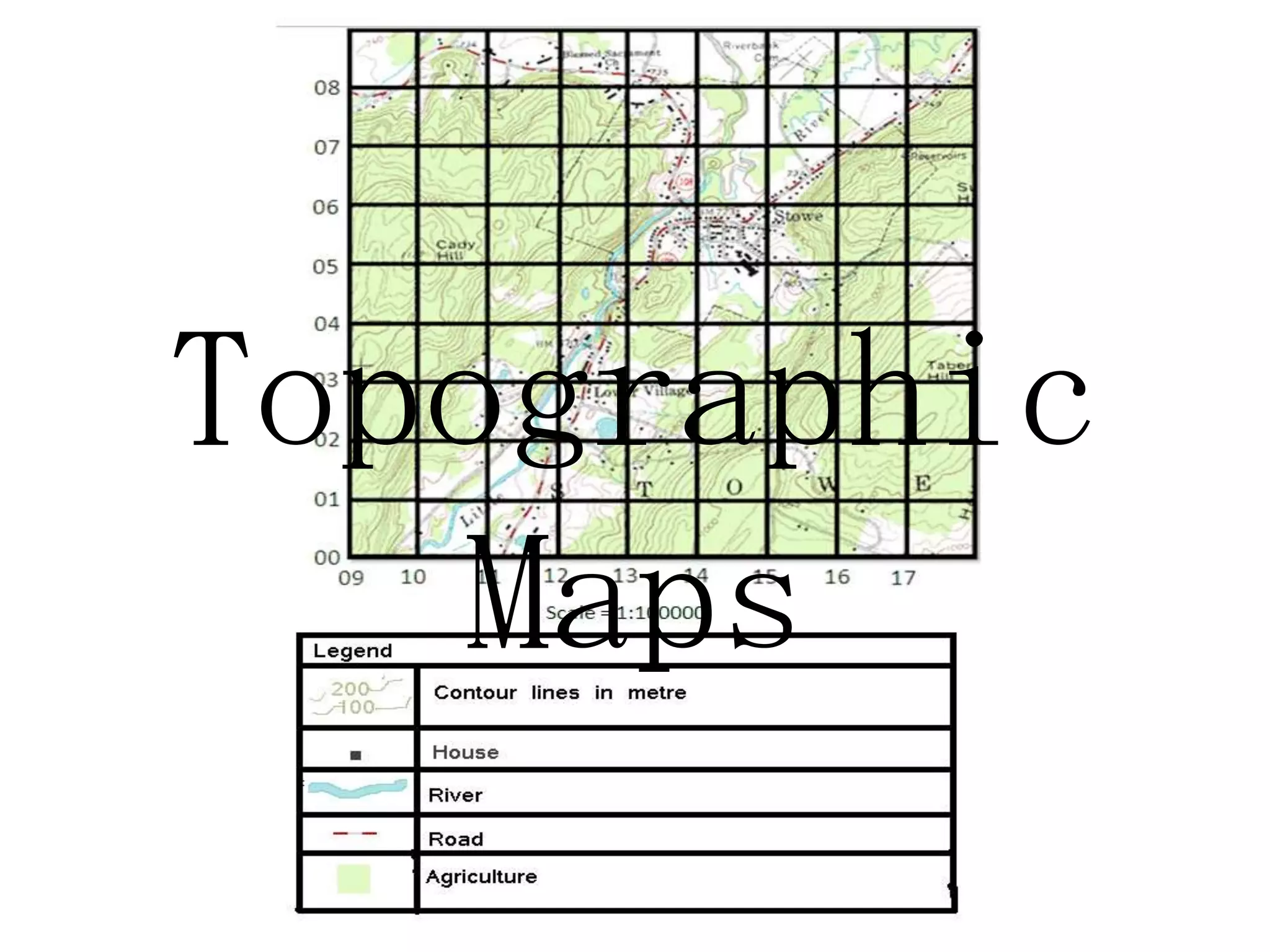
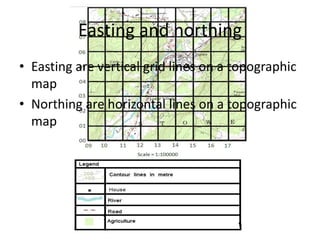
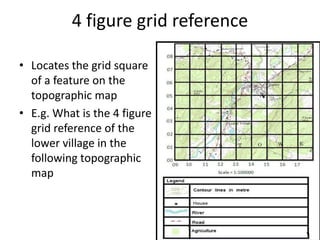
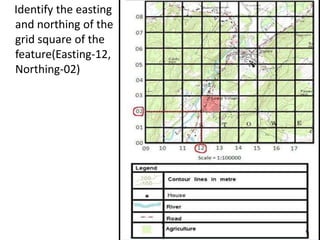
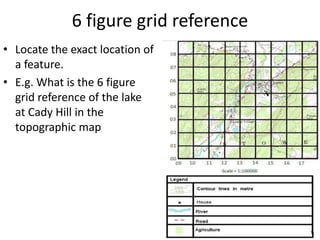
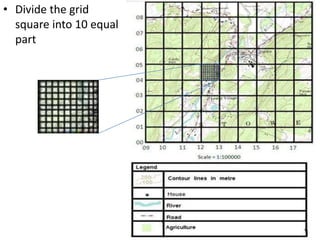
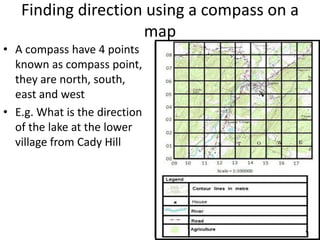
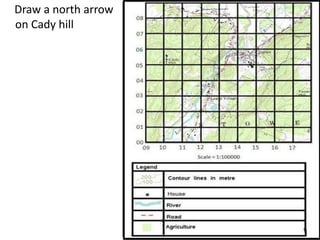
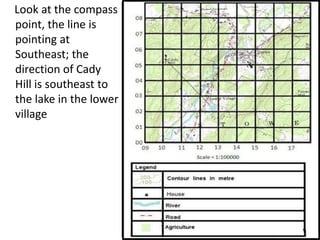
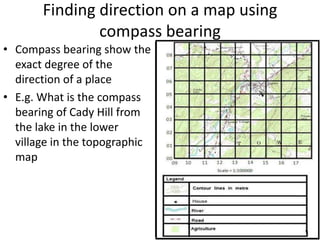
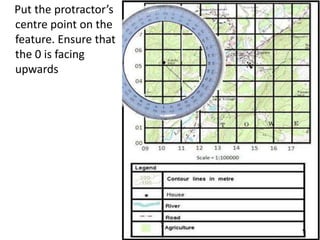
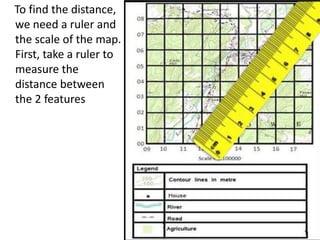
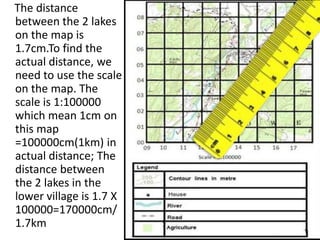
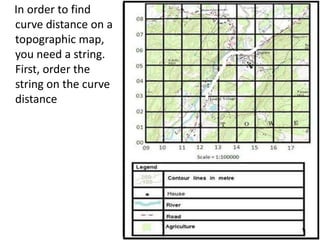
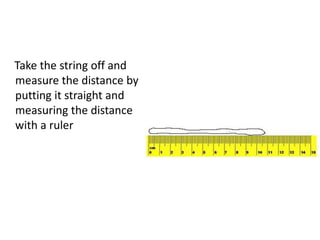
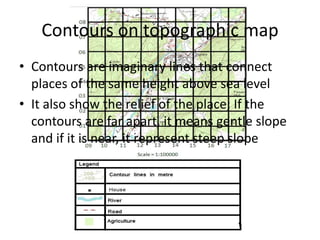
