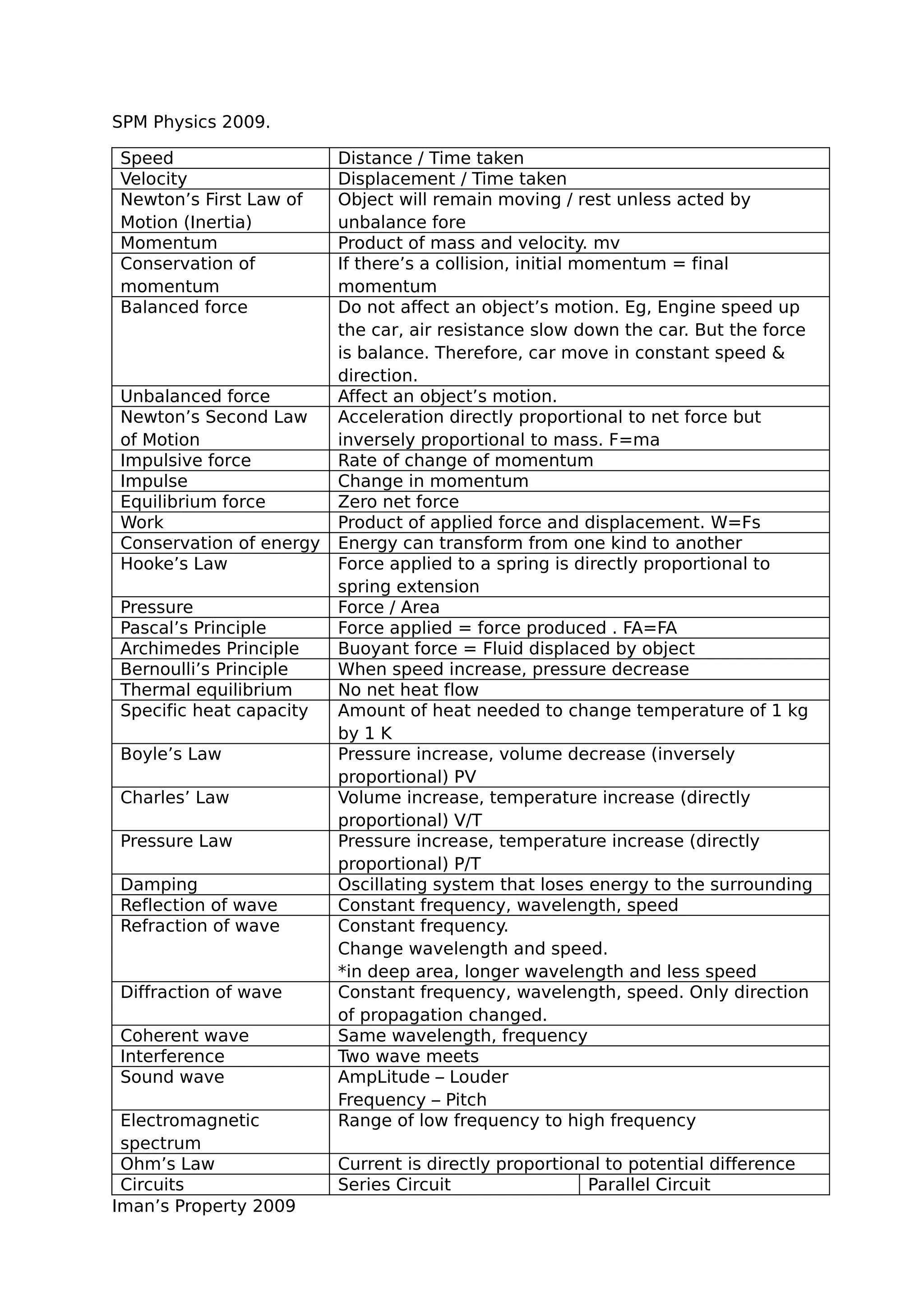
This document provides definitions and explanations of key concepts in SPM Physics 2009, including:
1) Definitions of speed, velocity, momentum, Newton's laws of motion, balanced and unbalanced forces, work, and energy.
2) Explanations of pressure, Pascal's principle, Archimedes' principle, and Bernoulli's principle.
3) Descriptions of wave reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, and sound waves.
4) Overviews of circuits, electromagnetism, induced current, and direct/alternating current.
5) Definitions of nucleon number, isotopes, radioactivity, nuclear fission, and nuclear fusion.