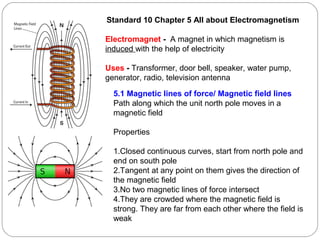
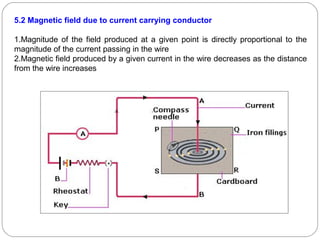
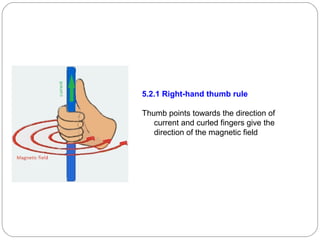
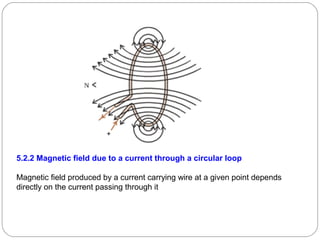
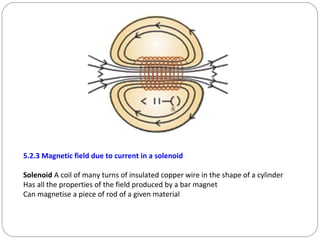
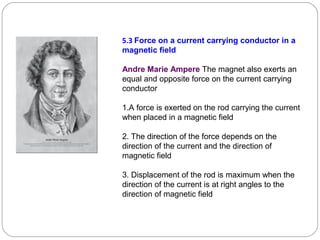
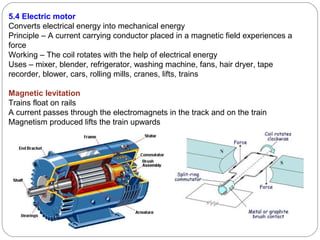
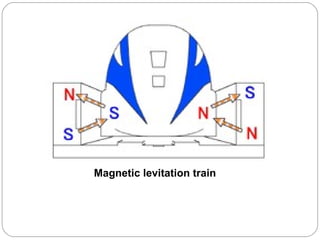
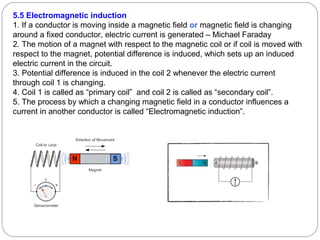
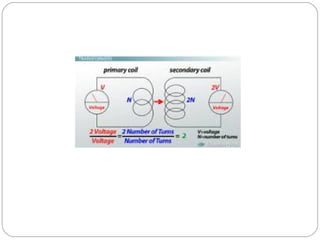
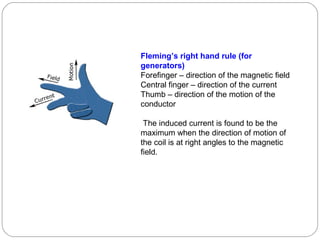
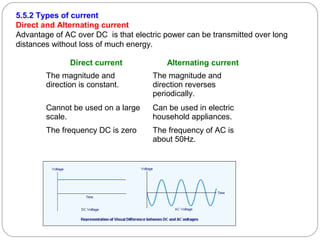
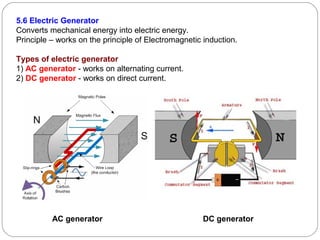
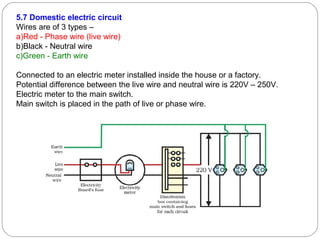
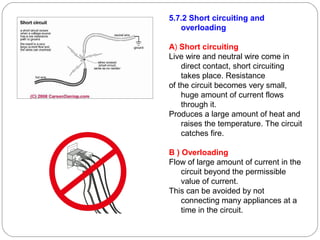
This document provides an overview of electromagnetism concepts covered in Standard 10, Chapter 5. It discusses magnetic field lines and their properties. It describes the magnetic field created by current-carrying conductors using the right-hand thumb rule. It also explains electromagnetic induction, electric motors, generators, and domestic electric circuits. Safety measures for electricity are outlined, including dangers of short circuits and overloading circuits. The document serves as a reference for key topics in electromagnetism for Standard 10 students.