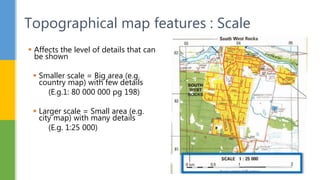
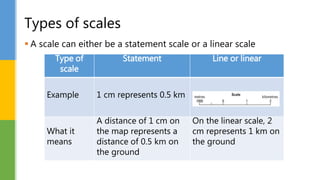
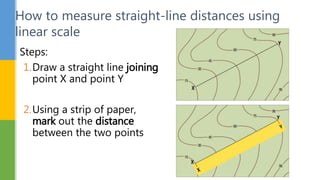
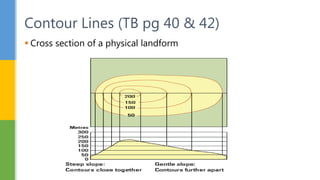
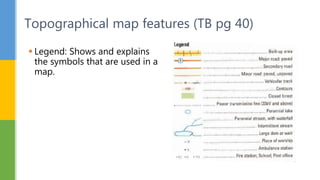
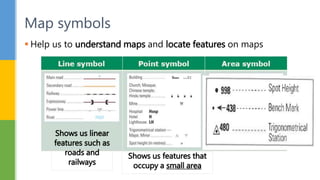
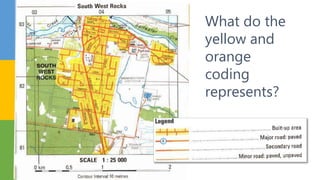
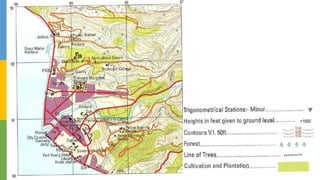
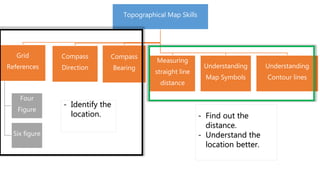
This document discusses various skills for reading topographical maps, including identifying compass direction and bearing, measuring straight-line distances, understanding contour lines and map symbols, and using scale. It provides steps for determining compass direction and bearing between two points using a protractor. It also outlines how to measure straight-line distances on a map using a linear scale or strip of paper. The objective is to use contour lines to describe land relief and map symbols to locate features.