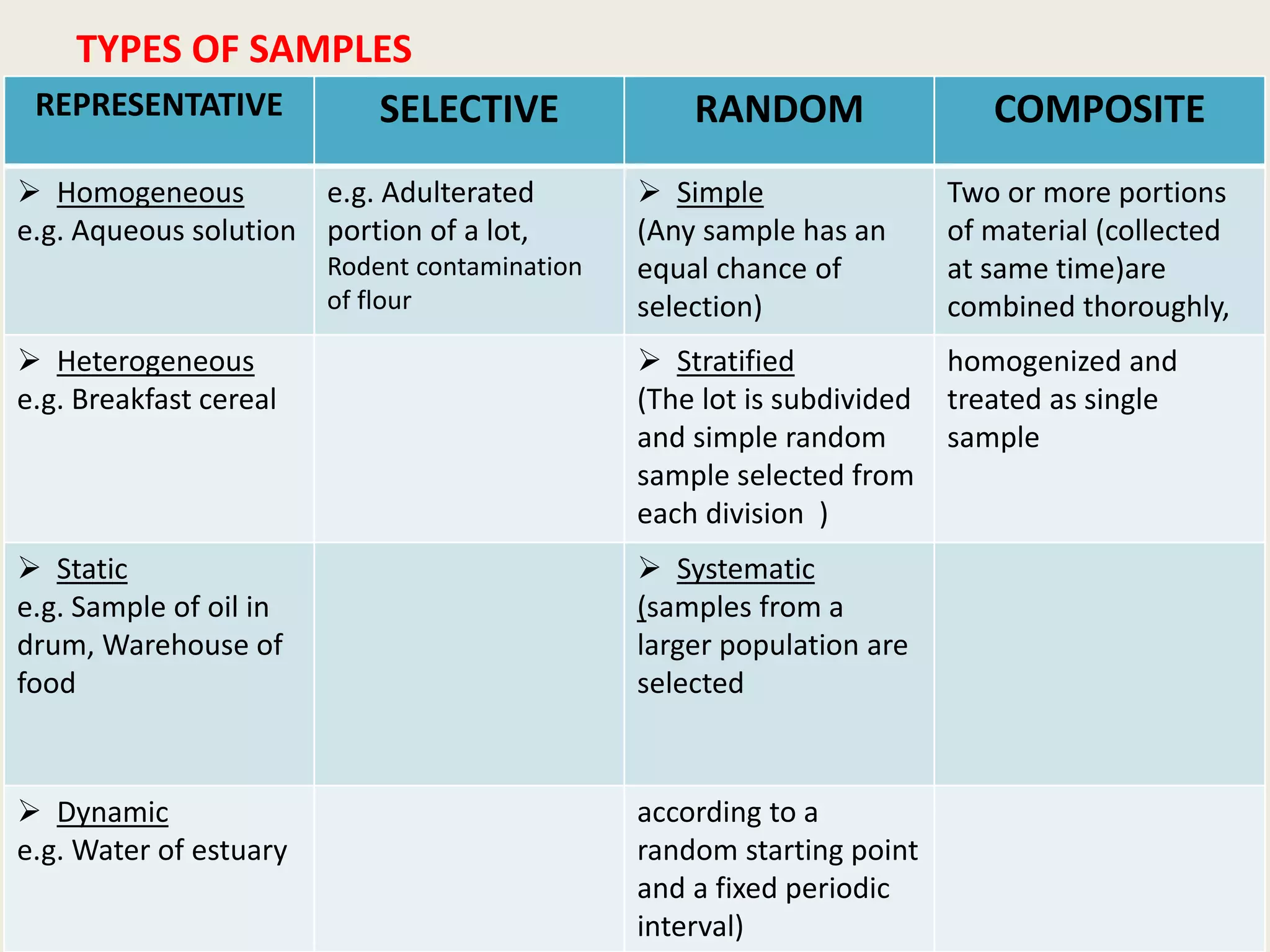
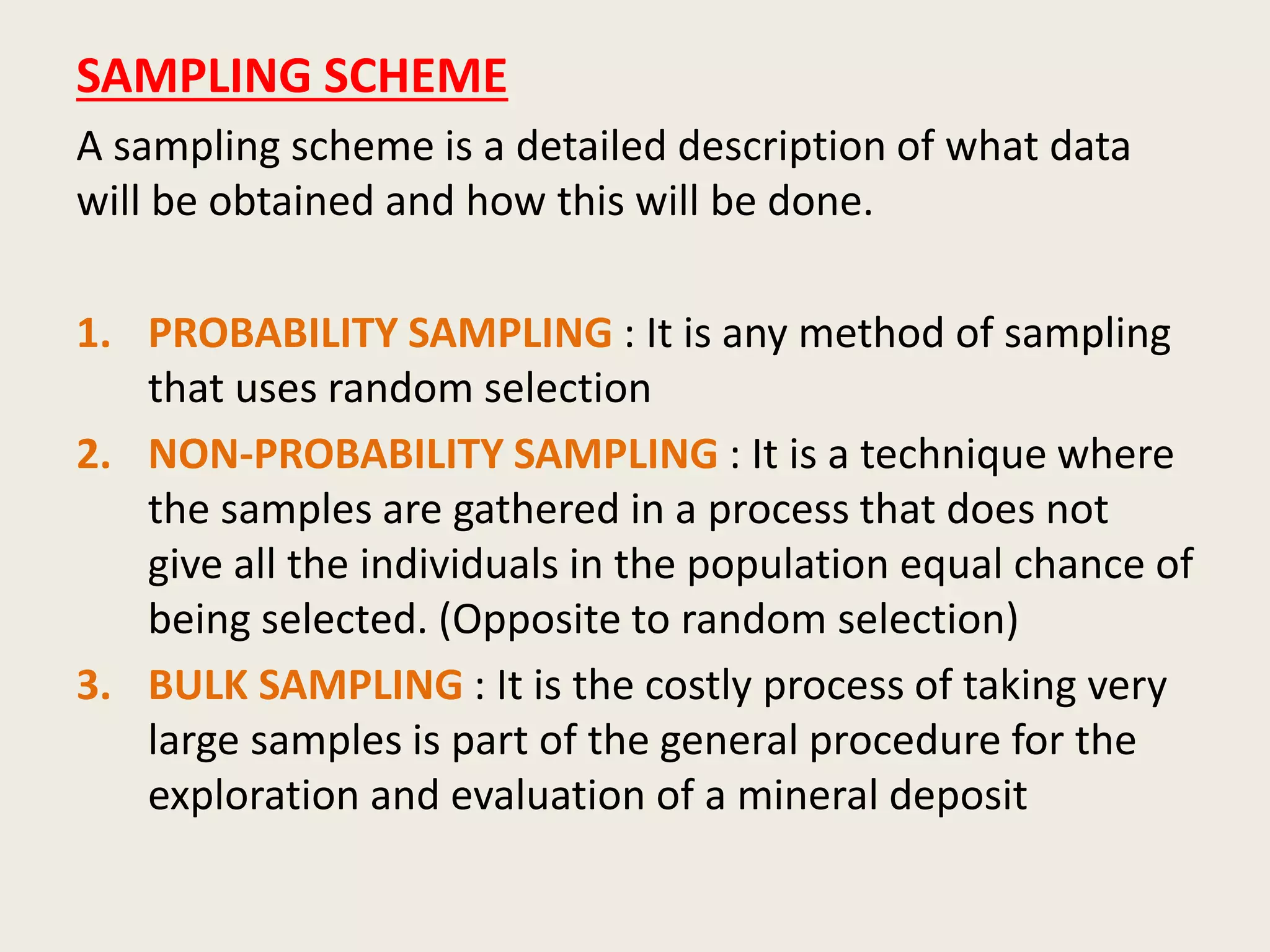
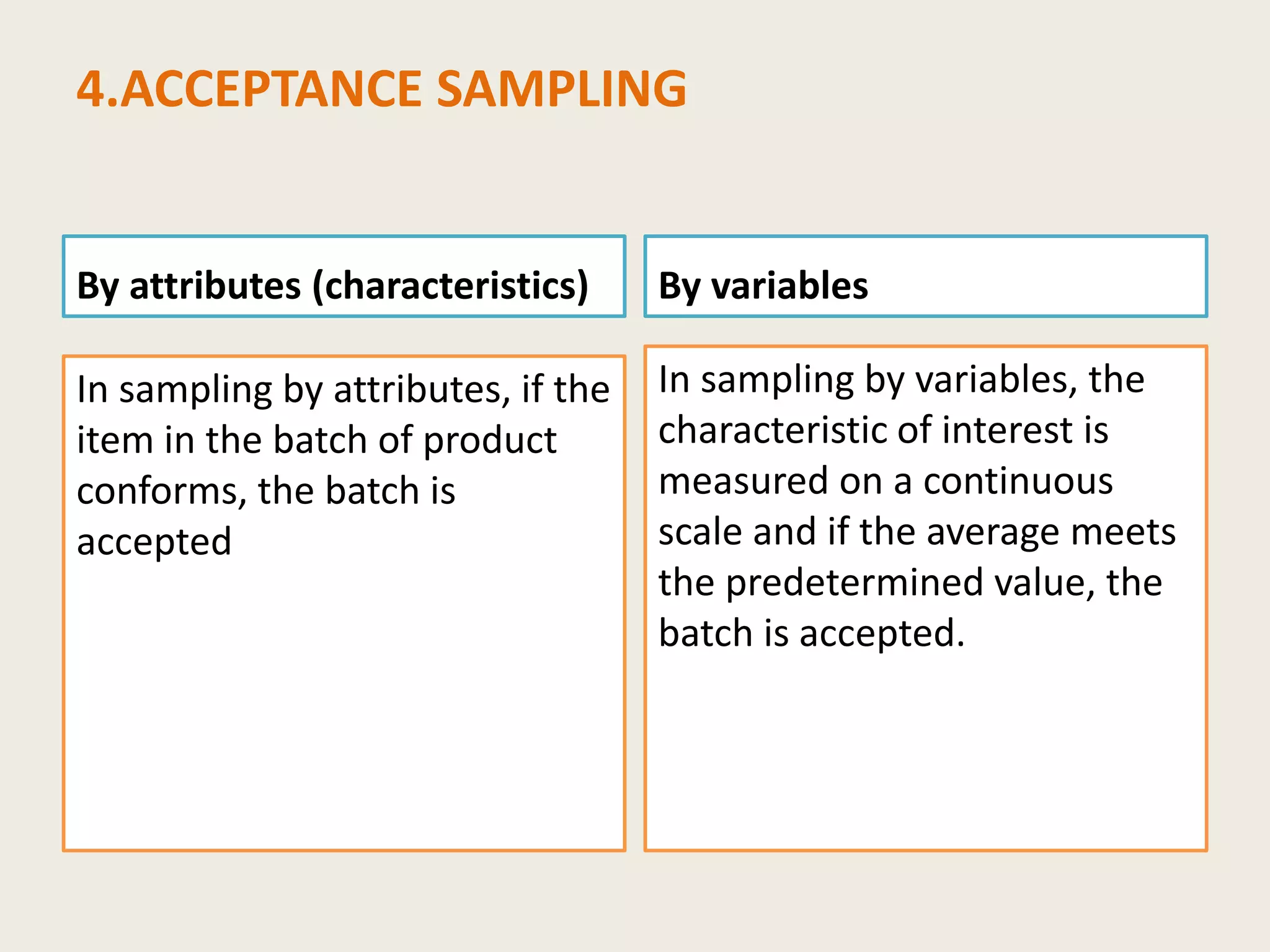
Sampling is the process of selecting a portion of material to represent a larger quantity. There are different types of samples including random, composite, and stratified. A sampling plan outlines measurements, materials, methods, and responsibilities. Samples must be representative and their quality preserved during collection, sub-sampling, storage, and analysis. Key details like the sample identity and collection details are documented in a sample register. Acceptance criteria ensure the sample's integrity and suitability for analysis.