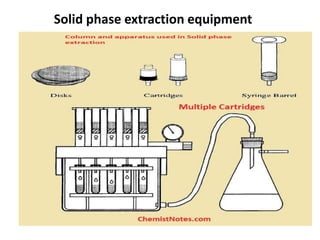
Solid phase extraction (SPE) is a sample preparation technique that focuses on concentrating and purifying analytes from a solution by selectively adsorbing them onto a solid phase, overcoming the limitations of traditional liquid-liquid extraction. The process involves four steps: conditioning the sorbent, loading the sample, washing the sorbent, and eluting the analytes, utilizing different types of sorbents such as normal phase, reverse phase, and ion exchange. SPE is widely used in various fields, including environmental and clinical applications, due to its advantages in reducing solvent use, improving accuracy, and facilitating automation.