Embed presentation
Downloaded 475 times



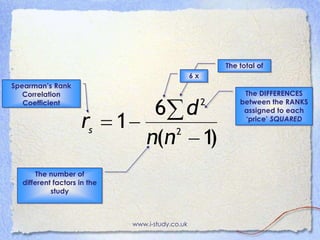




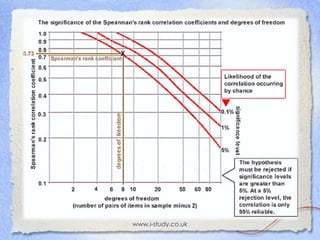

This document explains how to use Spearman's rank correlation coefficient to determine the strength and significance of the relationship between two variables. It provides steps to calculate the coefficient using birth rate and economic development data from 12 Central and South American countries. These steps are then applied to determine if there is a correlation between life expectancy and economic development in the same countries.









