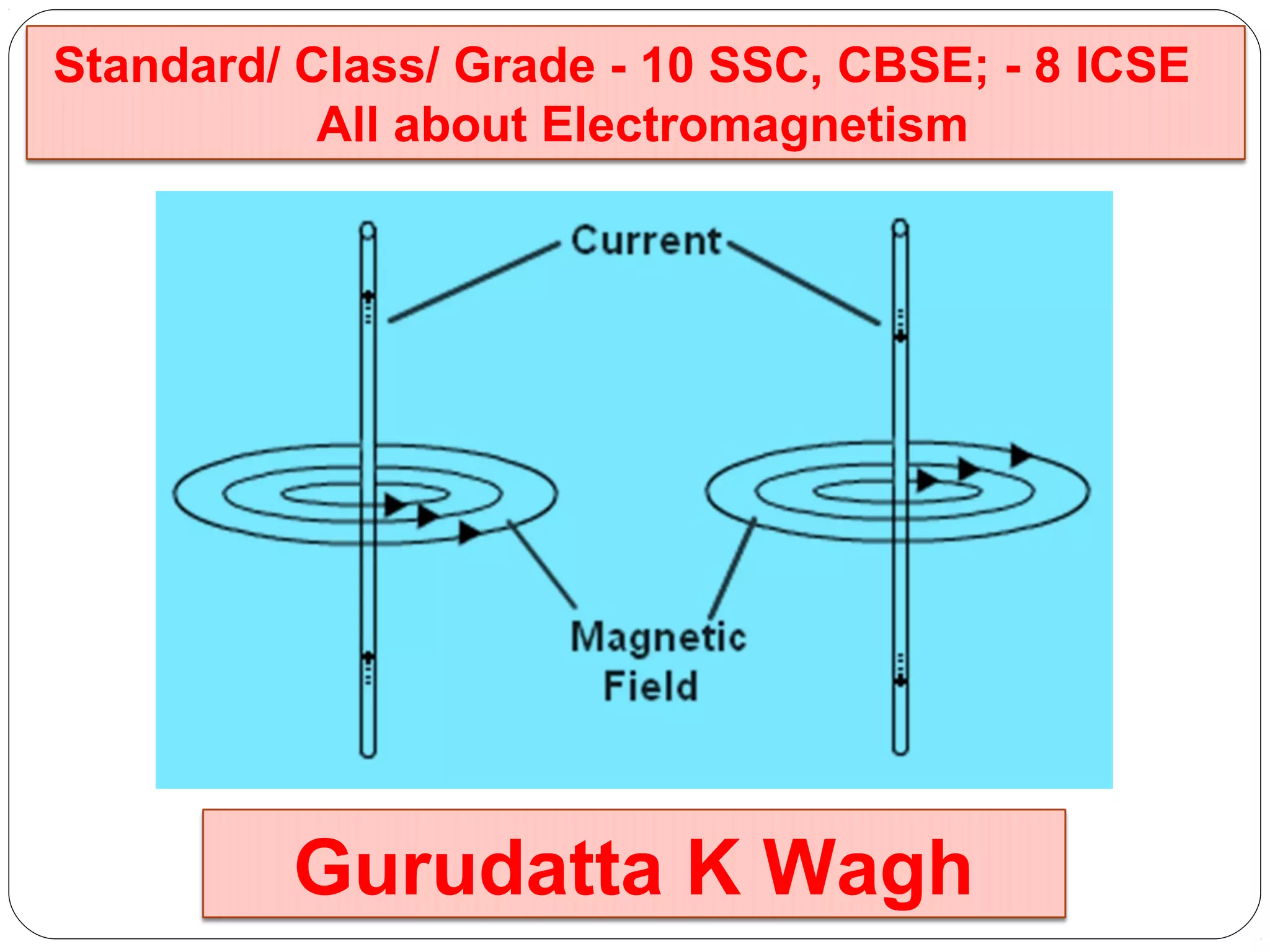
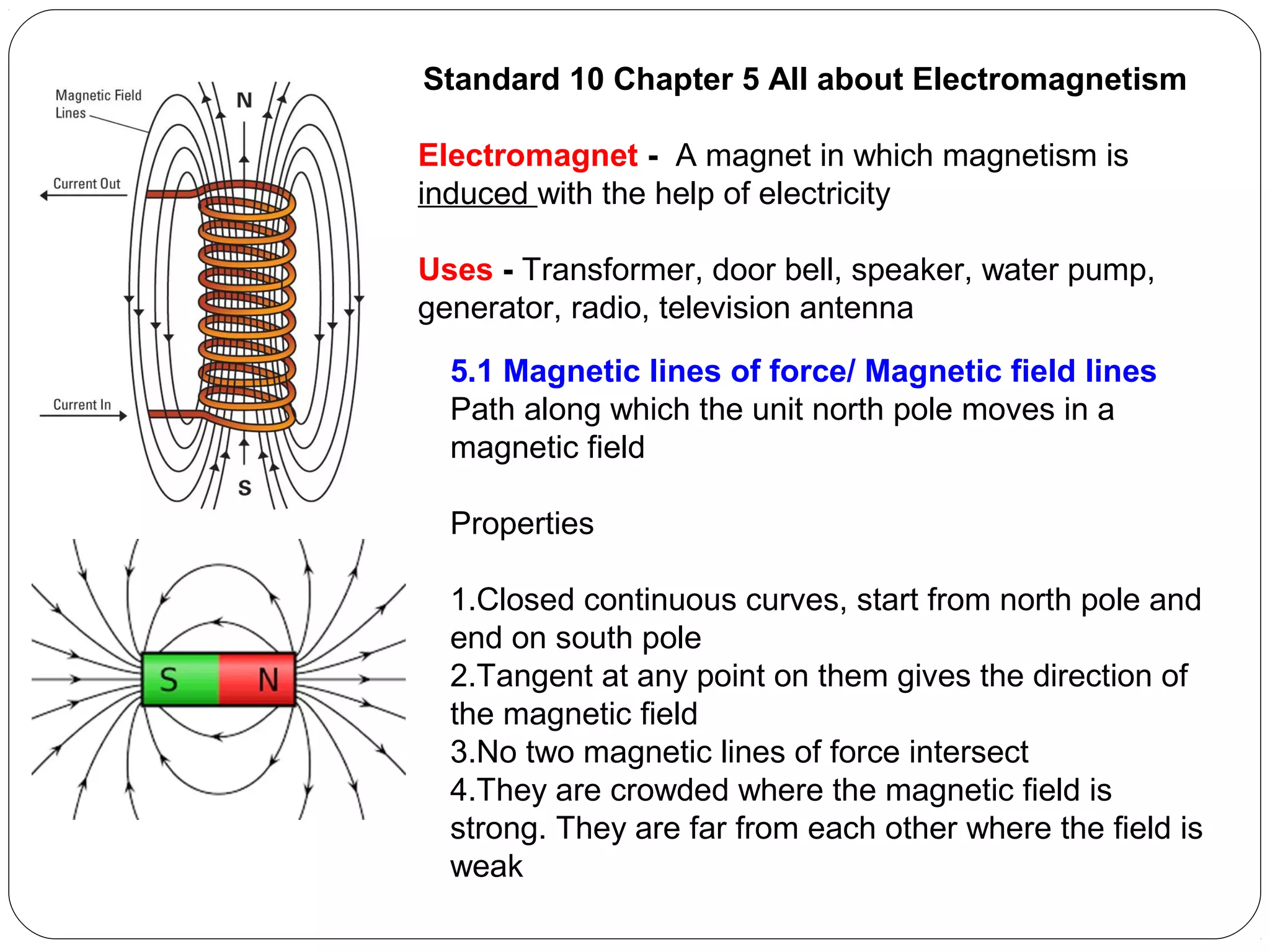
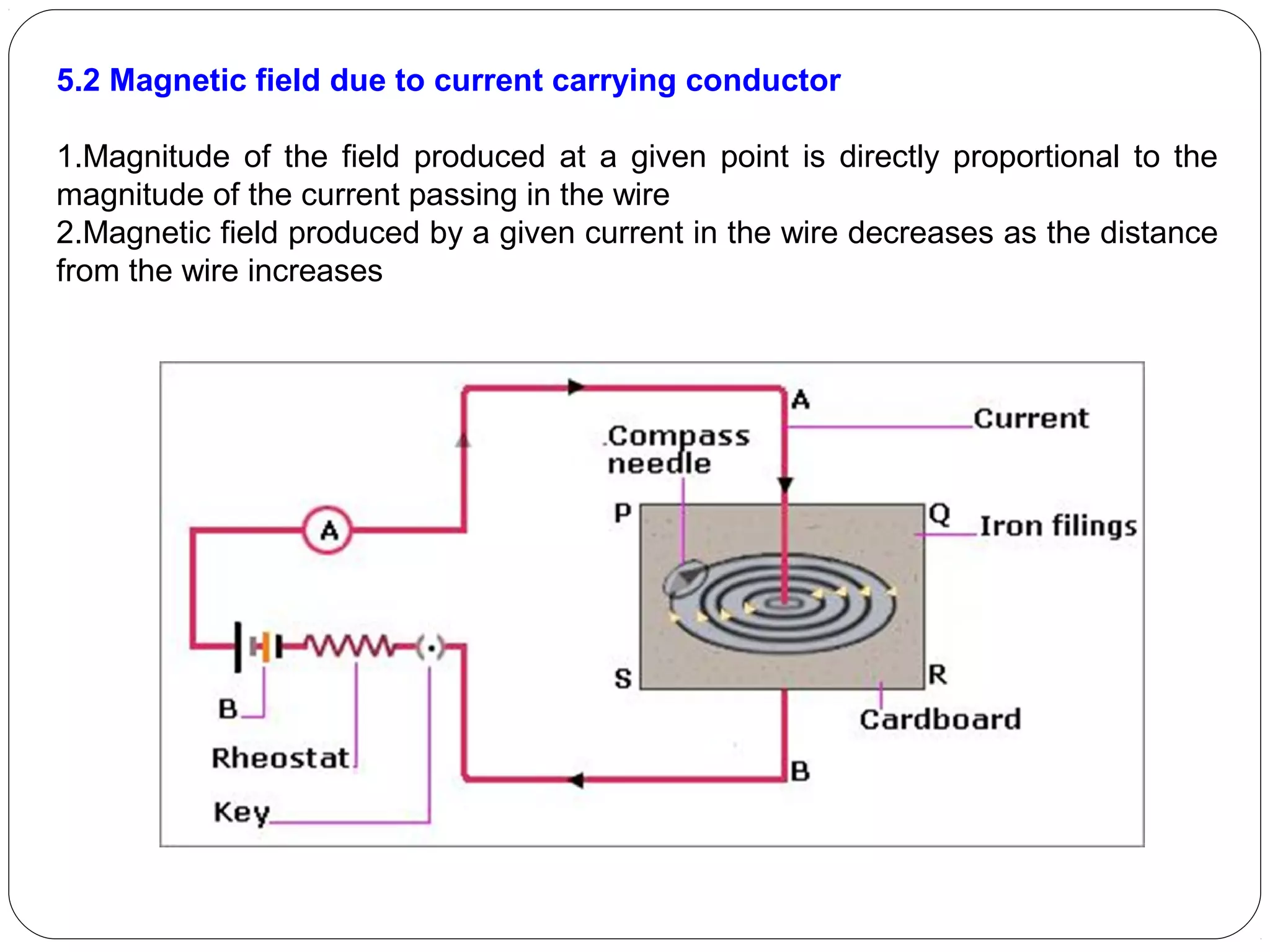
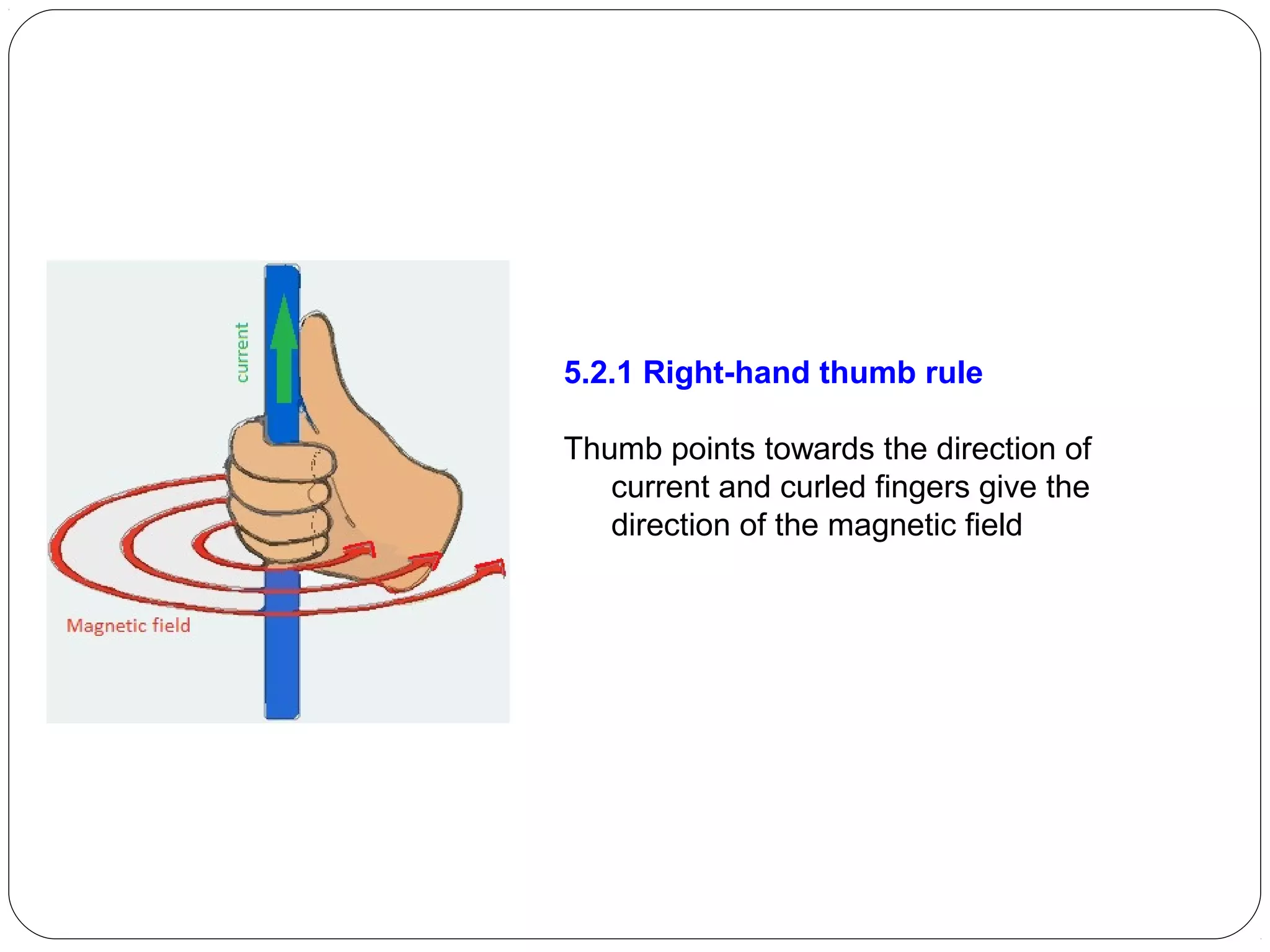
