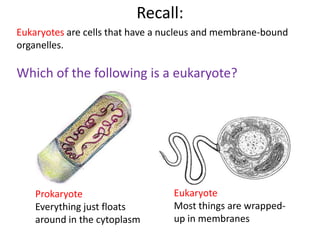
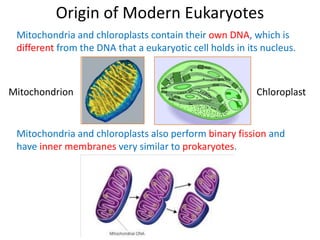
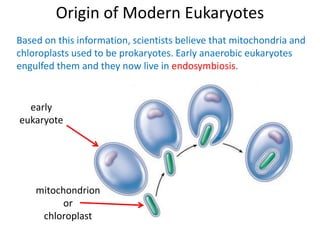
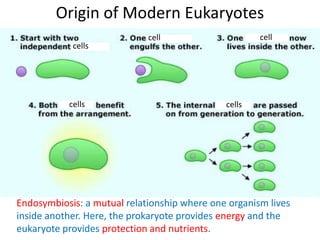
1) The document outlines the kingdoms of life and differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It describes how mitochondria and chloroplasts are thought to have originated from prokaryotes that engaged in endosymbiosis with early eukaryotes.
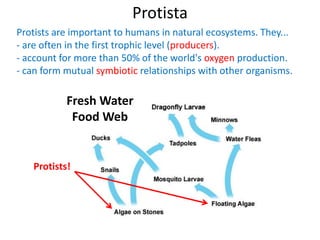
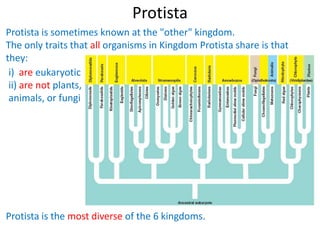
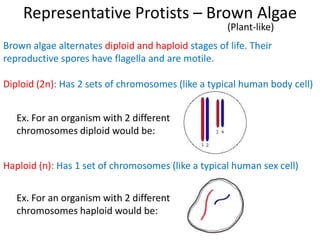
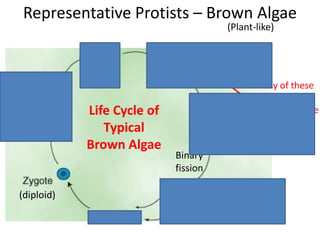
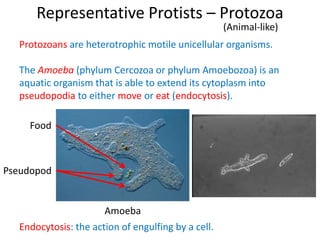
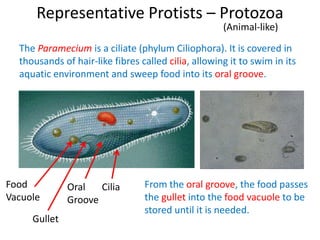
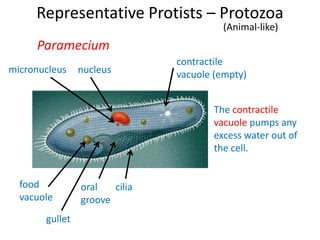
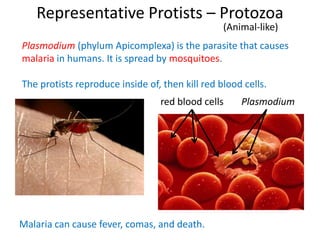
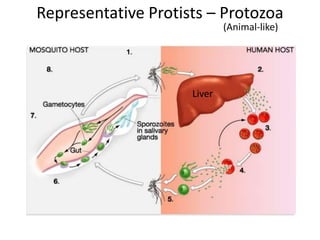
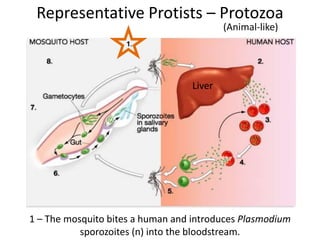
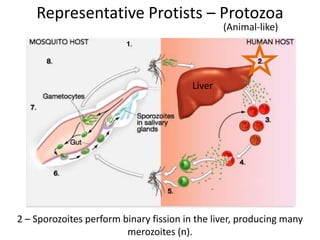
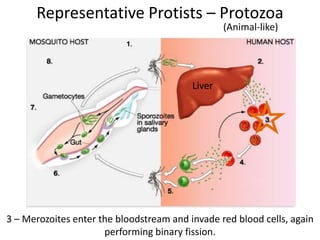
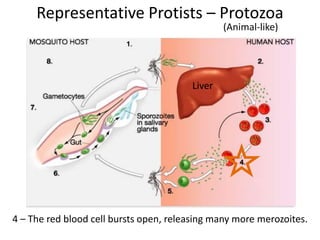
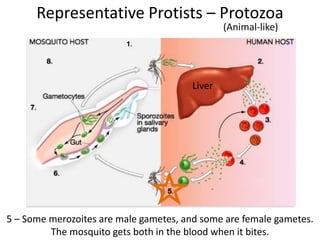
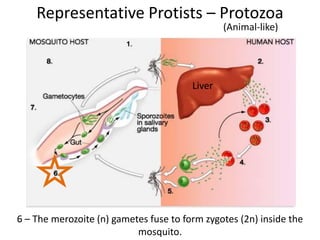
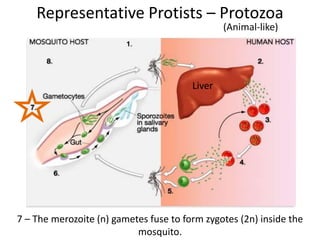
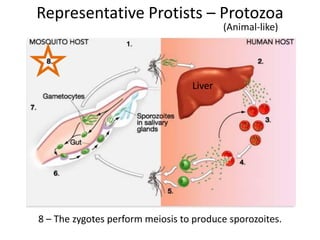
2) Representative protists are described, including slime moulds, red and brown algae, protozoa like amoebas and paramecium, and the malaria-causing plasmodium.
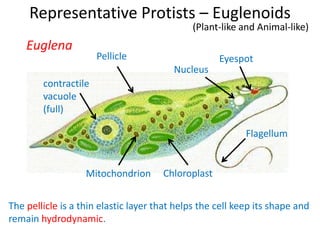
3) Euglena is presented as a protist that exhibits both plant-like and animal-like characteristics, being able to perform photosynthesis using chloroplasts but also ingest food via phagocytosis.