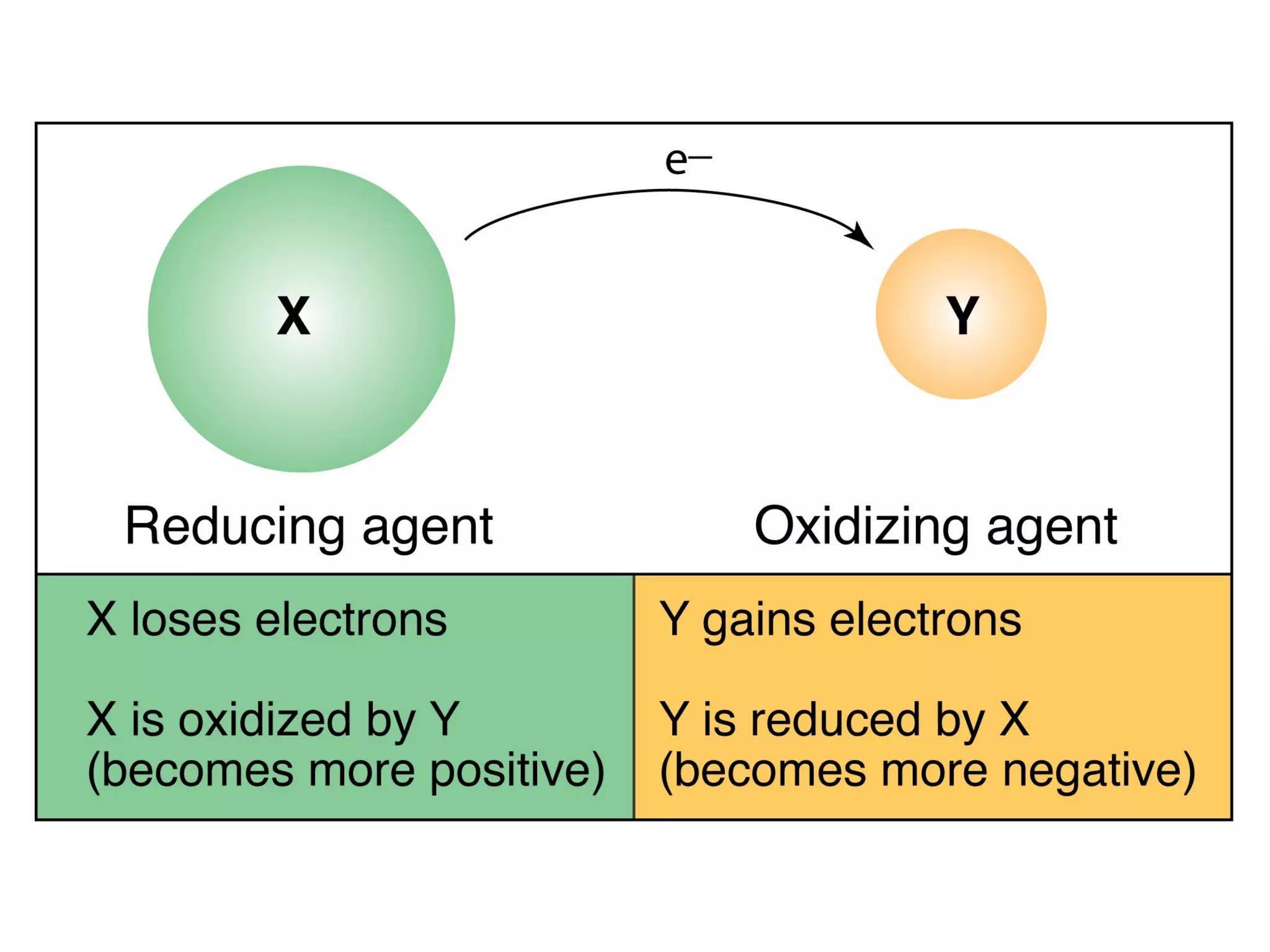



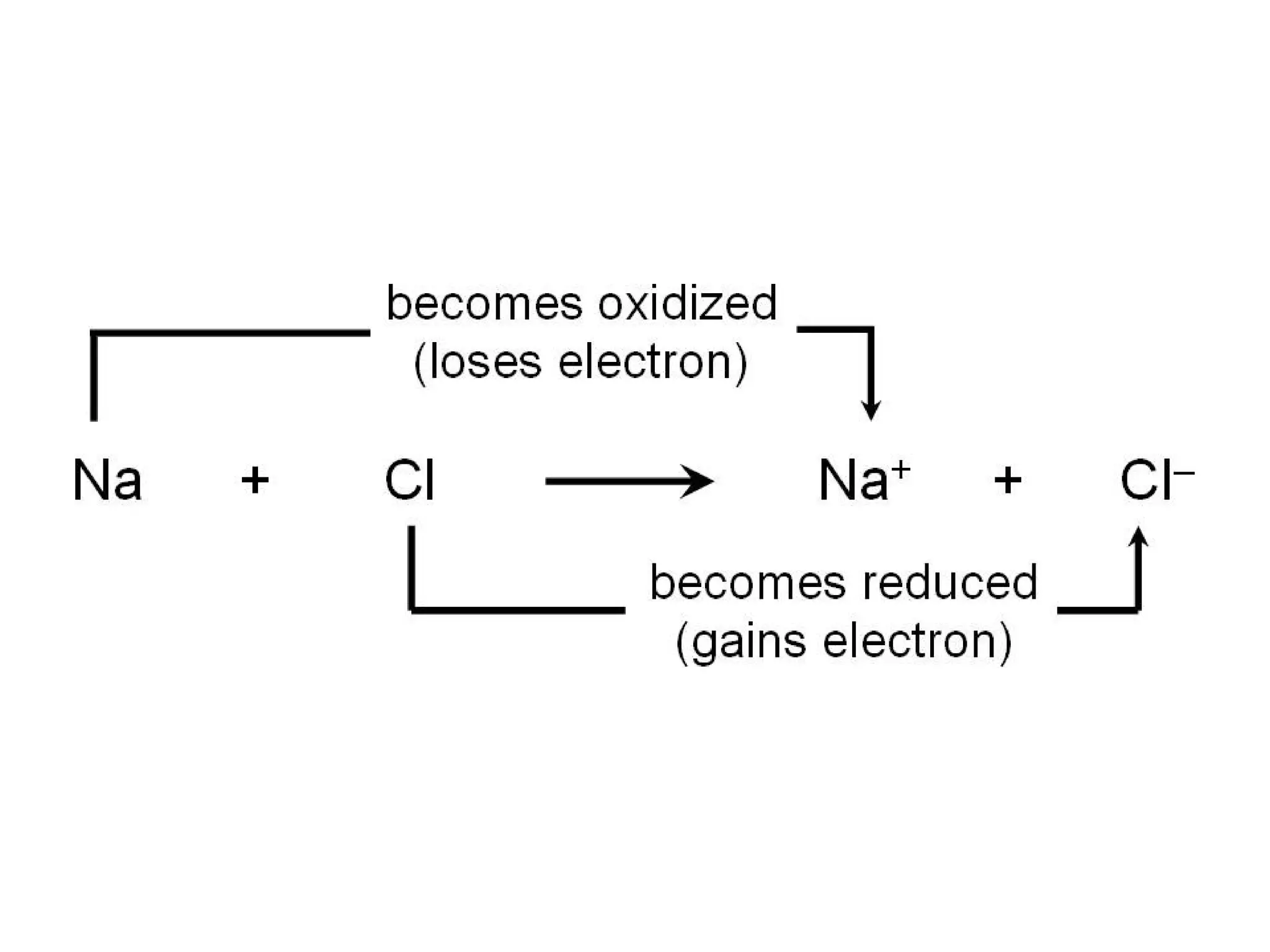


![03 light 02 + [O]
ozone → oxygen + nascent oxygen
Oxygen is freshly liberated. This oxygen is often
called freshly born or "Nascent" oxygen.
In a chemical equation, nascent oxygen is always
denoted by showing symbol of oxygen (O) in square
brackets such as [0].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/std10-ch2-chemical-reactions-160226162225/75/Std-10-Chapter-2-Chemical-Reactions-34-2048.jpg)