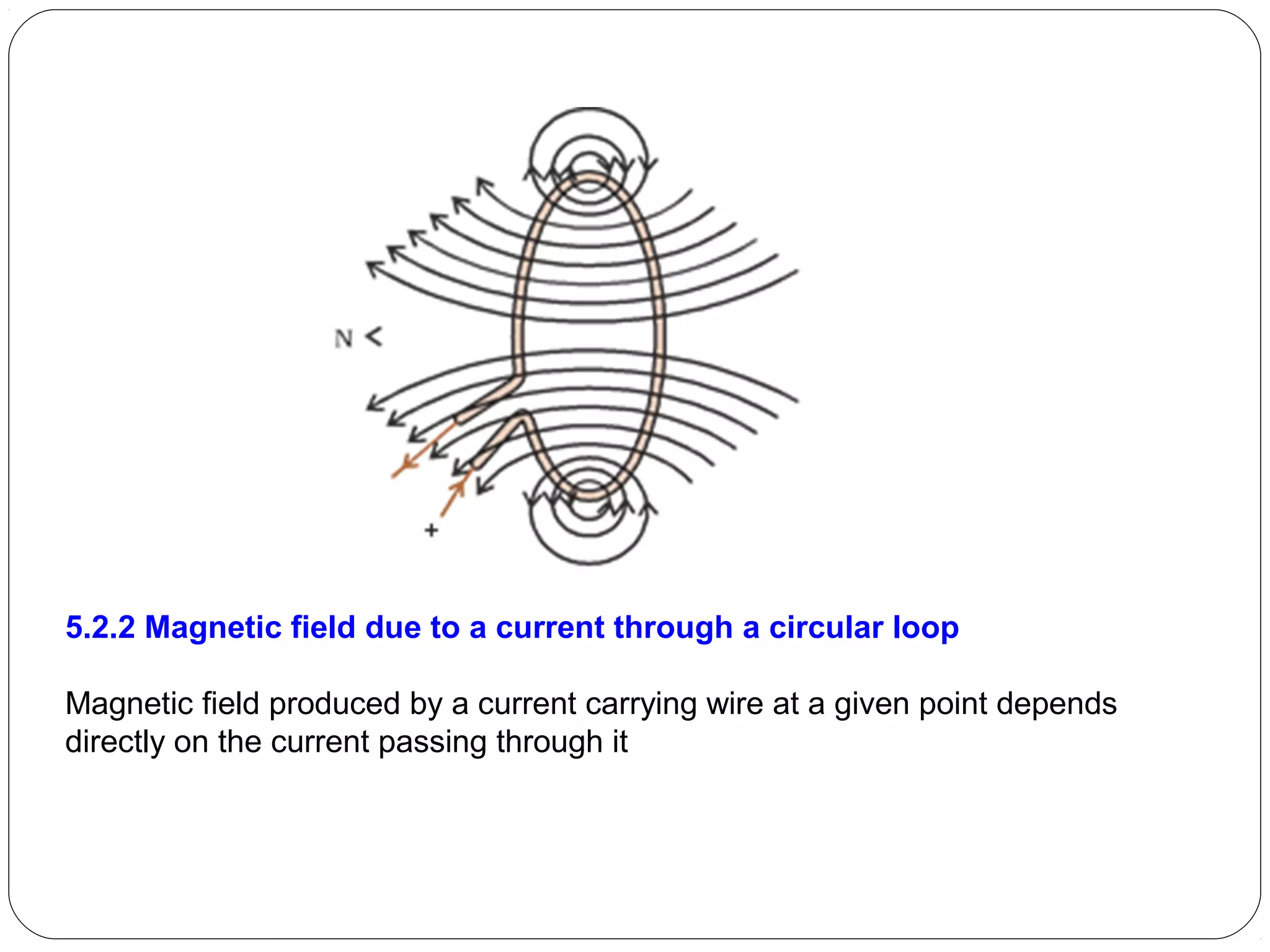
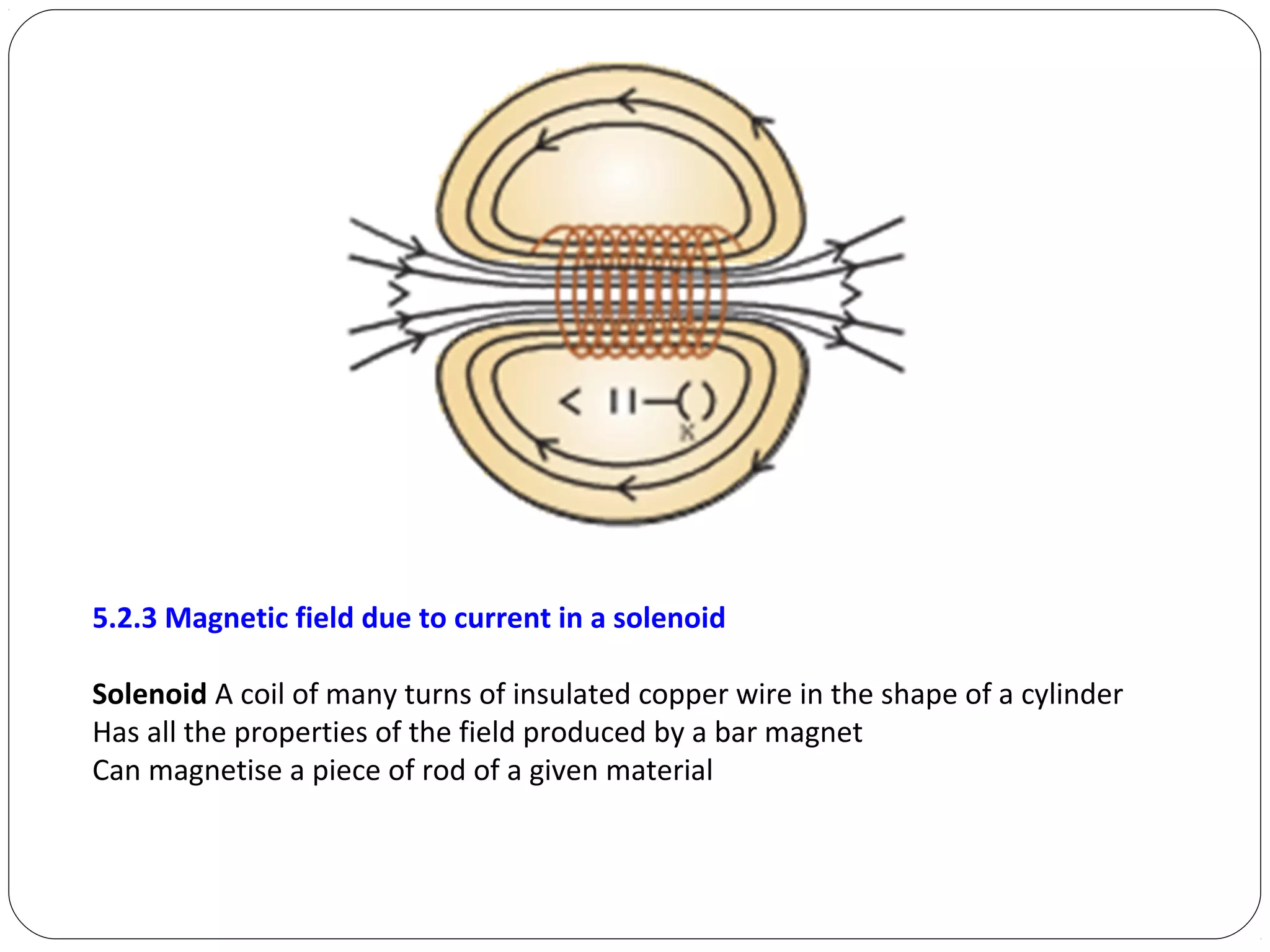
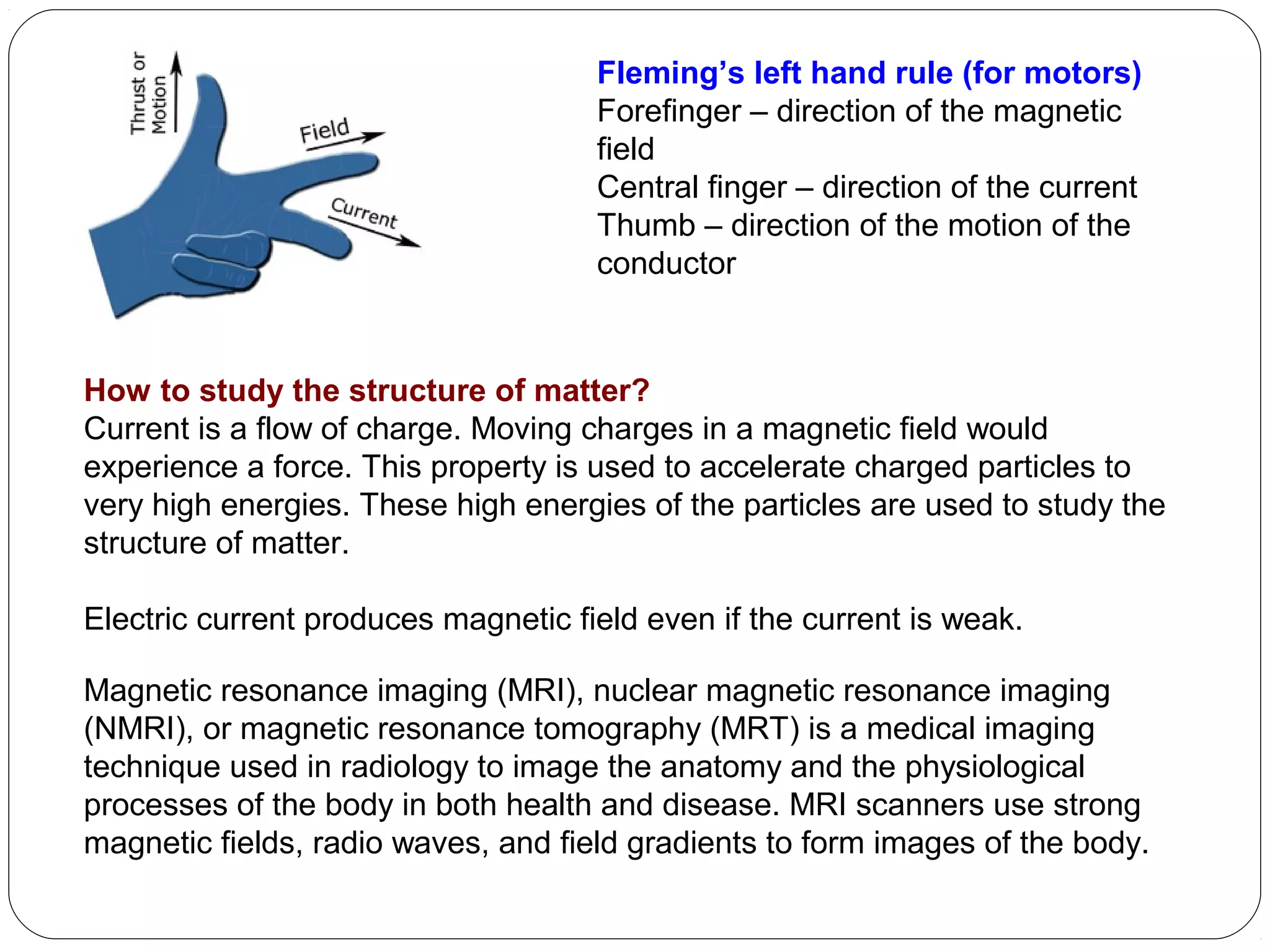
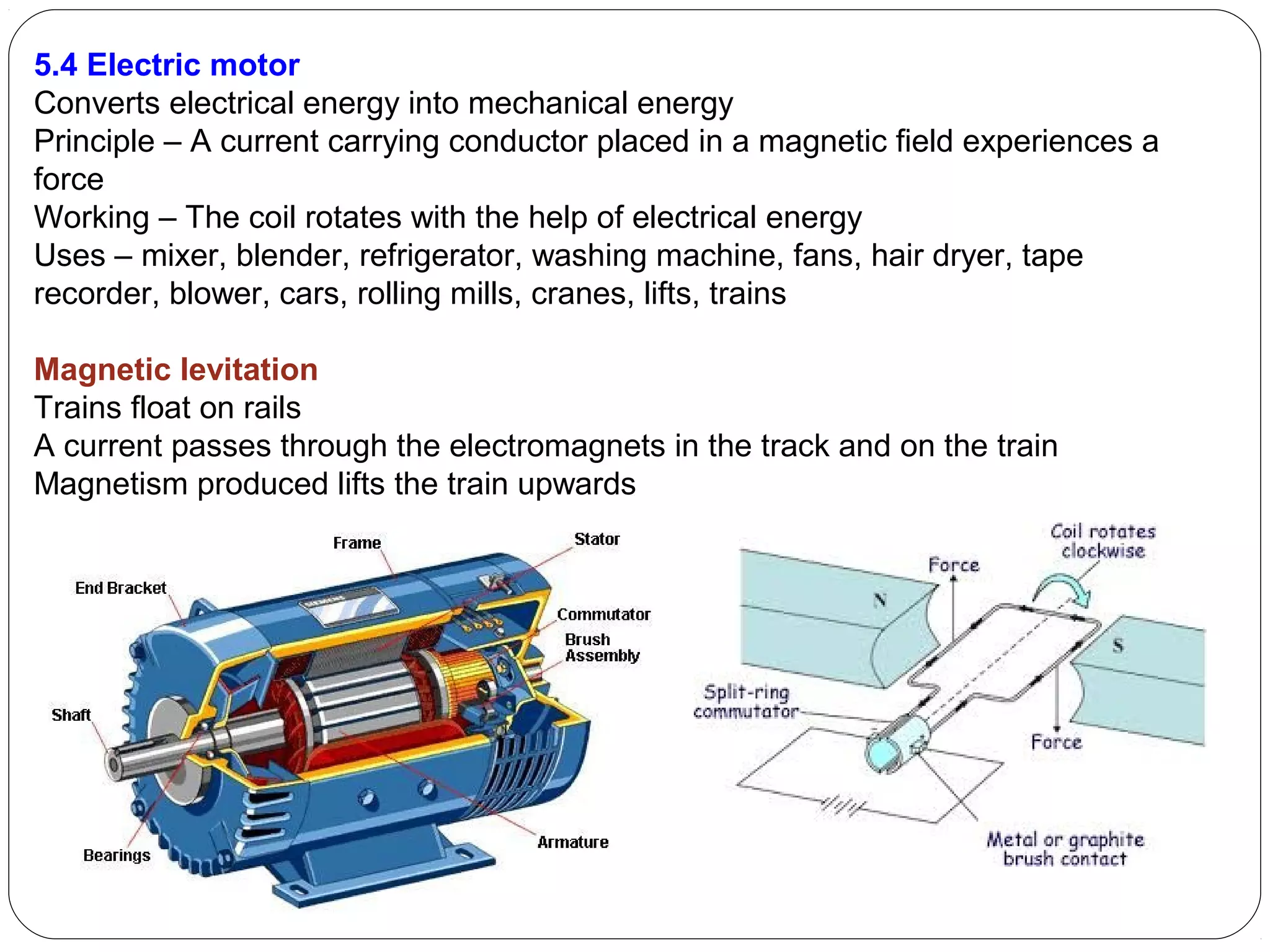
