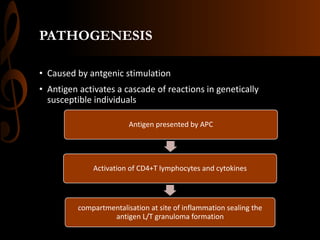
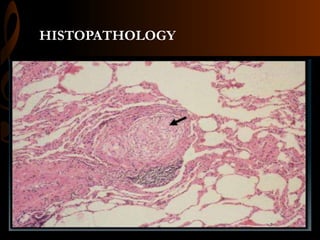
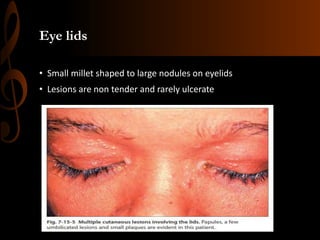
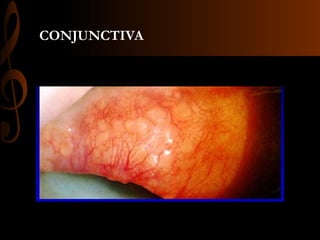
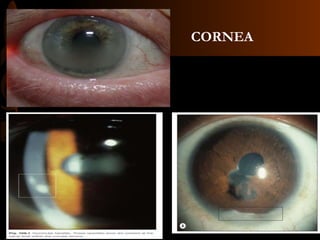
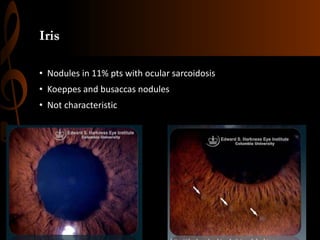
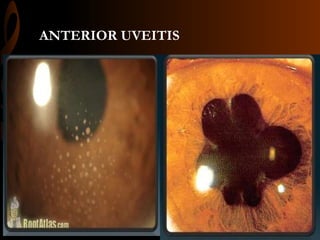
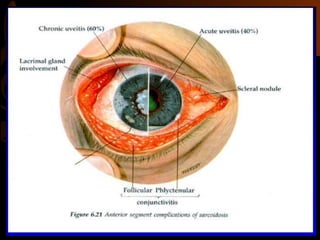
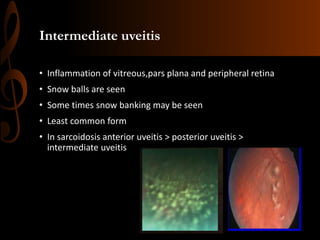
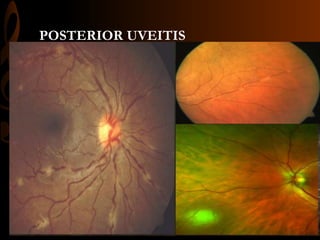
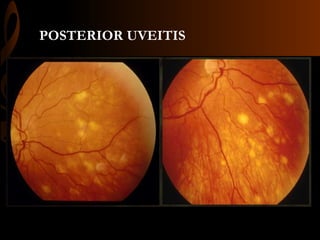
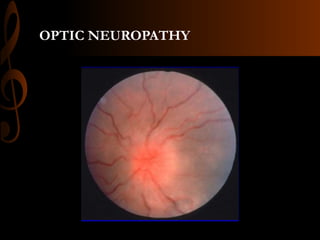
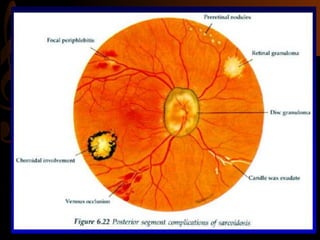
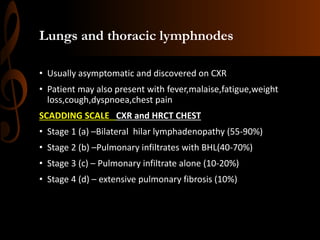
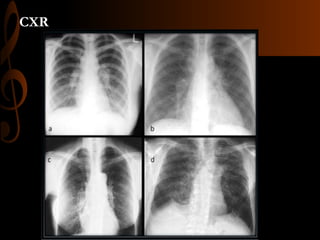
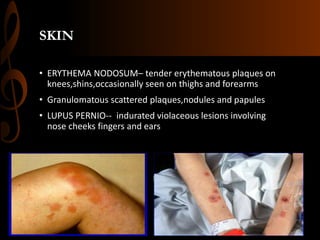
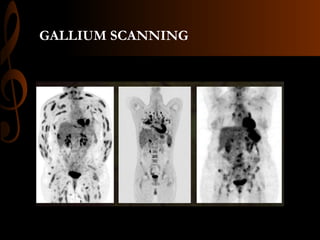
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of non-caseating granulomas in multiple organs. Ocular involvement occurs in 25-60% of sarcoidosis patients and most commonly manifests as chronic anterior uveitis. The document outlines the definition, epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical features involving the eyes and other organ systems, diagnostic criteria, treatment, and complications of ocular sarcoidosis. Investigations like lab tests, imaging, and biopsy are used to diagnose sarcoidosis and rule out other differentials when the clinical features are present.