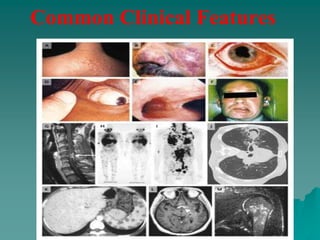
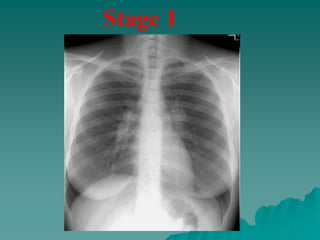
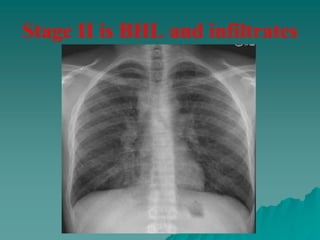
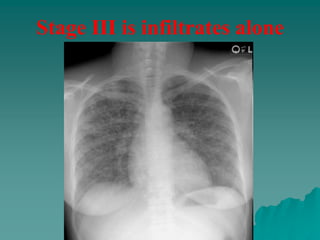
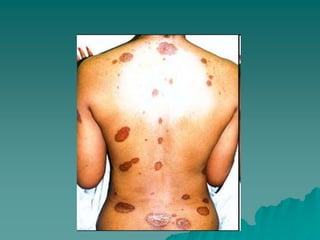
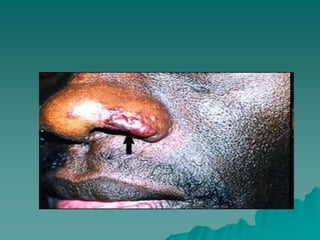
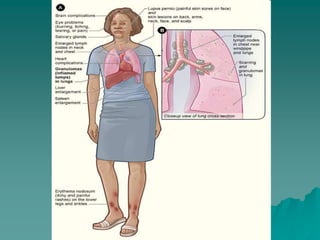
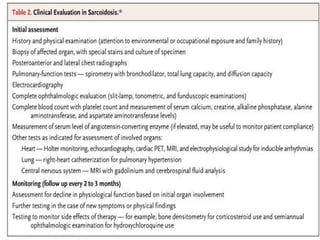
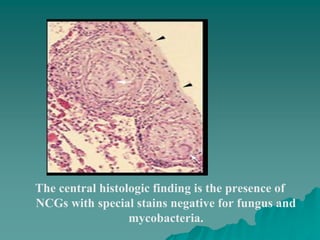
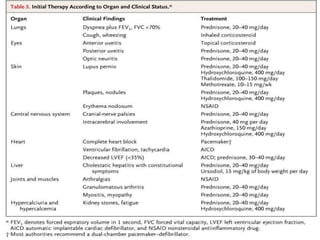
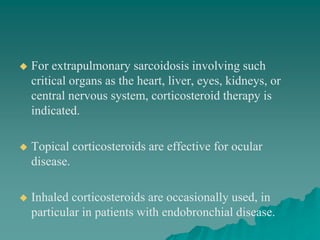
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease characterized by noncaseating granulomas in affected tissues. It most commonly affects the lungs and lymph nodes. While the cause is unknown, genetic and environmental factors are thought to play a role. Diagnosis requires clinical signs, radiologic findings, and histologic evidence of granulomas. Treatment involves corticosteroids, with methotrexate and hydroxychloroquine as alternatives for refractory or extrapulmonary disease. Prognosis depends on organ involvement, with cardiac and neurological disease carrying the worst outcomes.