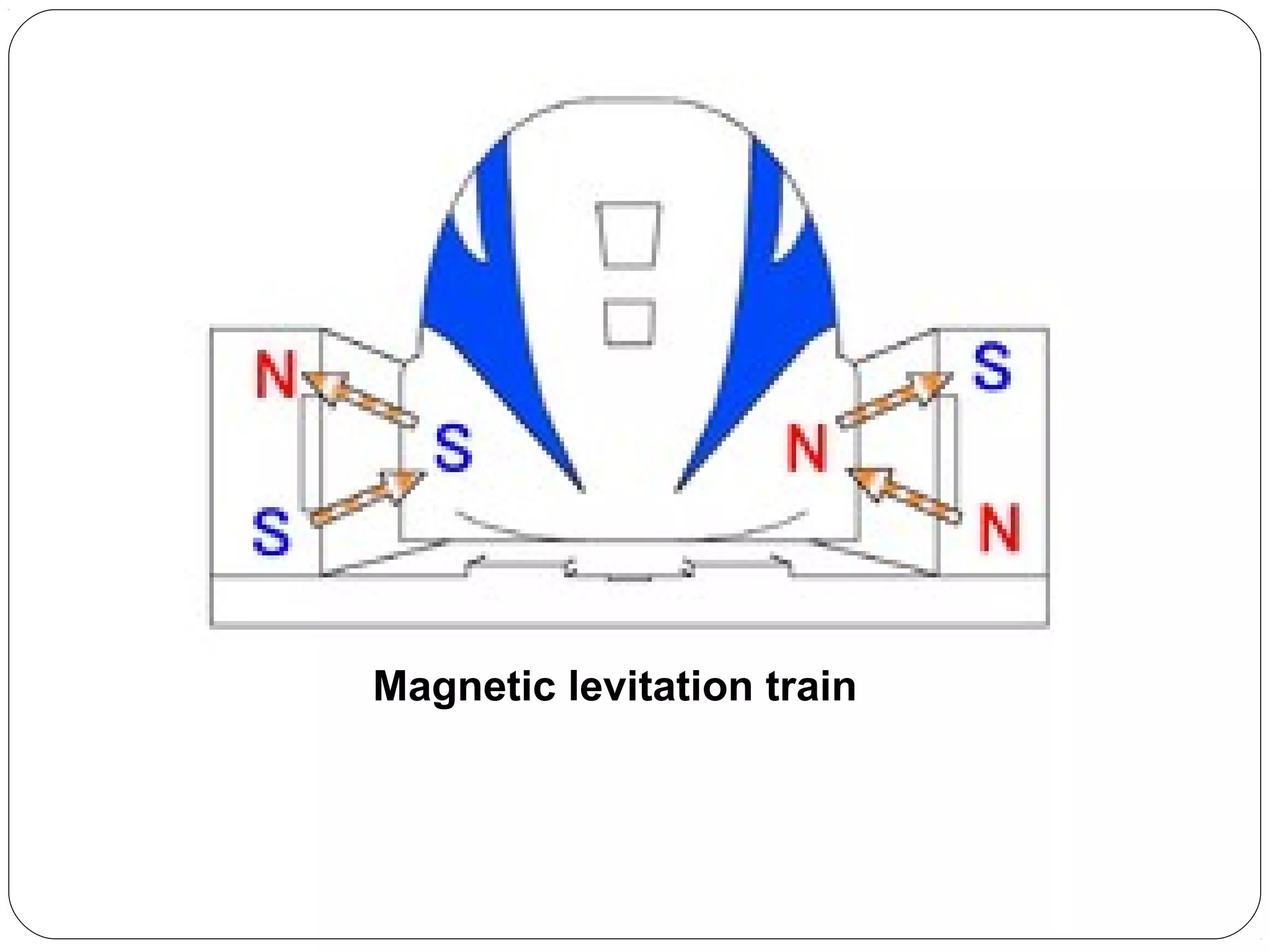
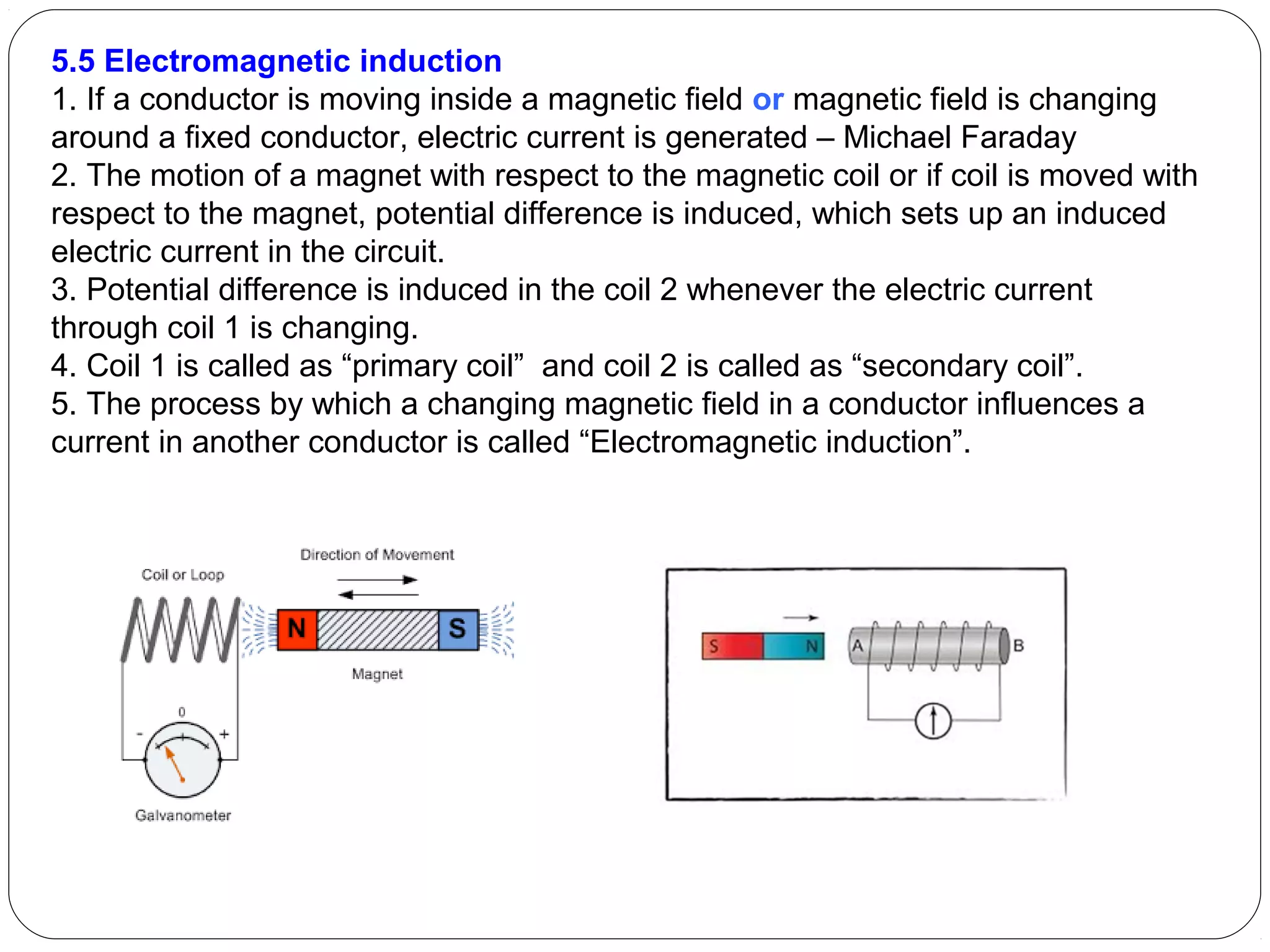
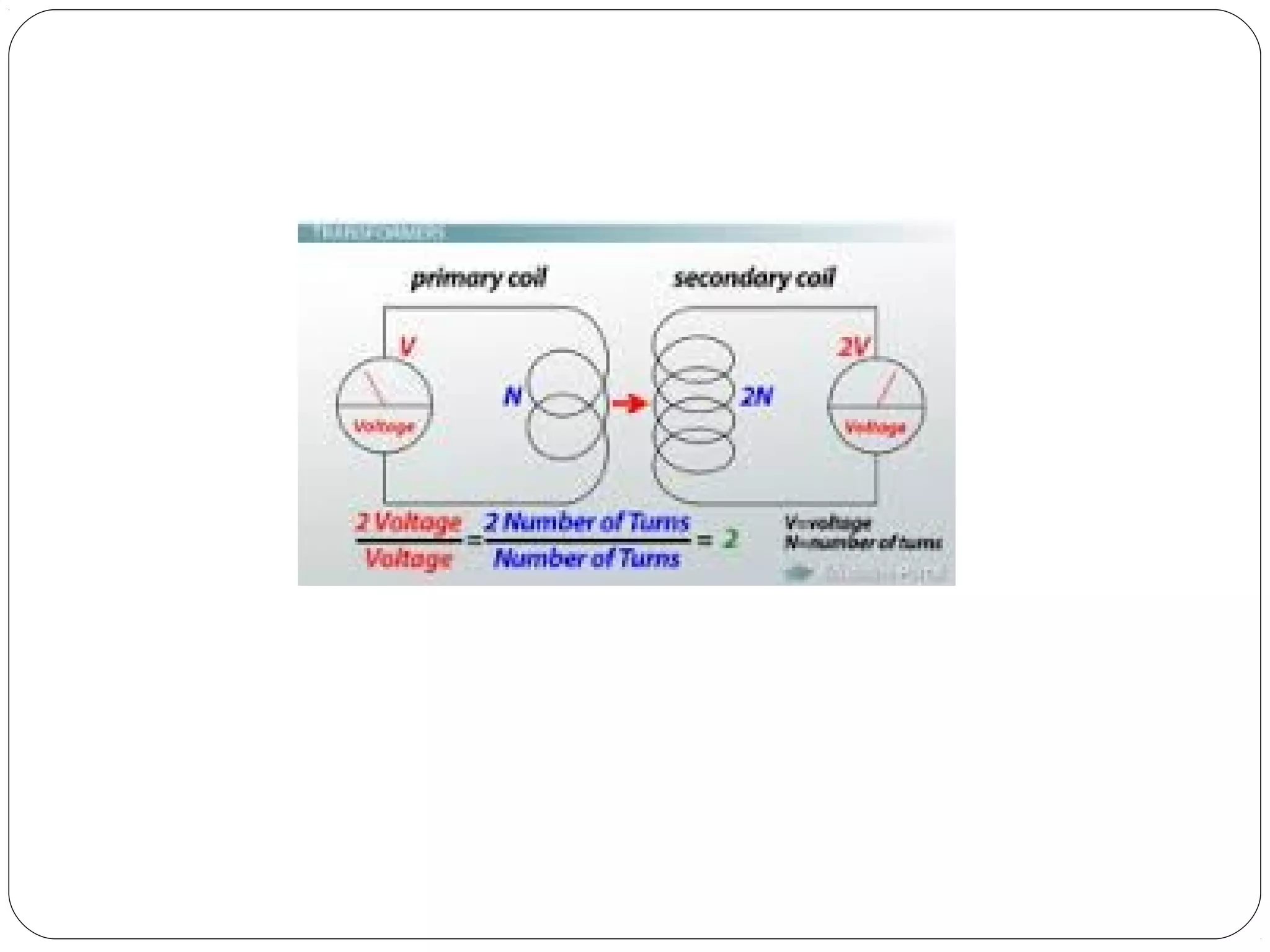
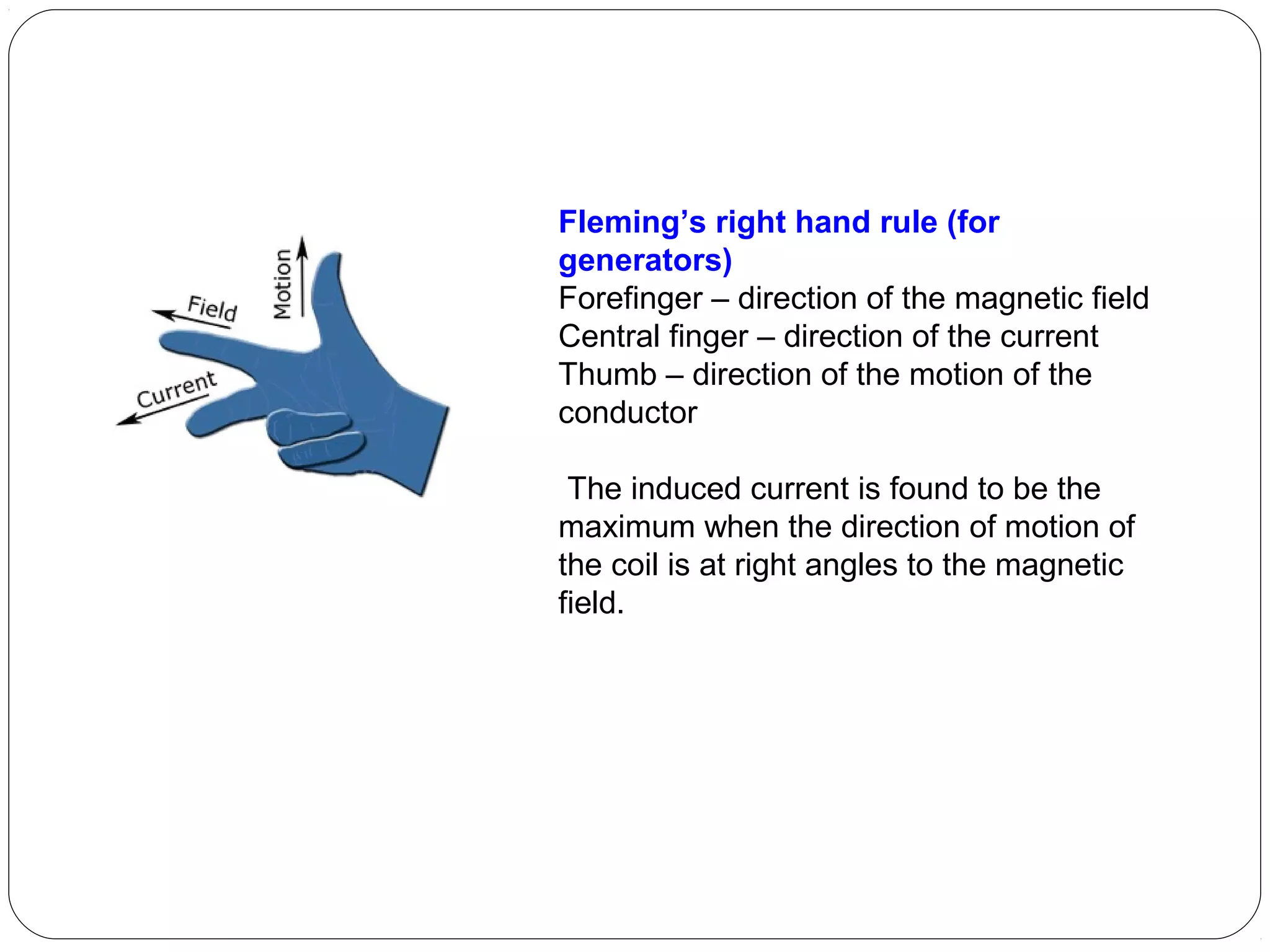
