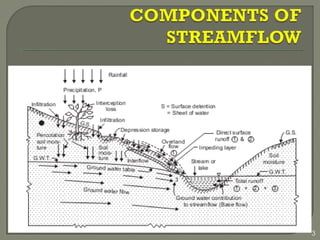
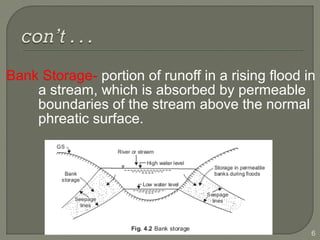
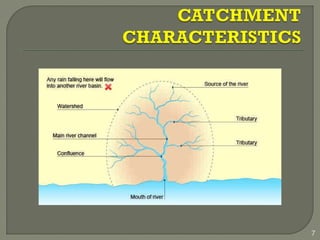
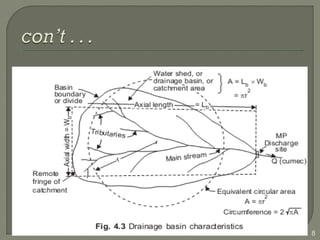
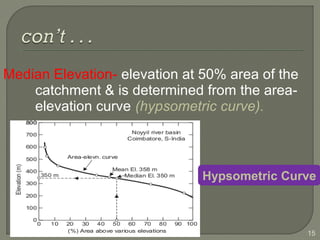
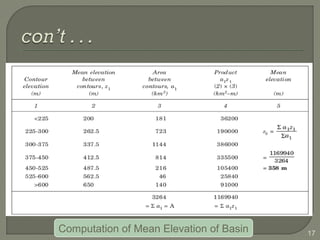
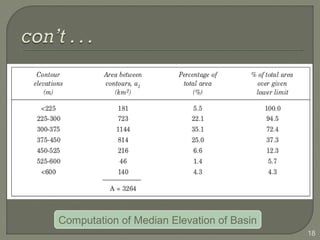
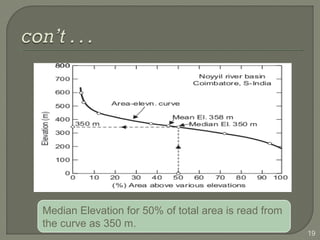
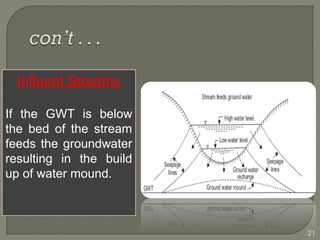
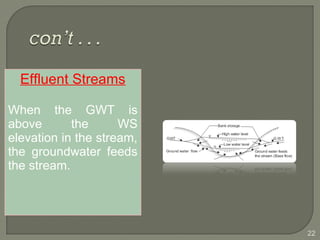
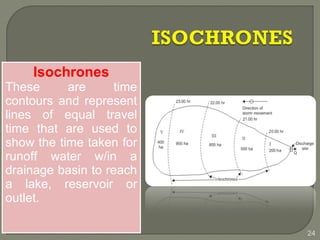
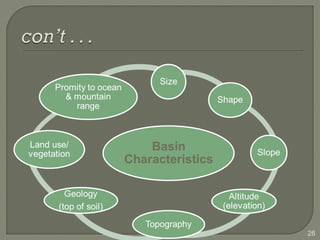
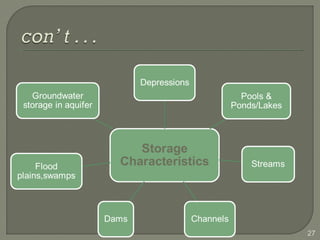
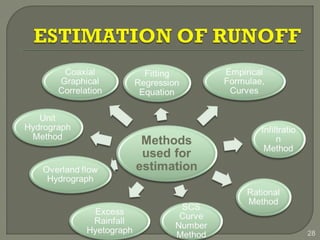
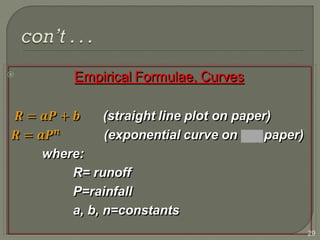
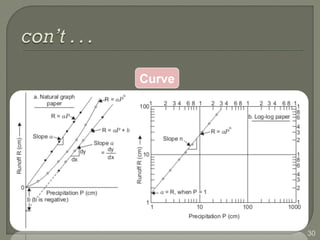
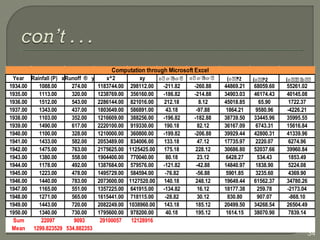
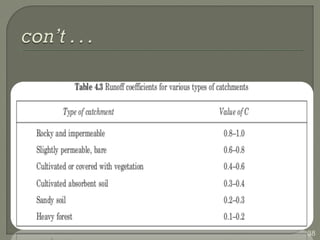
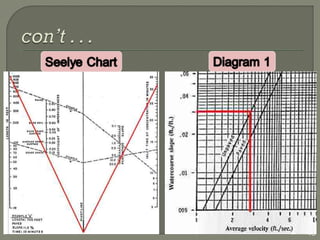
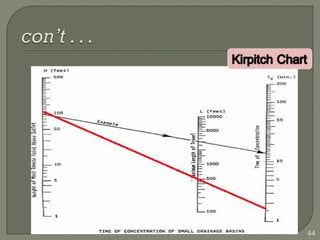
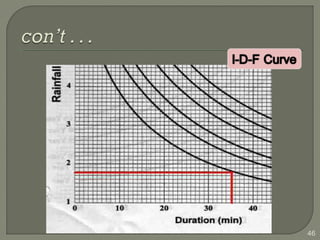
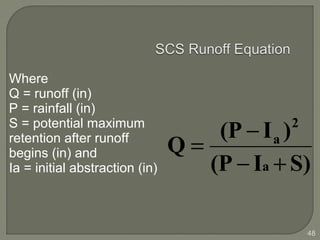
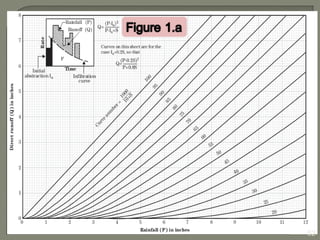
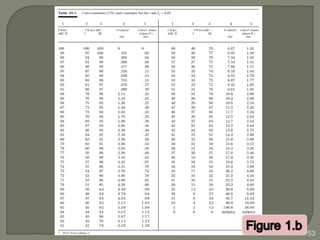
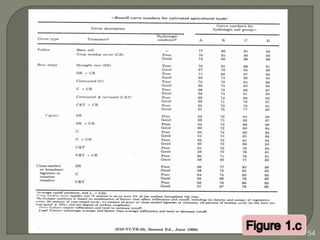
