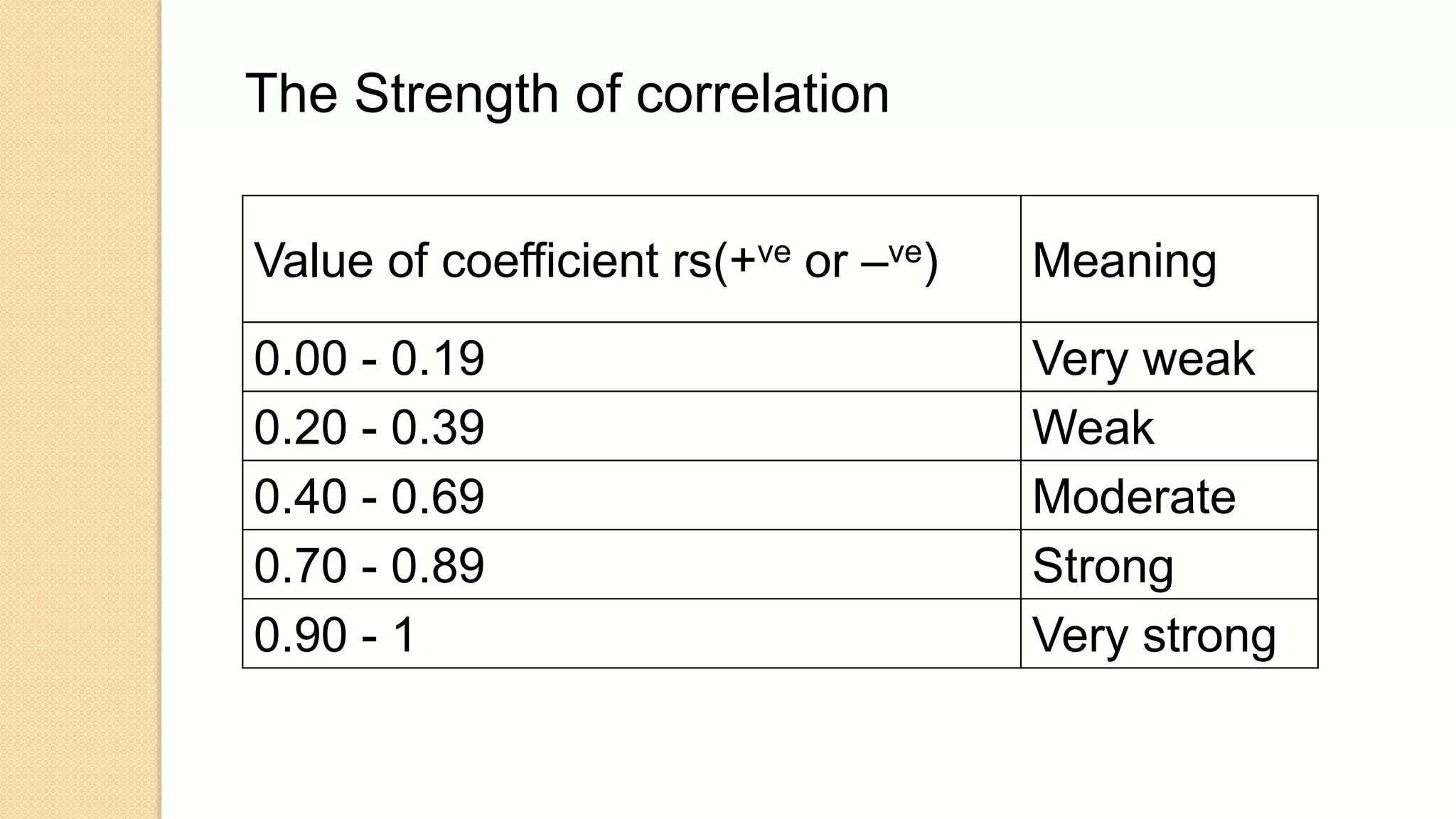
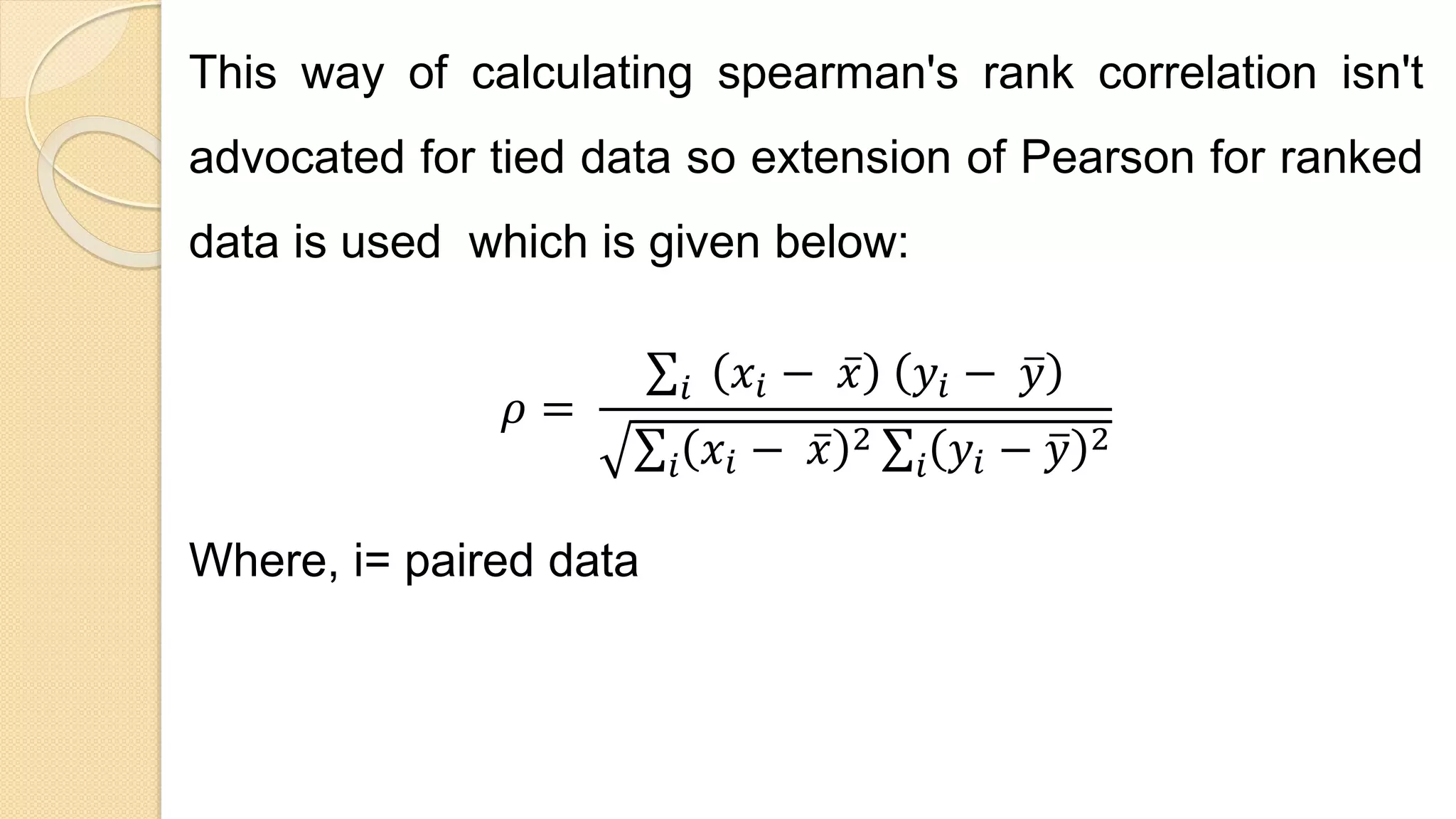
Spearman's rank correlation is a non-parametric measure of statistical dependence between the rankings of two variables. It assesses how well the relationship between two variables can be described using a monotonic function. Unlike Pearson's correlation, Spearman's correlation makes no assumption about the distributions of the variables and is thus suited for both continuous and ordinal data. It is calculated based on the ranked values of the variables rather than the actual values. Spearman's correlation is commonly used in genetics and plant breeding research to identify associations between traits and genes.