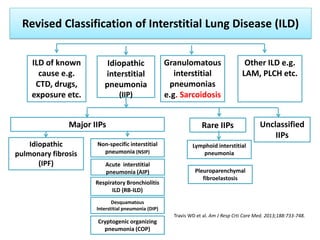
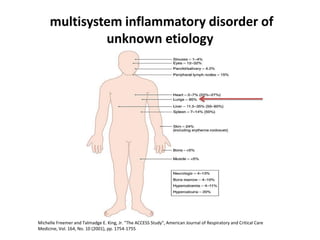
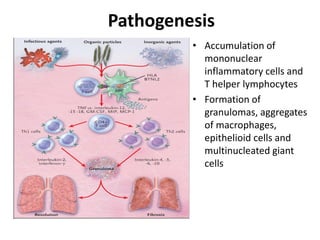
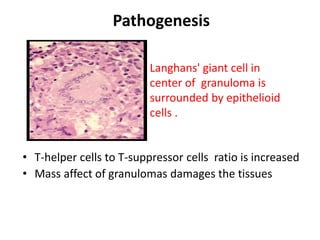
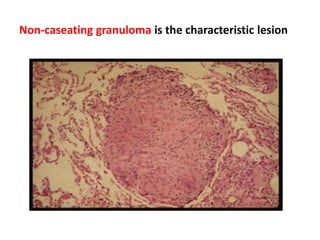
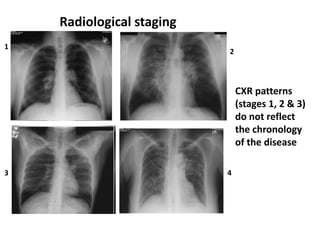
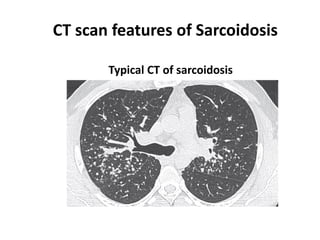
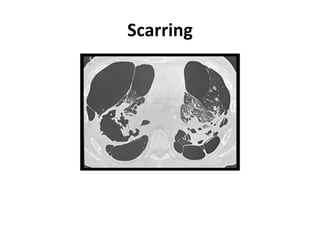
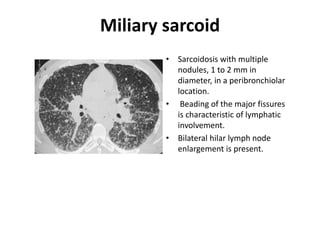
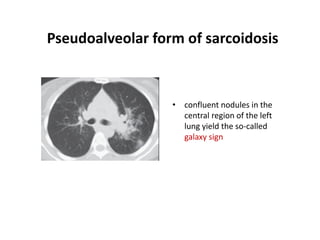
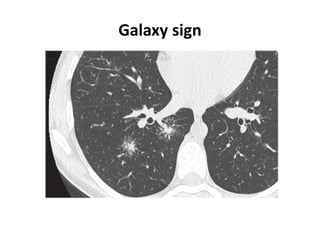
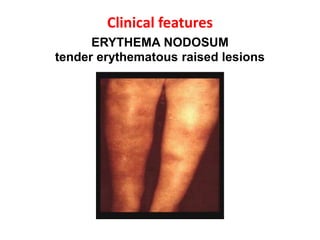
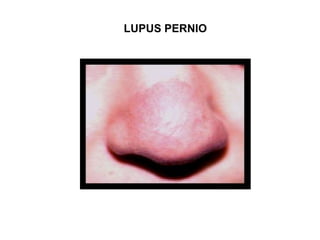
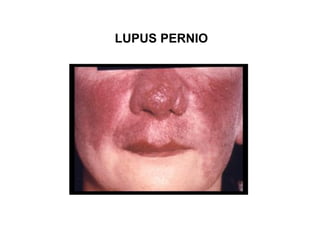
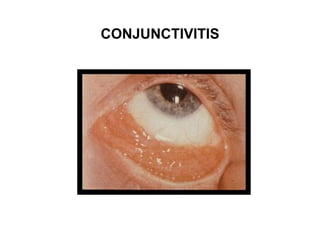
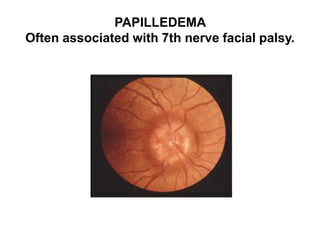
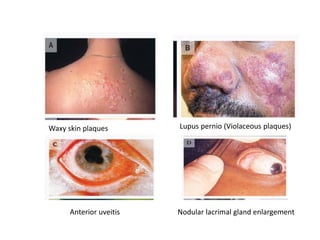
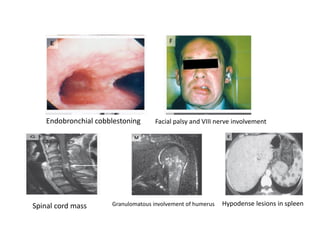
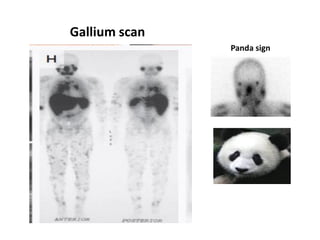
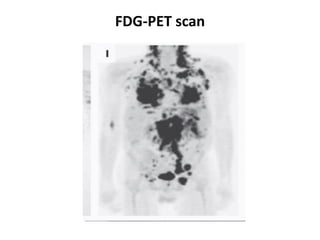
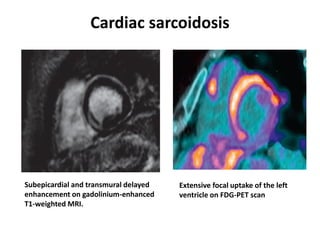
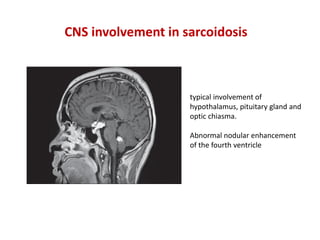
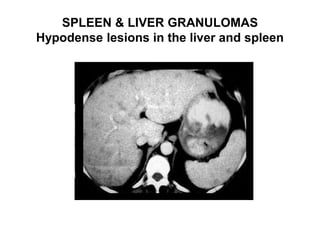
