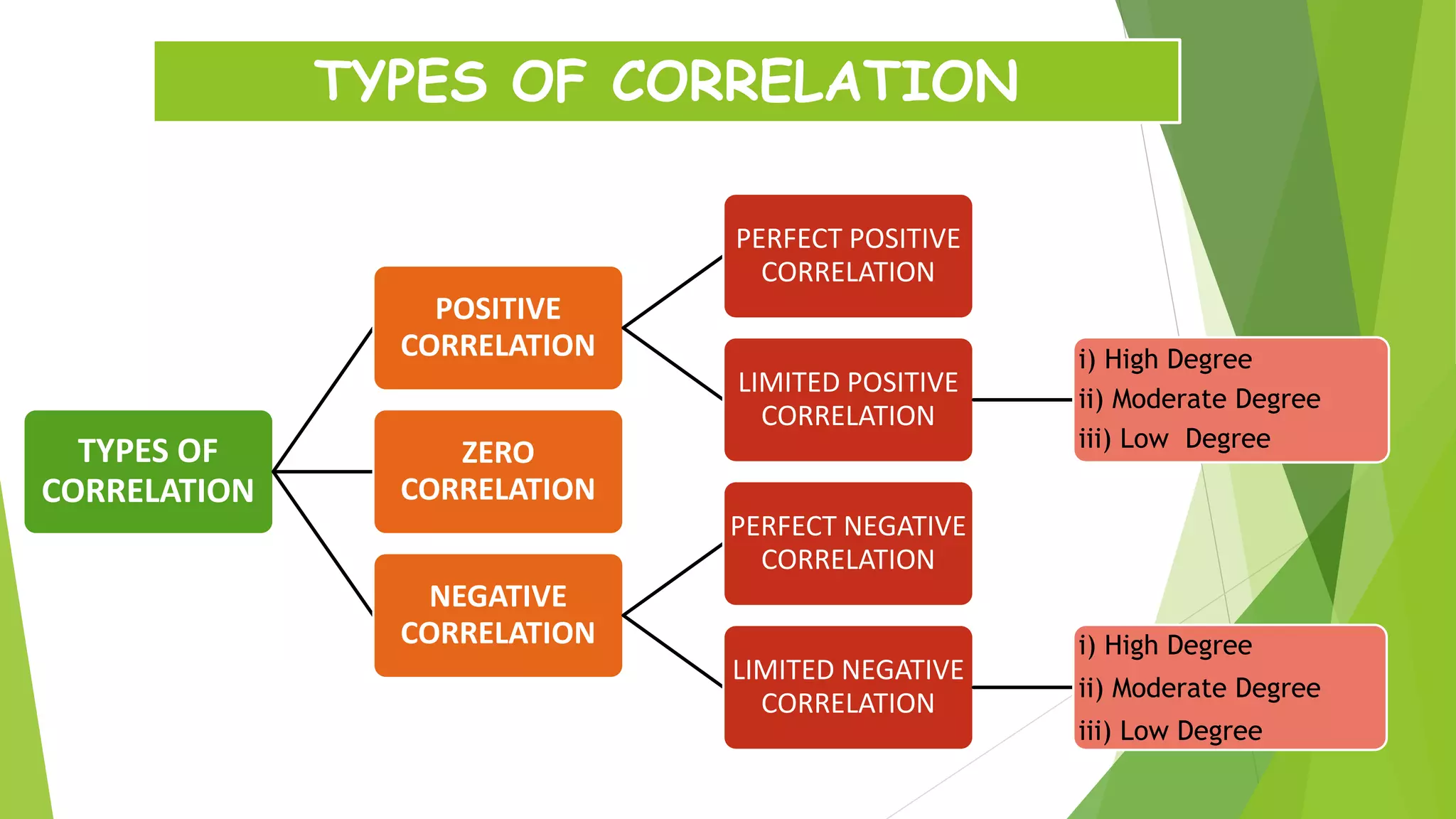
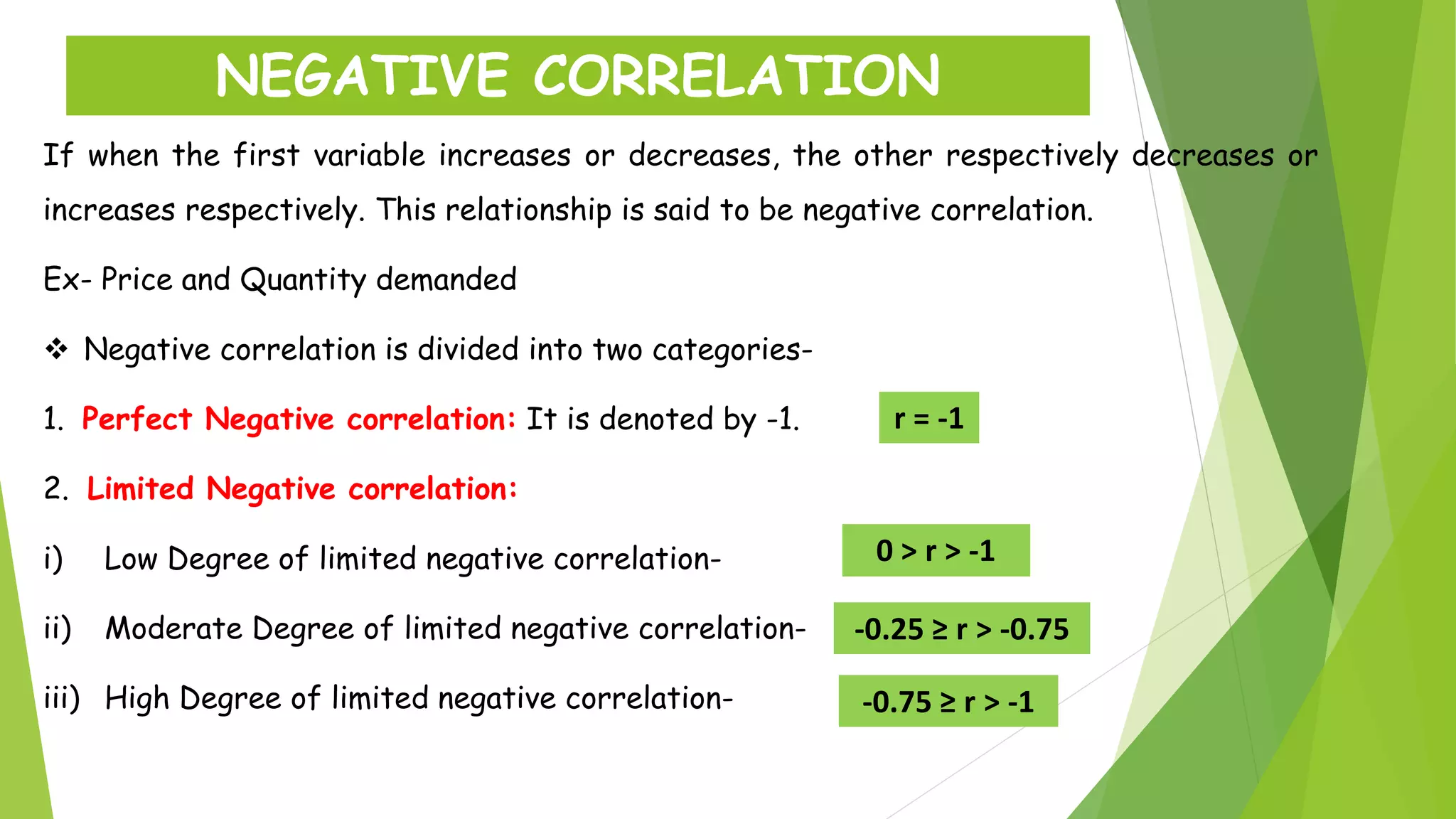
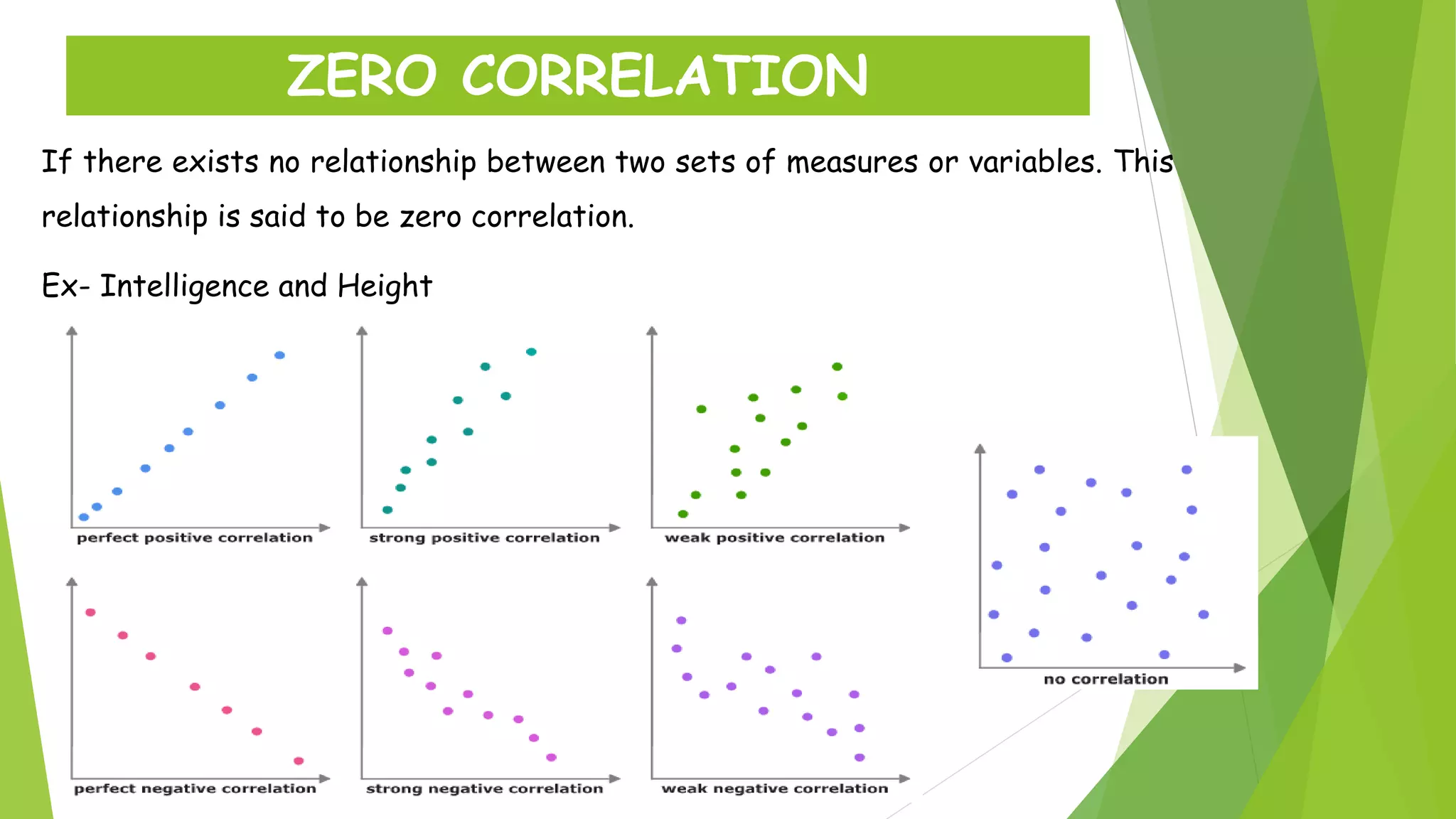