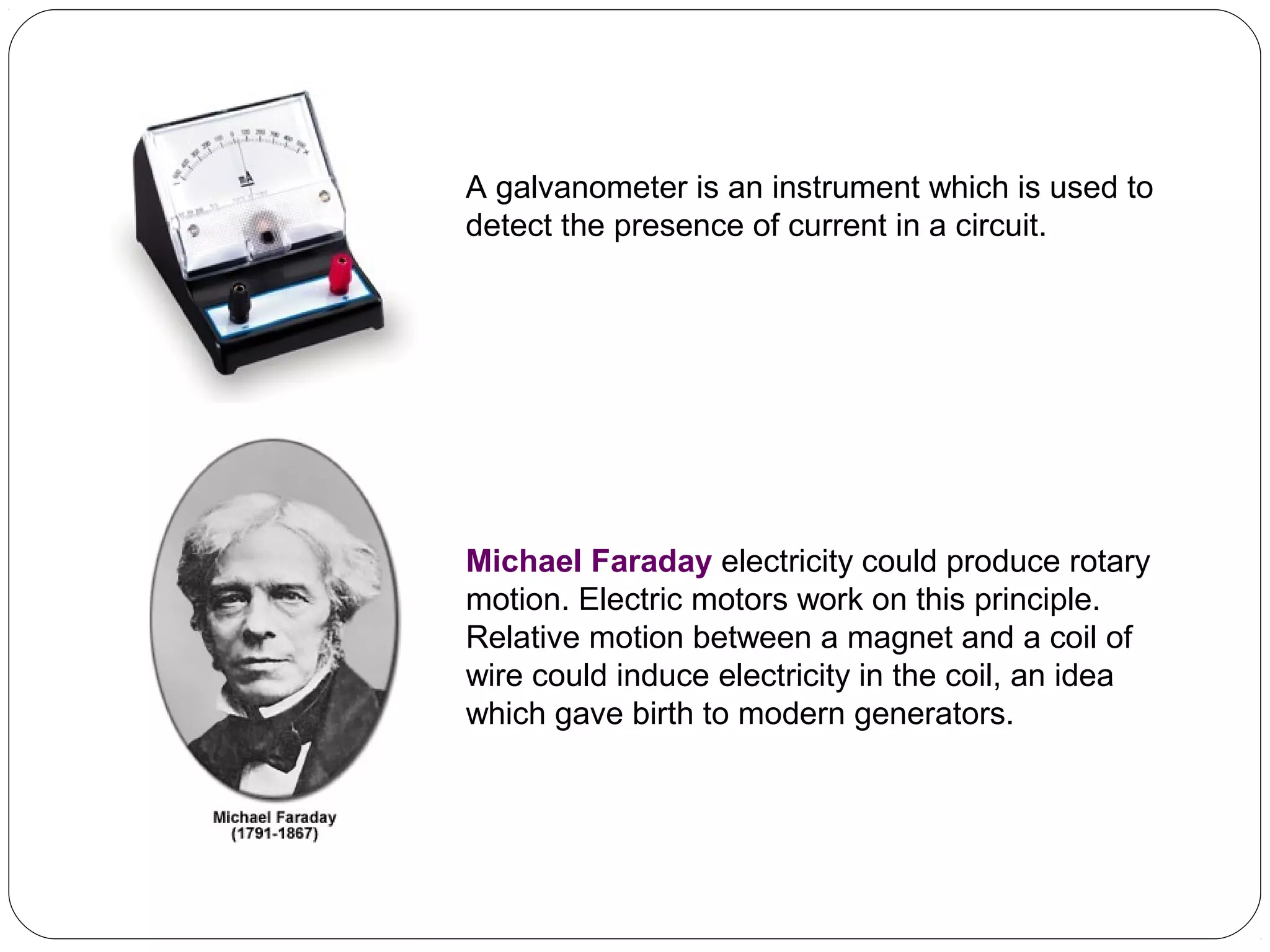
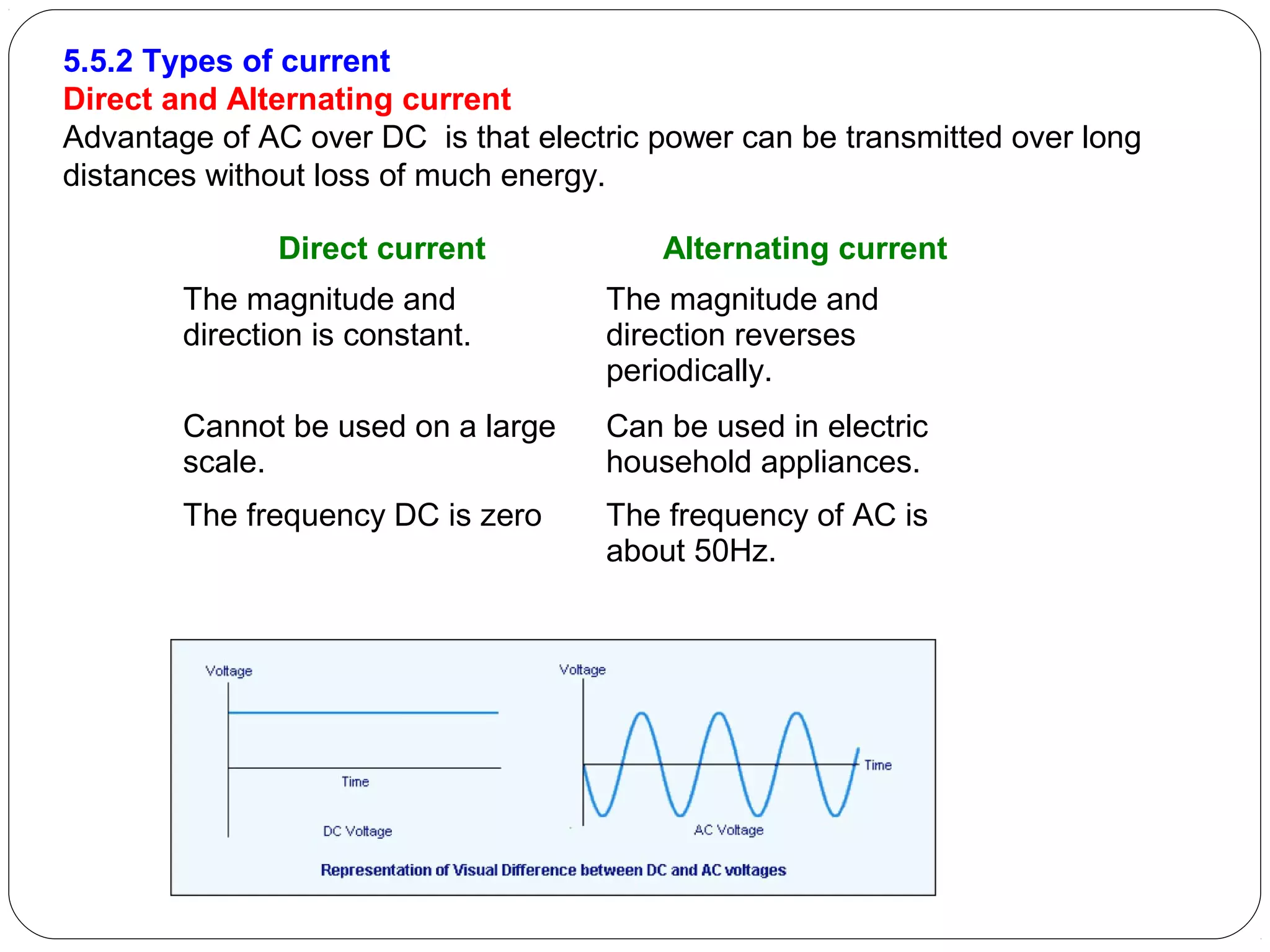
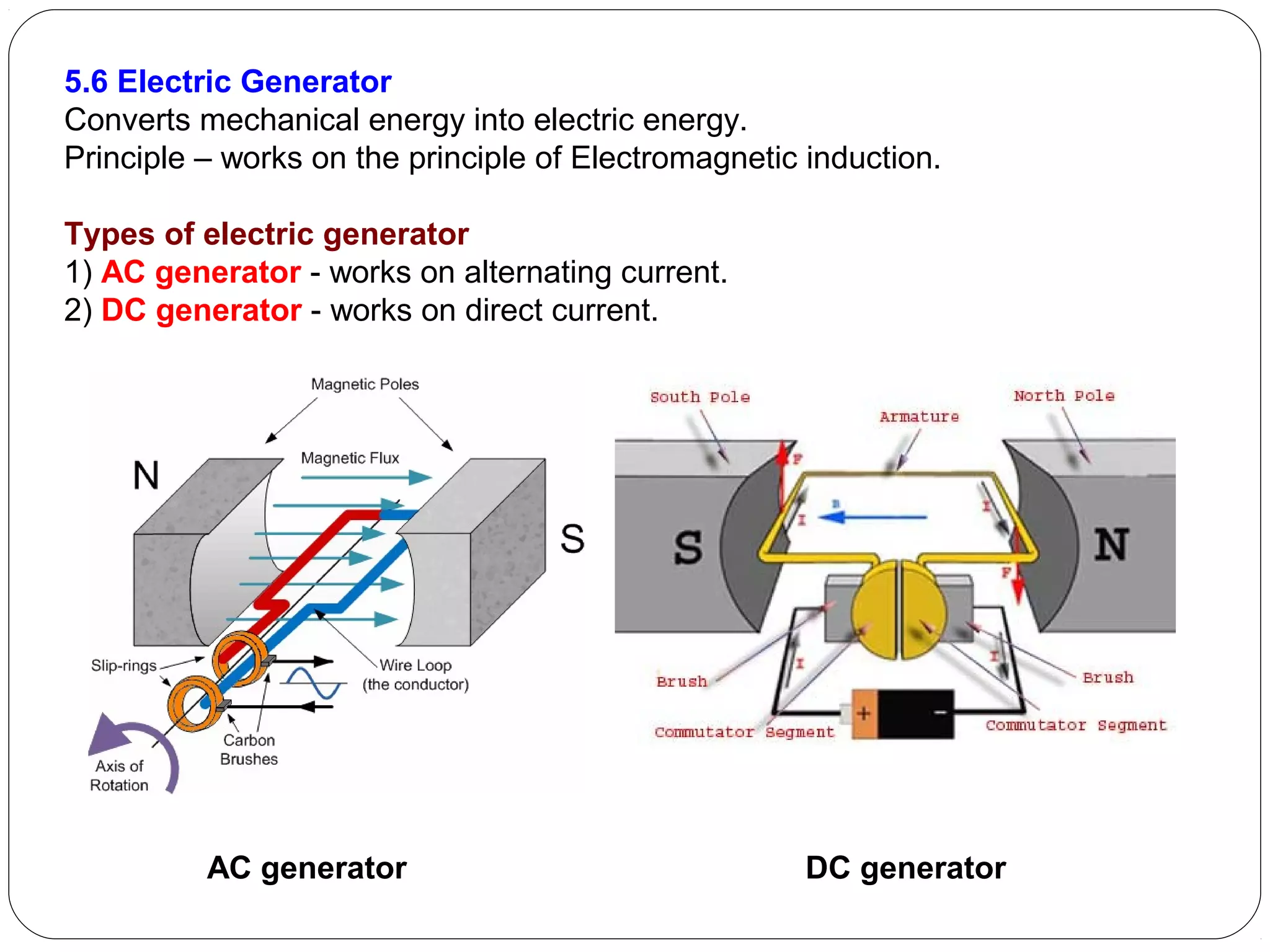
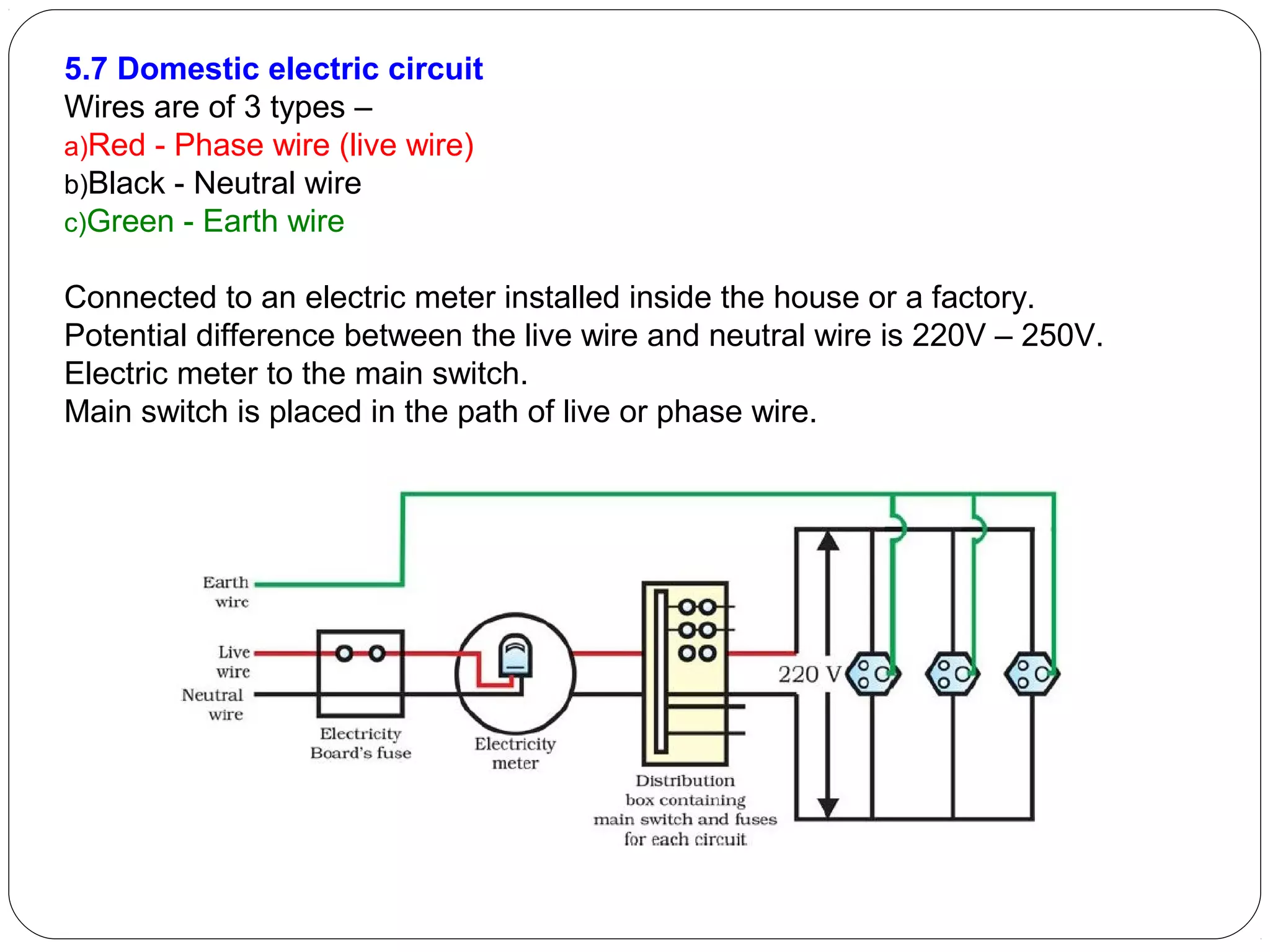