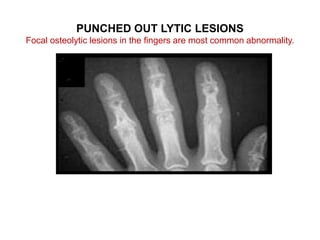
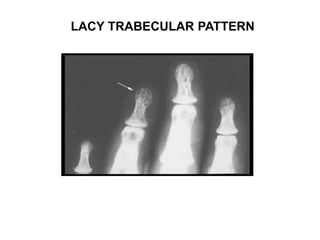
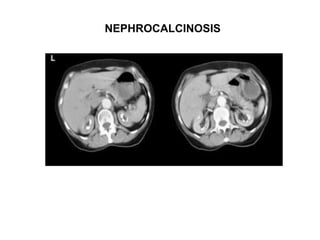
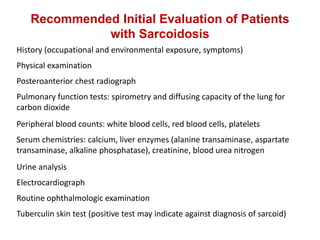
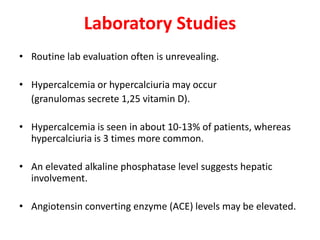
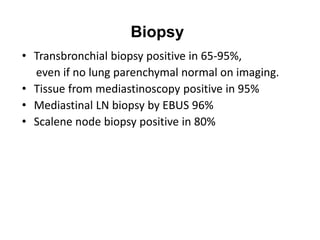
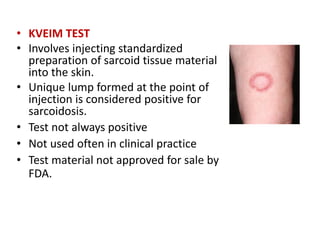
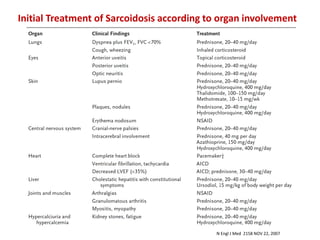
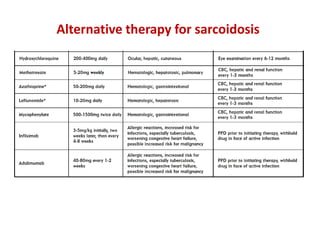
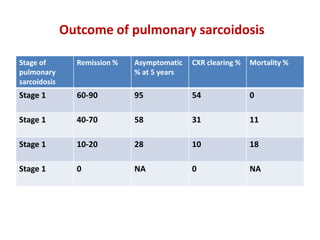
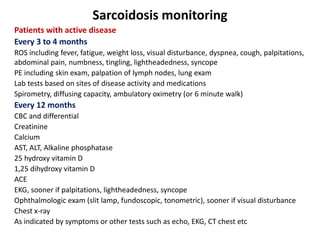
Pulmonary sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease of unknown etiology characterized by non-caseating granulomas. It most commonly affects the lungs, skin, eyes and lymph nodes. The pathogenesis involves accumulation of inflammatory cells and T lymphocytes forming granulomas that can damage tissues. Diagnosis is based on clinical features, radiological evidence of non-caseating granulomas on biopsy with other causes excluded. Treatment depends on severity and organ involvement but may include corticosteroids.