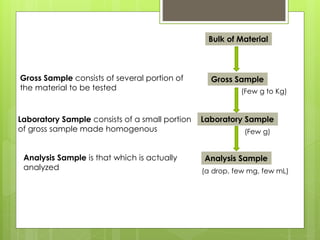
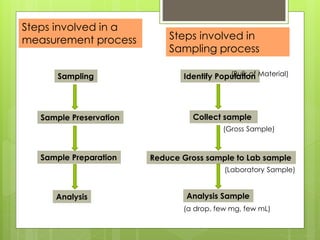
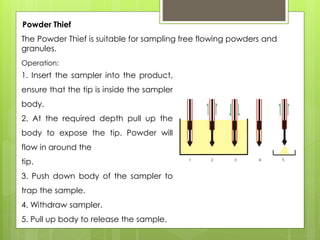
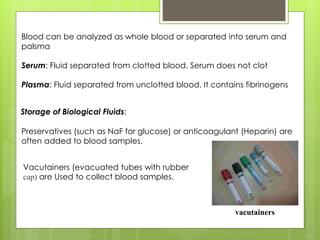
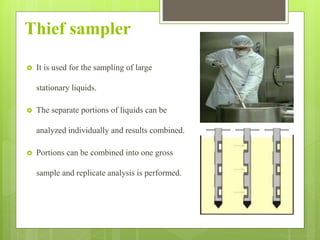
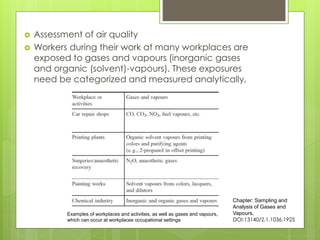
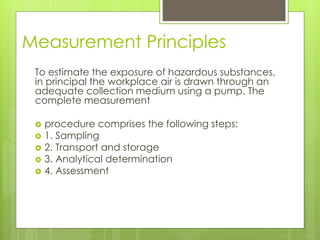
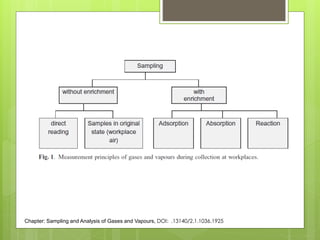
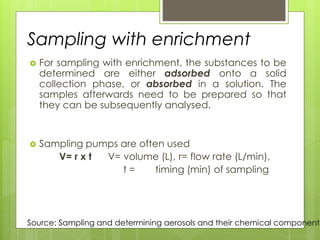
Sampling is the process of obtaining representative samples of materials like solids, liquids, and gases. It is a critical step in analysis. For heterogeneous solids, several individual samples are taken and combined into a gross sample. For liquids, grab samples or devices like thieves or impingers are used. Gases can be sampled directly or with enrichment using adsorption tubes, impingers, or chemical reactions. The key steps are sampling, transport, analysis, and assessment. Careful sampling ensures accurate results.


























![[24] DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) Analysis of hazardous substances in air,Volumes 1 – 8 (1991– 2003). From Vol. 9
(2005) the title changes to: The MAK-Collection for Occupational Health and Safety, Part III,Wiley-VCH Verlag,Weinheim.
Chapter: Sampling and Analysis of Gases and Vapours, DOI: .13140/2.1.1036.1925](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samplinginanalyticalchemistrysajjadullah-190323032829/85/Sampling-in-analytical-chemistry-sajjad-ullah-36-320.jpg)






![Resources
http://www.sampling.com/manual_samplers.html
Hebisch R., Fricke H.-H., Hahn J.-U., Lahaniatis M., Maschmeier C.-P.,
Mattenklott M. (2005) Sampling and determining aerosols and their chemical
components. In: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Greim H., Parlar H. eds.),
The MAK-Collection for Occupational Health and Safety, Part III: Air Monitoring
Methods”,Vol. 9. Wiley-VCH,Weinheim.
Giese U. (2000) Materialien zur Adsorption von organischen stoffen aus Luft In:
“Analytische Methoden zur Prüfung gesundheitsschädlicher Arbeitsstoffe”,
Band 1: Luftanalysen (Greim H., Hrsg.), 12. Lieferung. Teil II: Spezielle
Vorbemerkungen Kap. 8, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.
Chapter: Sampling and Analysis of Gases and Vapours, DOI:
.13140/2.1.1036.1925
[24] DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft) Analysis of hazardous
substances in air,Volumes 1 – 8 (1991– 2003). From Vol. 9 (2005) the title
changes to: The MAK-Collection for Occupational Health and Safety, Part
III,Wiley-VCH Verlag,Weinheim.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/samplinginanalyticalchemistrysajjadullah-190323032829/85/Sampling-in-analytical-chemistry-sajjad-ullah-43-320.jpg)