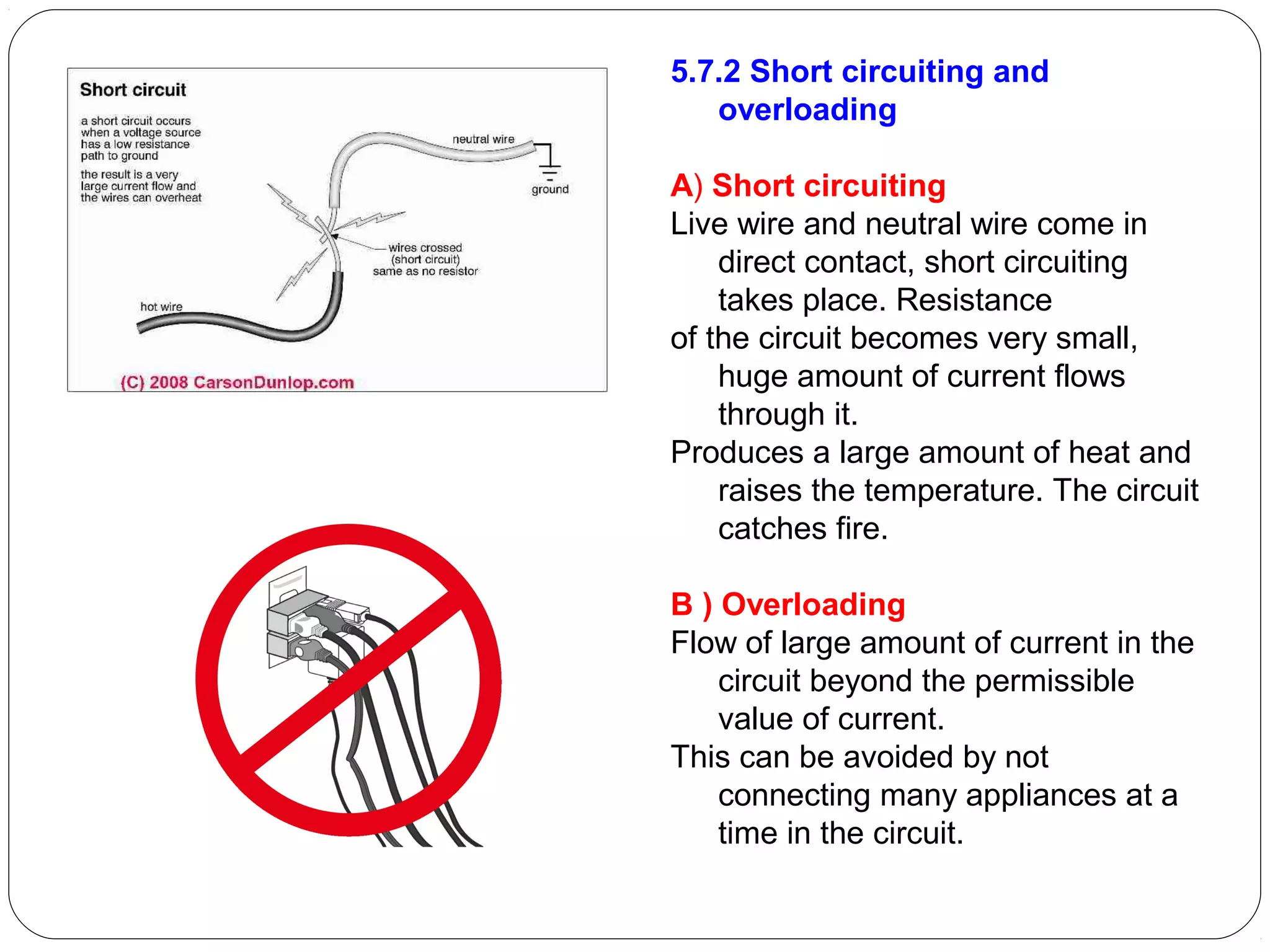
This document provides an overview of electromagnetism concepts for 10th grade students. It discusses magnetic field lines and their properties, the magnetic field created by current-carrying conductors using the right-hand rule, and the force experienced by conductors in magnetic fields. It also describes electromagnetic induction, the working principles of electric motors and generators, different current types, domestic electric circuits, and safety measures for working with electricity. Real-world applications of these concepts in technologies like MRI machines, trains, and power transmission are also mentioned.