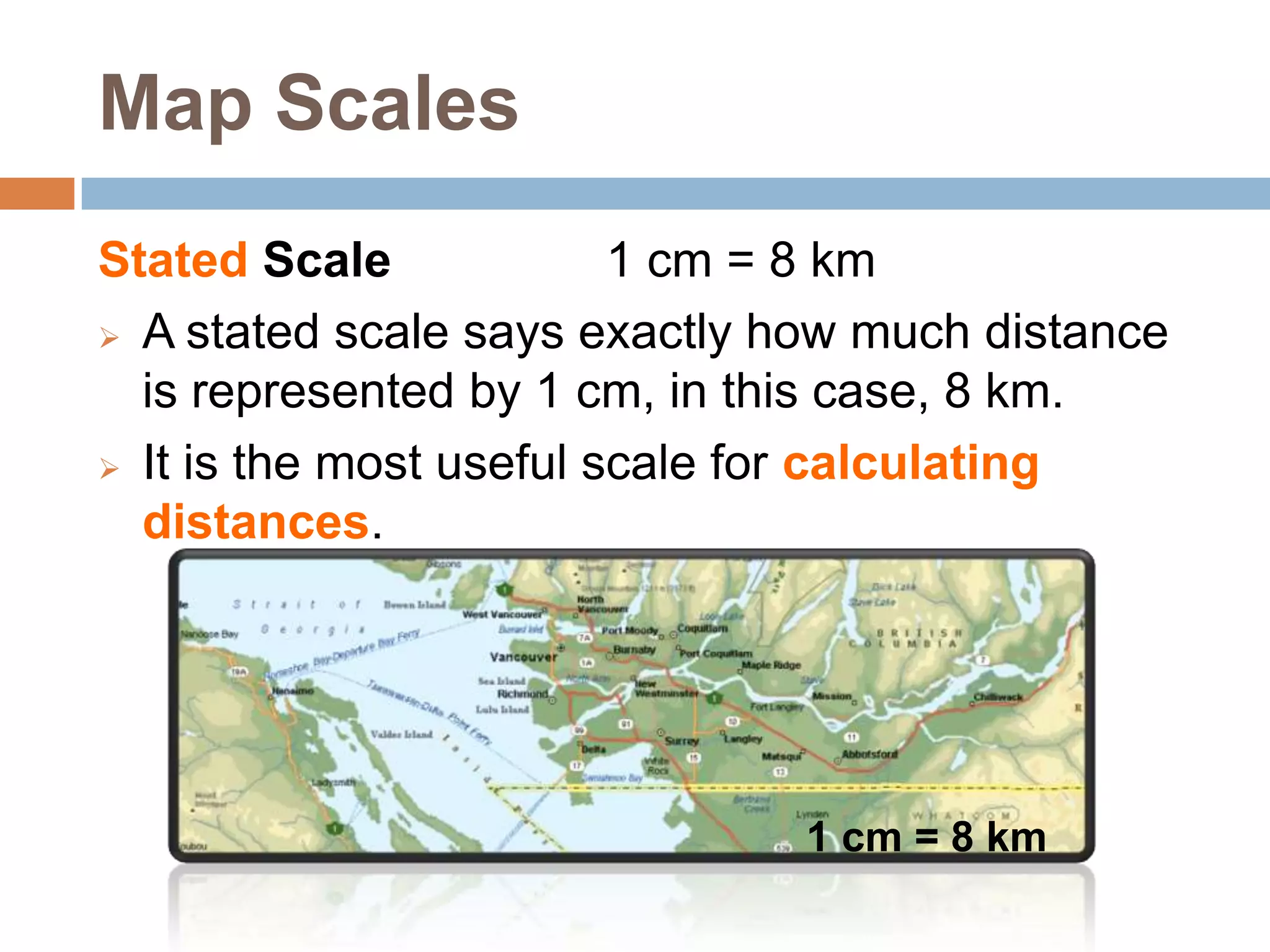
The document discusses map scales. It defines three types of scales: stated scale, linear scale, and ratio scale. It explains how to convert between ratio scales and stated scales using the metric system and decimal places. It provides examples of calculating distances on maps using cross-multiplication and five steps: find the ratio scale, convert to stated scale, measure map distance, use cross-multiplication, and write a conclusion statement. Finally, it describes the difference between large scale and small scale maps in terms of the level of detail shown and area covered.