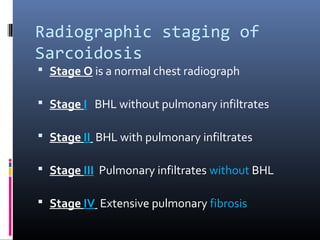
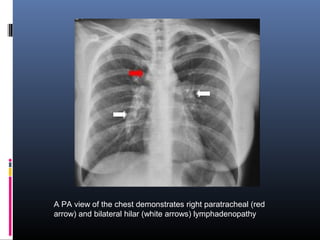
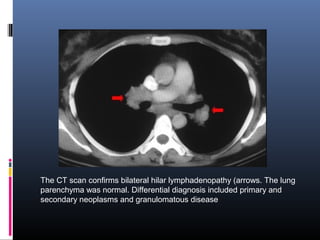
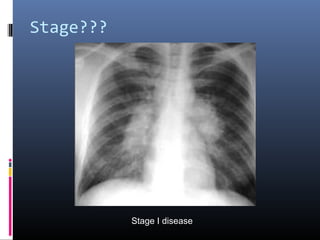
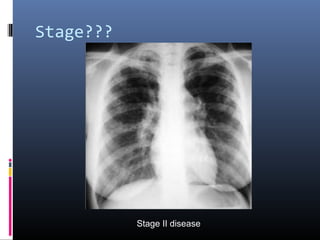
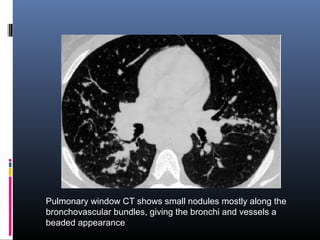
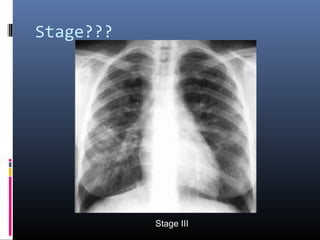
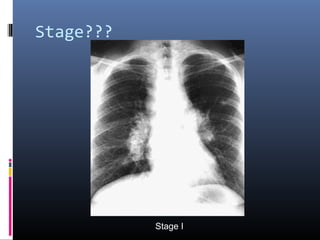
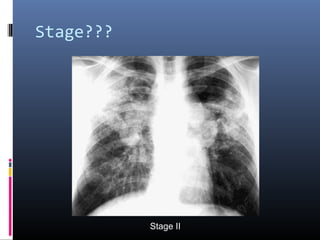
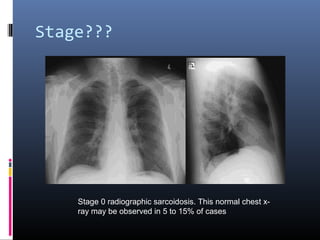
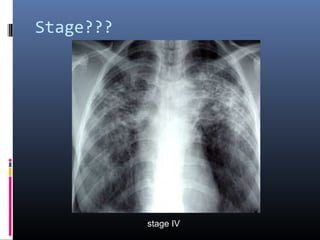
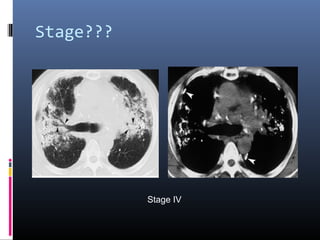
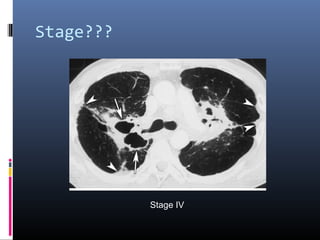
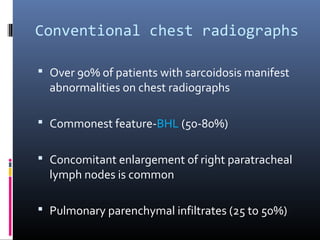
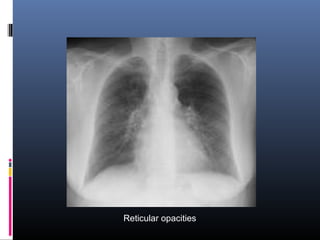
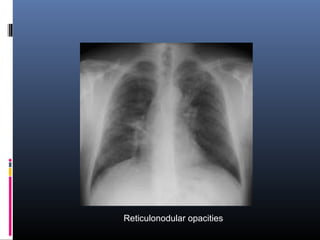
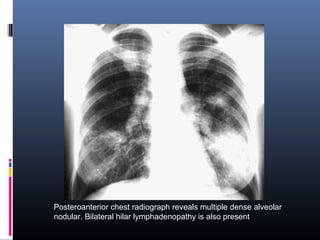
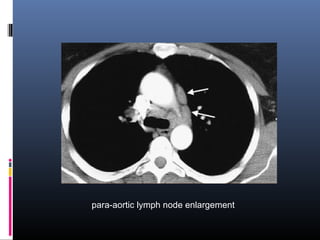
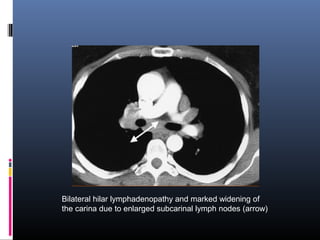
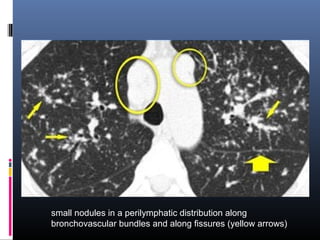
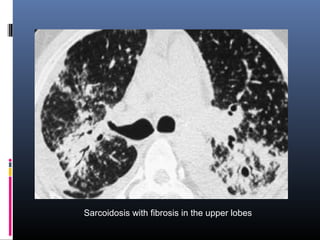
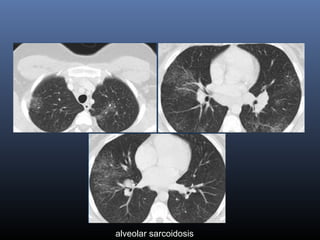
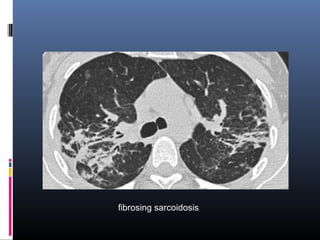
Sarcoidosis is a systemic granulomatous disease of unknown origin characterized by non-caseating granulomas that commonly affect the lungs. Pulmonary manifestations are present in 90% of patients and include bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy and pulmonary infiltrates. While two thirds of patients experience remission within ten years, one third have progressive disease that can lead to pulmonary fibrosis and, in rare cases, death. Computed tomography is more sensitive than chest x-rays in detecting lymph node enlargement and lung abnormalities associated with sarcoidosis.