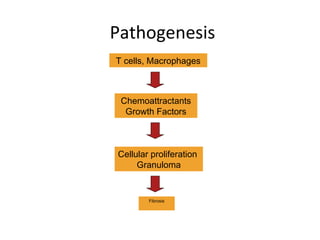
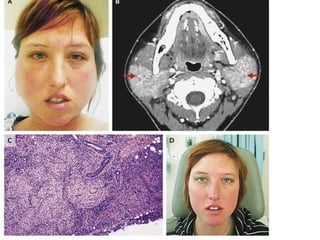
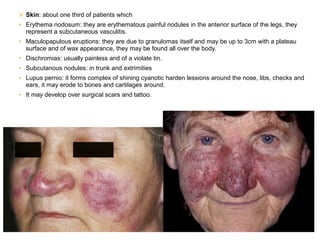
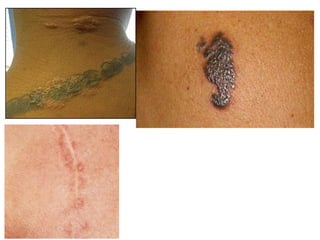
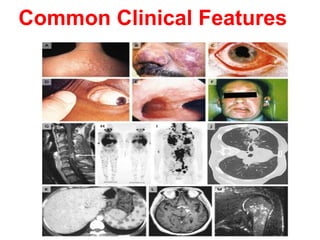
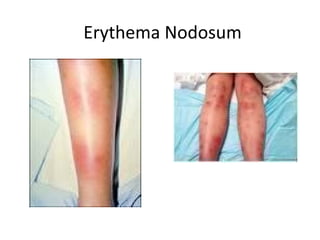
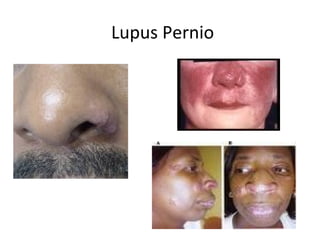
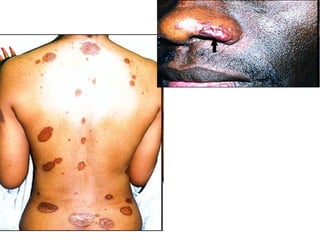
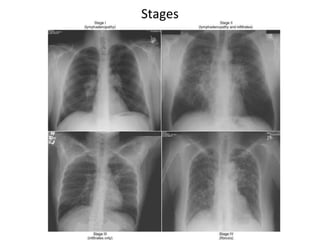
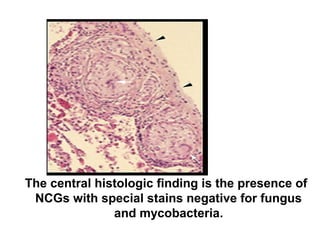
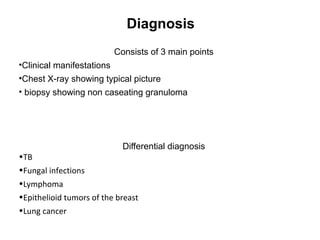
Sarcoidosis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of non-caseating granulomas in multiple organs, most commonly affecting the lungs. It has unknown causes but is thought to involve genetic and environmental factors. Historically, it was first described in the skin in 1899 and was later found to also affect the lungs and lymph nodes. It presents variably from being asymptomatic to causing respiratory symptoms or lesions in other organs. Diagnosis involves clinical features, chest imaging typically showing bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, and biopsy demonstrating granulomas. Treatment involves observation of asymptomatic cases but corticosteroids for symptomatic or progressive disease. Prognosis is generally good with many cases resolving spontaneously but advanced lung fibrosis can occasionally occur