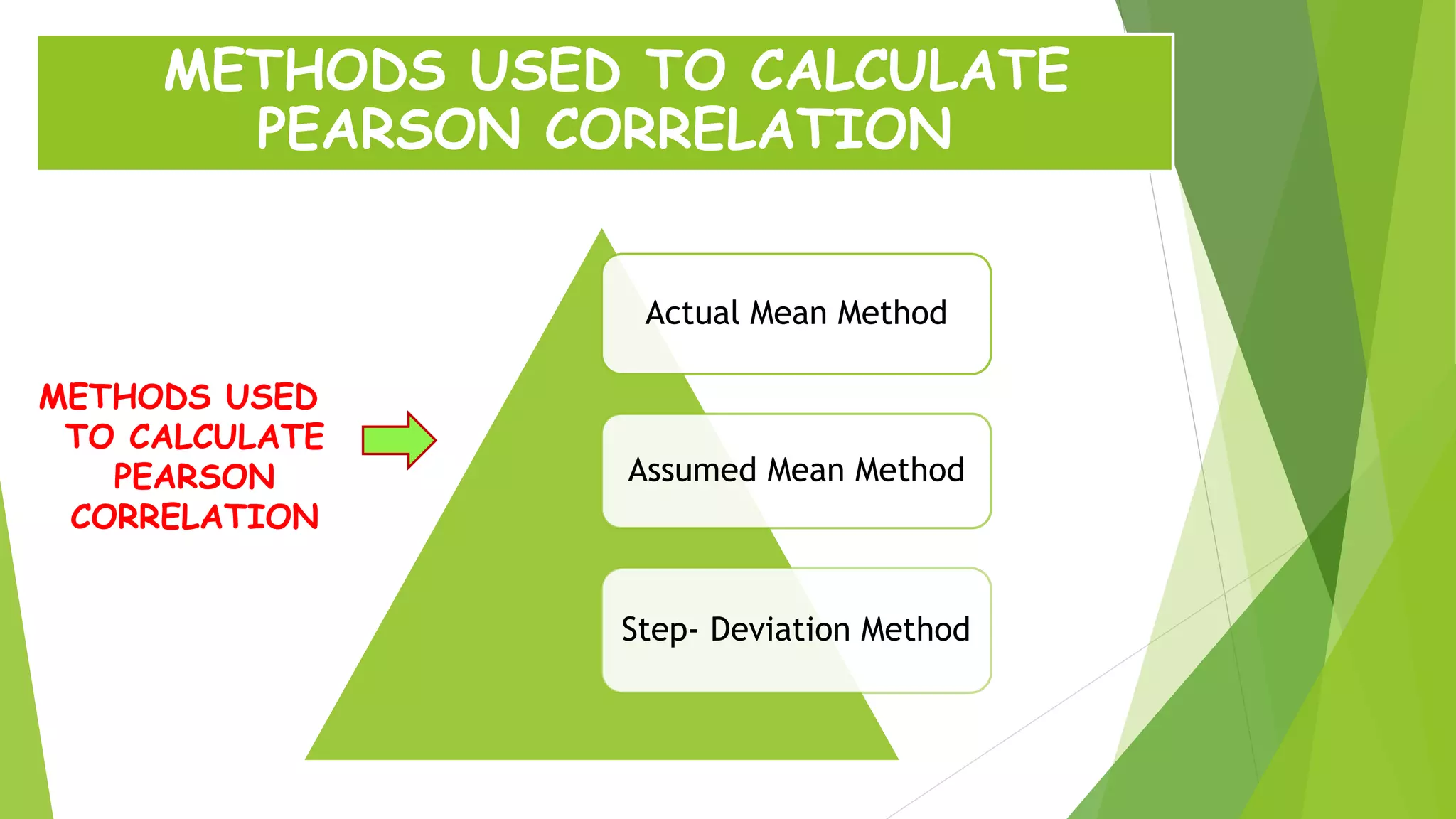
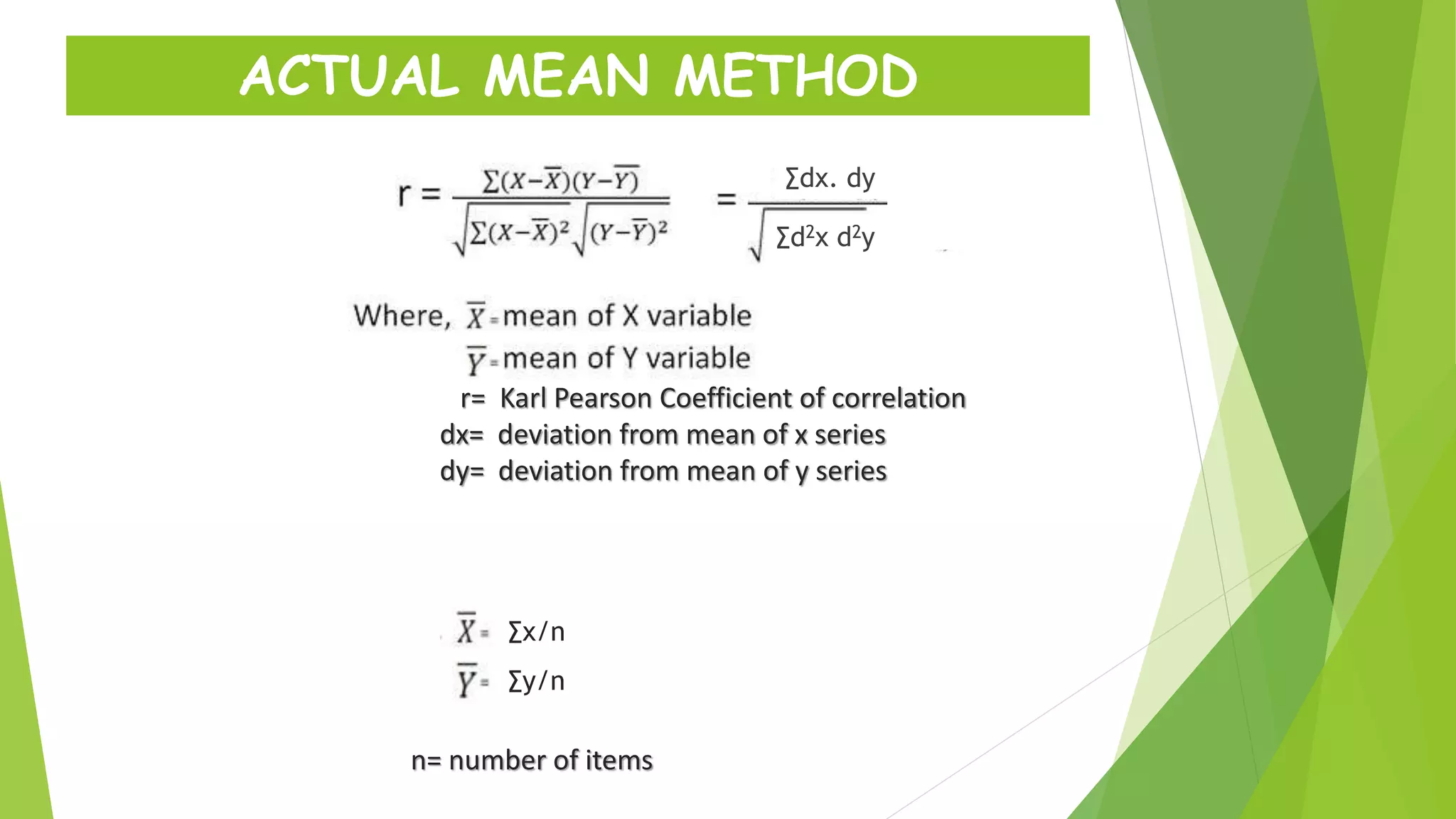
