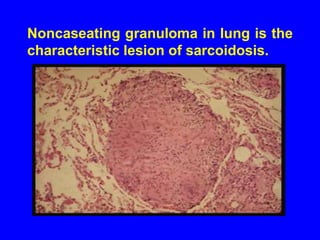
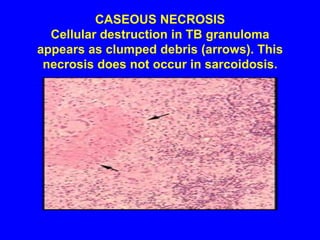
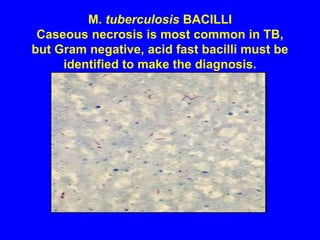
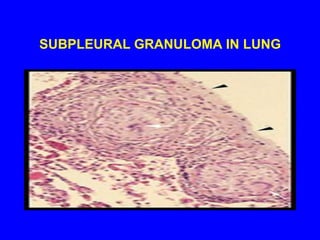
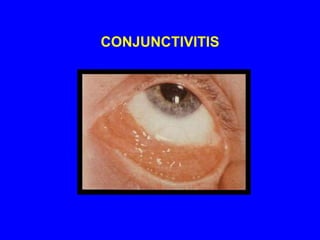
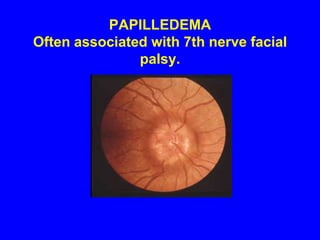
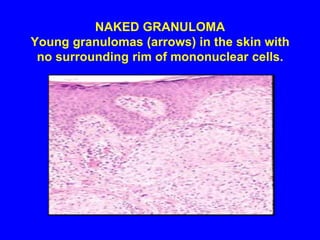
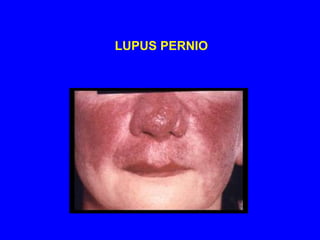
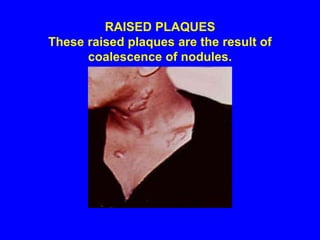
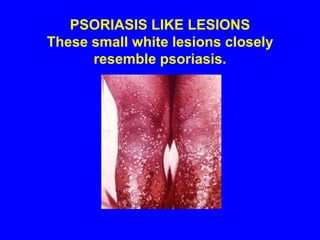
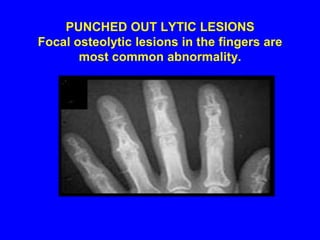
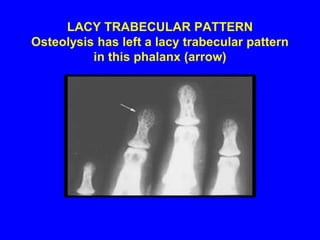
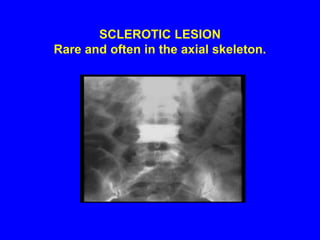
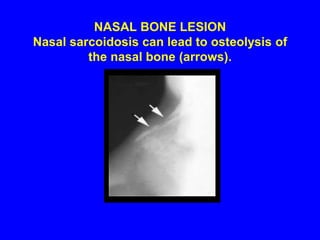
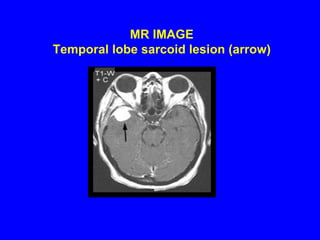
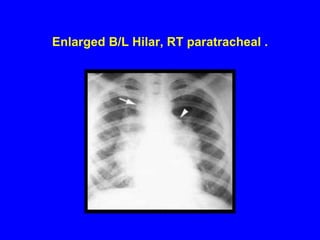
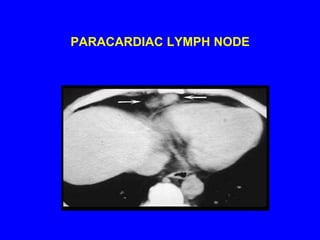
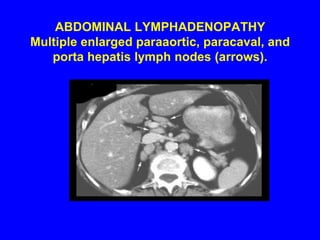
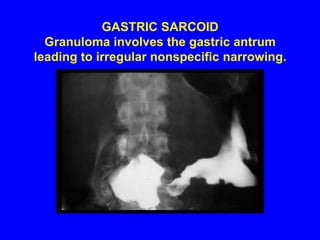
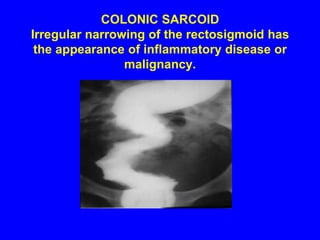
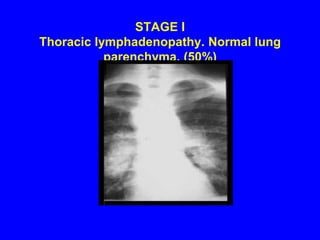
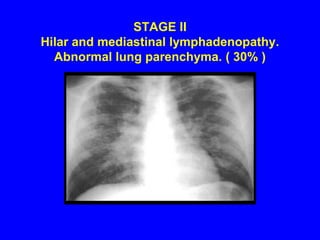
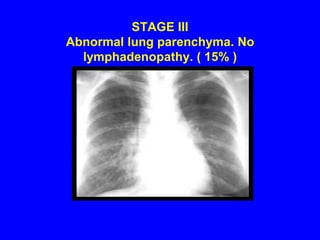
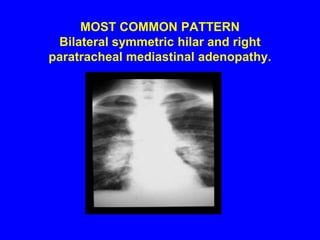
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem disorder characterized by the formation of noncaseating granulomas in multiple organs. It most commonly involves the lungs, lymph nodes, skin, and eyes. The cause is unknown but believed to be due to an abnormal immune response to unknown antigens in genetically predisposed individuals. Diagnosis is based on clinical features and identification of granulomas on biopsy, and exclusion of other conditions. While often asymptomatic, it can cause respiratory symptoms as well as involvement of other organs. Treatment involves corticosteroids, with hydroxychloroquine or methotrexate as steroid-sparing options. Prognosis is generally good, though some degree of permanent organ dysfunction occurs in about half of








![All granulomas, regardless of cause, may contain additional cells and matrix. These include lymphocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, fibroblasts and collagen [fibrosis].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sarcoidosis-110910130958-phpapp01/85/Sarcoidosis-9-320.jpg)