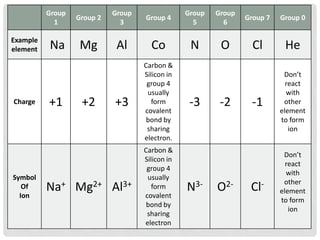
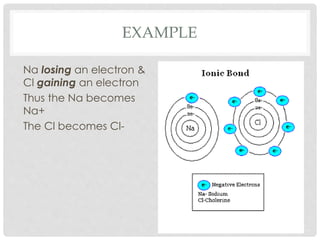
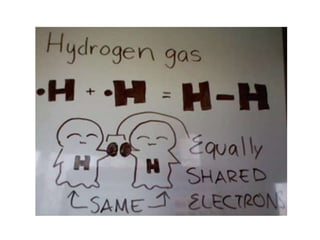
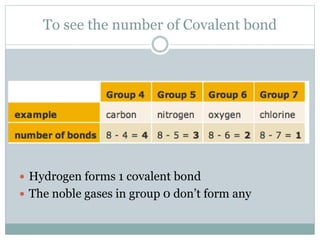
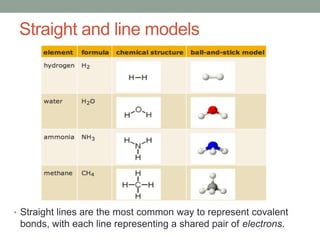
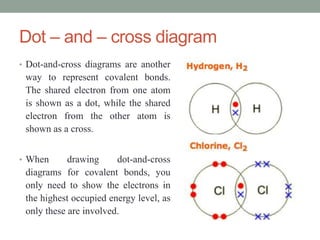
An ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost electrons, giving it a positive or negative charge. Atoms can become ions through ionization, where metals typically lose electrons to form cations and nonmetals gain electrons to form anions. Ionic compounds are formed when oppositely charged ions bond via ionic bonds, while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between nonmetal atoms.