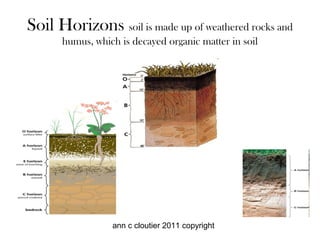
Water, temperature changes, and chemical reactions are key factors in weathering and erosion. Water is particularly powerful in mechanically and chemically breaking down rock. Moving water, glaciers, wind, and gravity transport eroded materials and deposit them elsewhere. Over time, this leads to soil formation and changes in landforms, as seen with caves and karst topography. Different soil types such as loess are suitable for certain agricultural uses. Plant roots and acids like acid rain also contribute to chemical weathering of rocks.