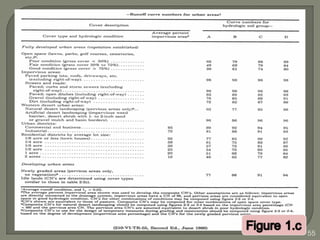
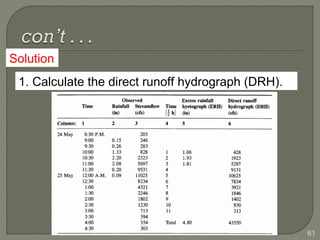
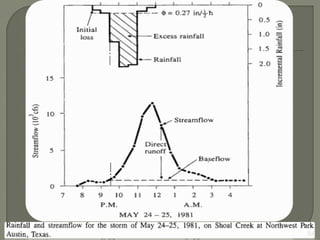
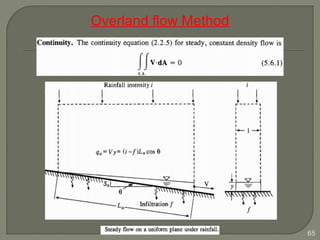
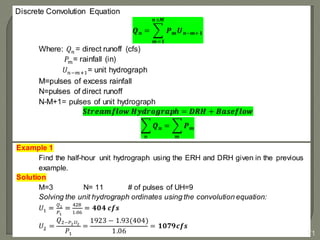
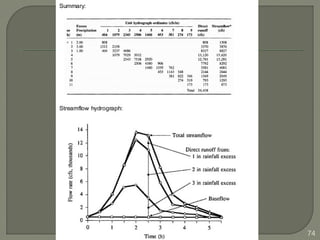
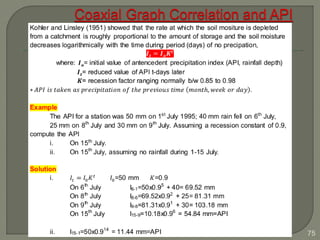
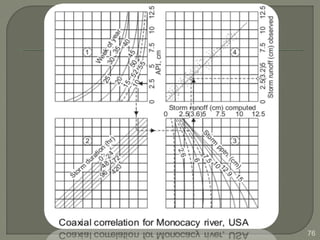
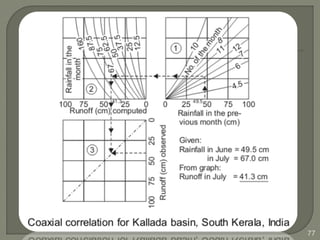
This document discusses various methods for estimating runoff from rainfall. It begins by defining components of stream flow such as overland flow, interflow, and baseflow. It then discusses catchment characteristics and methods for classifying streams. Various factors that affect runoff are identified, including drainage area, soil type, land use, and antecedent moisture conditions. Two primary methods for estimating runoff are presented: the Rational Method and the SCS Curve Number Method. Worked examples are provided to demonstrate how to apply both methods to calculate peak runoff rates from given rainfall and catchment property data.