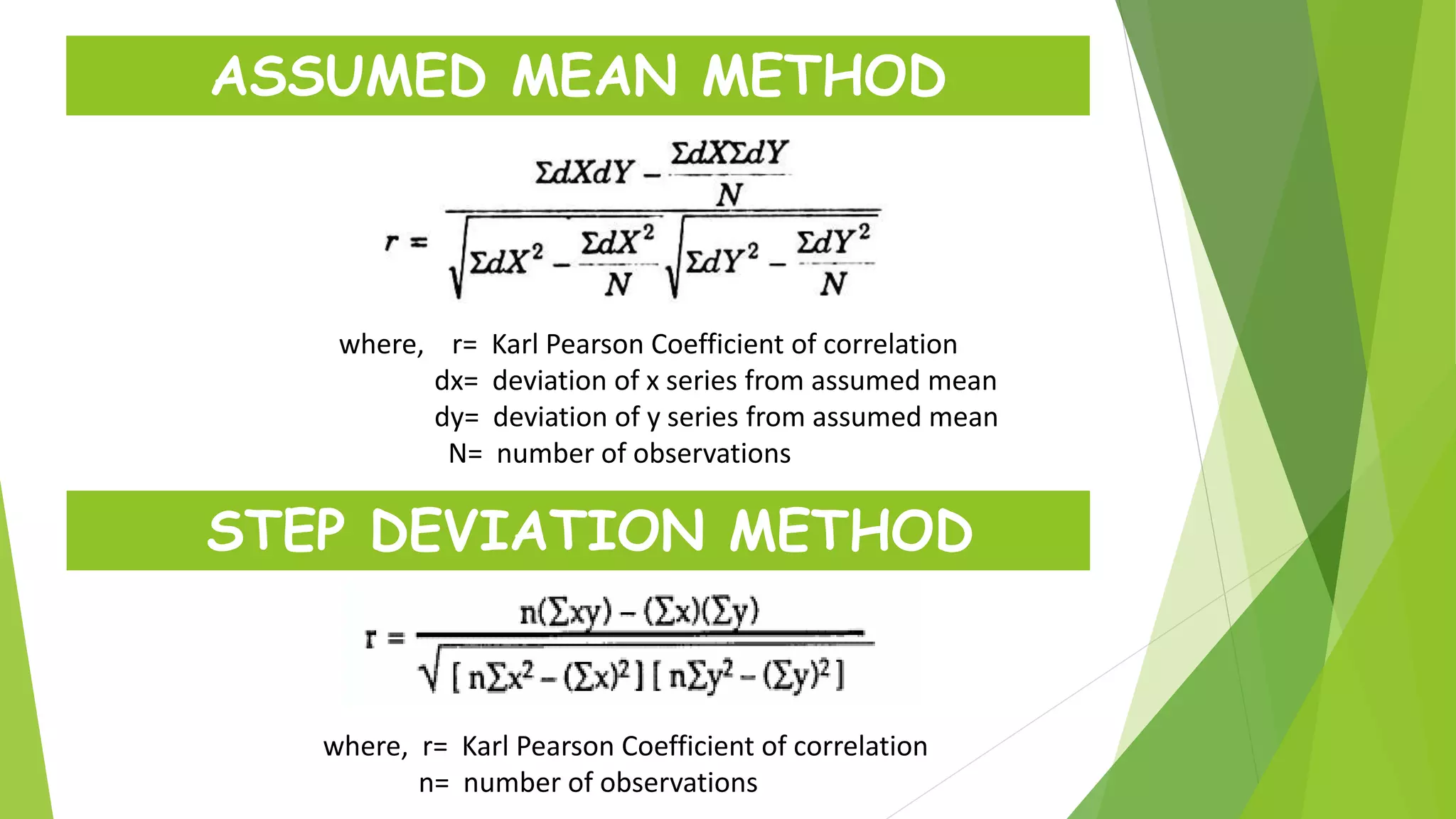
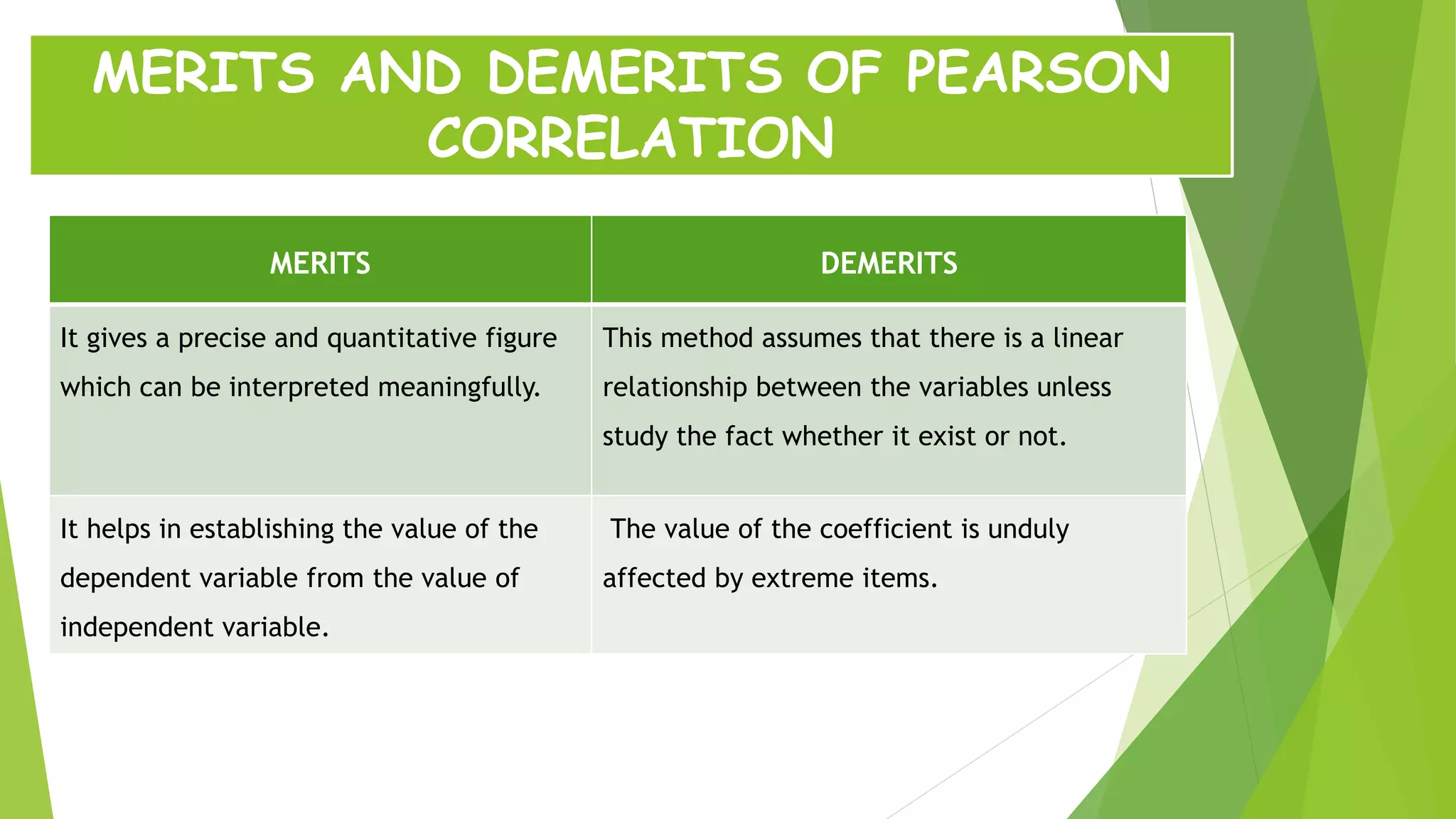
The document discusses the Karl Pearson coefficient of correlation, a statistical tool used to measure the degree of relationship between two variables. It details types of correlation, including positive, negative, and zero correlations, as well as methods for calculating the coefficient, such as the actual mean, assumed mean, and step deviation methods. The document also highlights the merits and demerits of using Pearson's correlation method in statistical analysis.