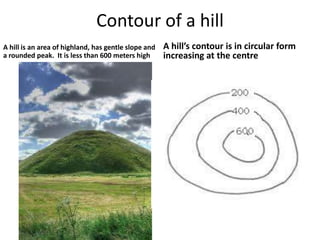
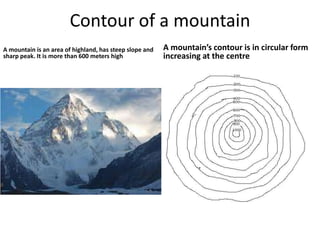
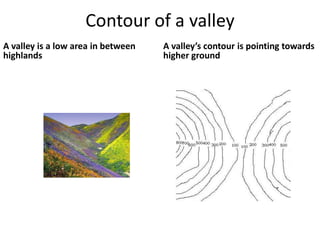
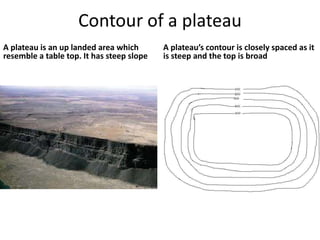
Topographic maps use a grid system of eastings and northings to locate features. Grid references specify the grid square and exact location of a feature. Compass directions and bearings are used to determine the orientation between locations. Distances on a map are measured using a ruler and scale, while curved distances use a string. Contours connect areas of equal height and indicate terrain features like hills, mountains, valleys, plateaus and ridges based on their shape and steepness.