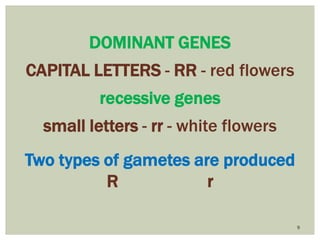
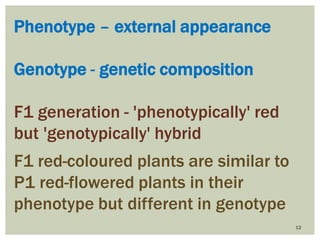
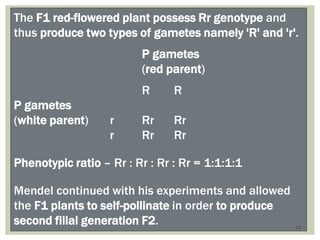
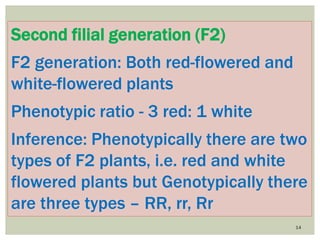
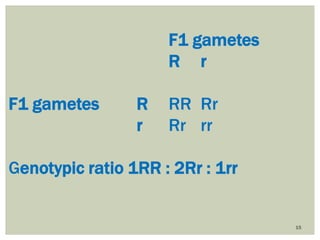
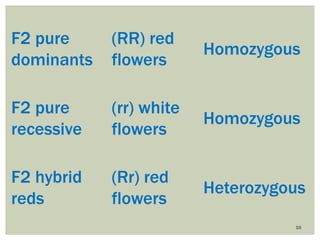
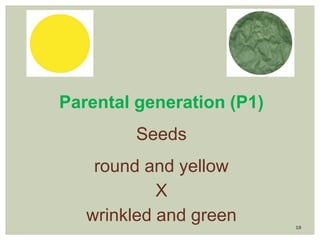
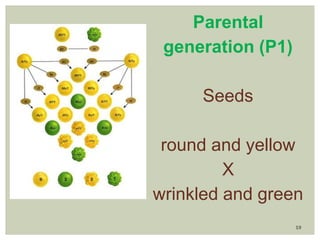
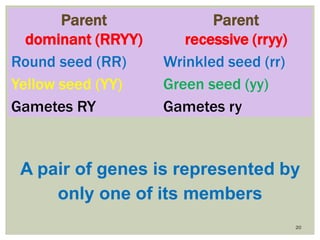
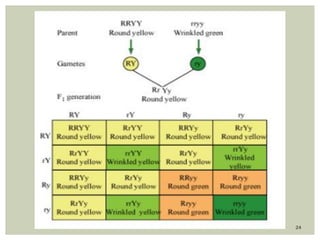
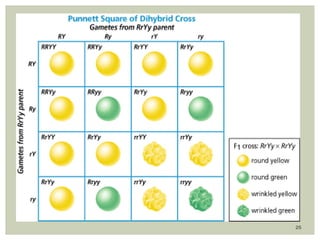
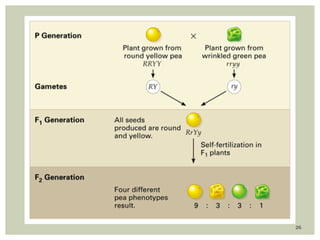
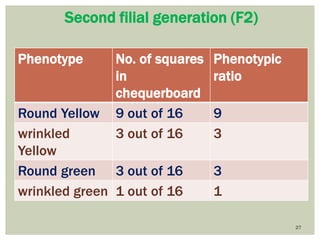
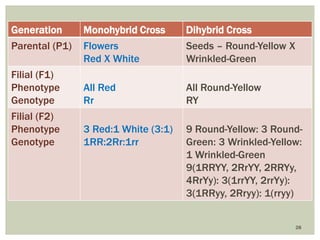
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants to study inheritance of traits. In monohybrid crosses involving one trait like flower color, he found that one factor (red color) dominated the recessive trait (white color) in the offspring (F1 generation). When the F1 plants were self-pollinated to produce F2 offspring, there was a 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive traits. In dihybrid crosses involving two traits like seed shape and color, the F1 offspring exhibited dominant traits for both. The F2 offspring showed a 9:3:3:1 ratio for different combinations of traits. Mendel's experiments established basic principles of heredity and were the foundation of classical