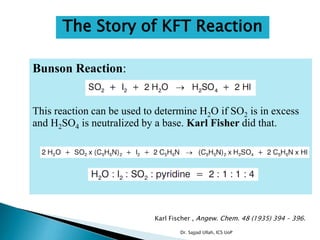
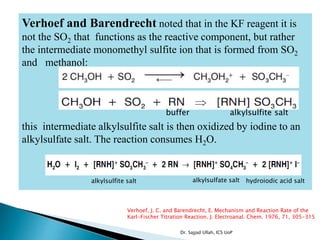
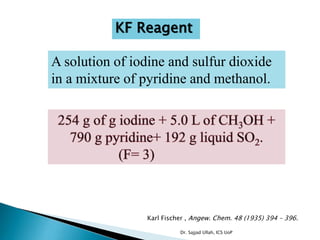
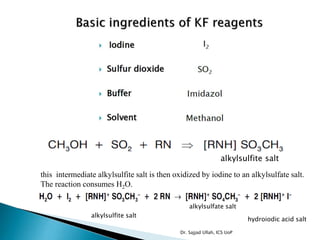
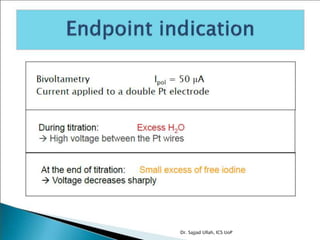
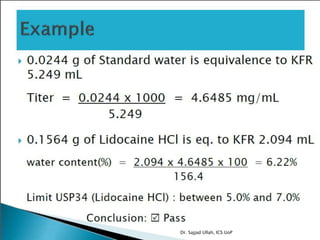
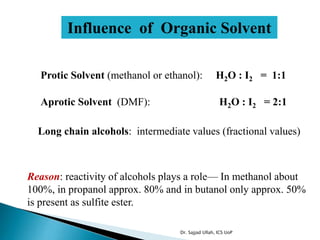
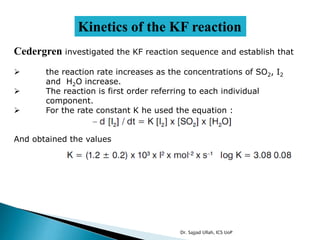
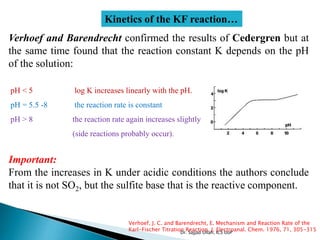
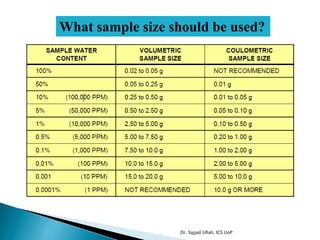
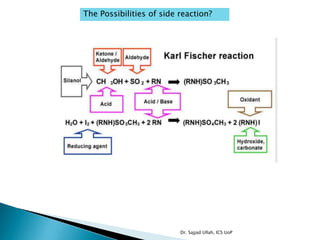
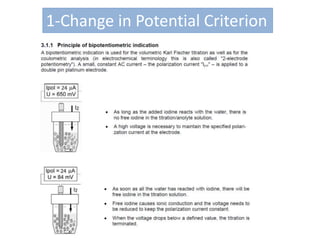
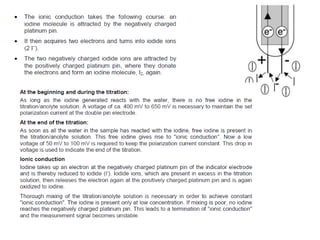
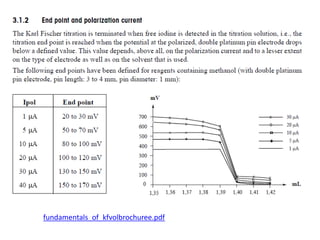
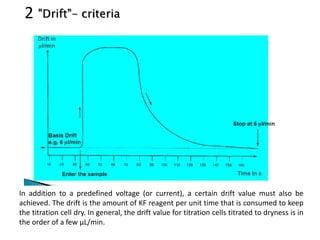
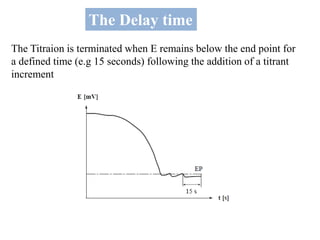
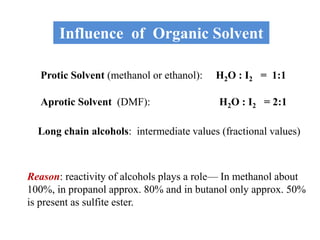
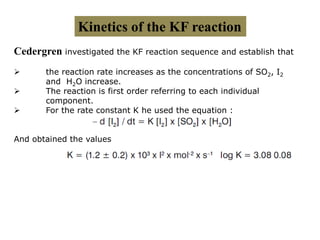
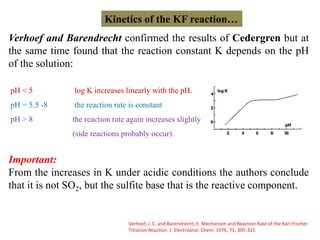
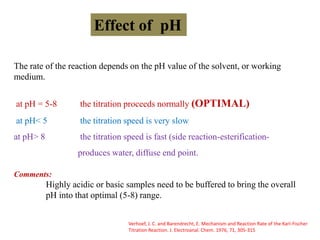
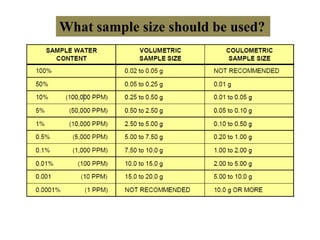
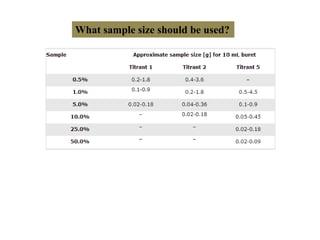
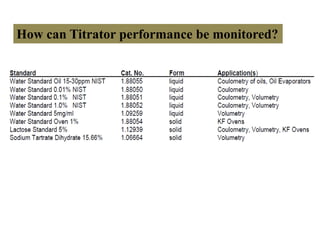
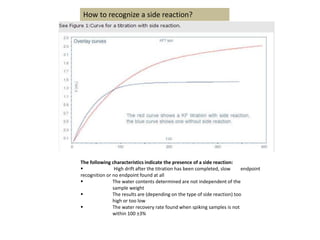
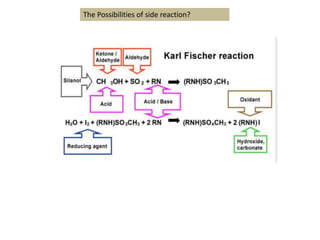
The document discusses Karl Fischer titration (KFT) techniques for determining water content. It describes two common methods - volumetric KFT, which uses a burette to dispense Karl Fischer reagent, and coulometric titration, which generates iodine electrochemically. The key reaction involves iodine oxidizing an intermediate alkylsulfite to alkylsulfate, consuming water. Factors like solvent choice, water content, pH, and kinetics are discussed. The document also outlines how volumetric and coulometric titrators function and how the endpoint is detected.