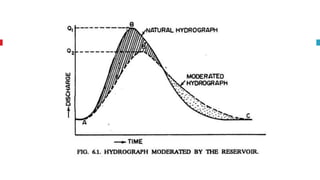
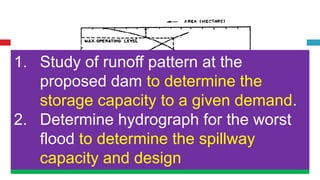
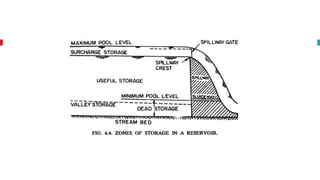
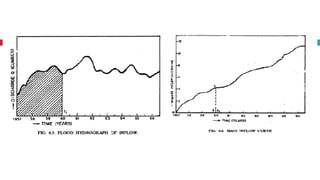
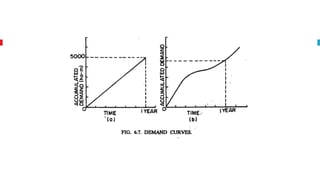
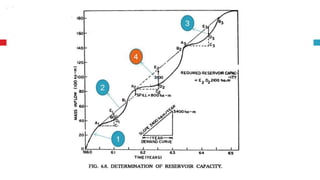
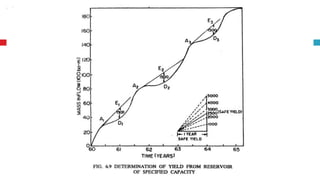
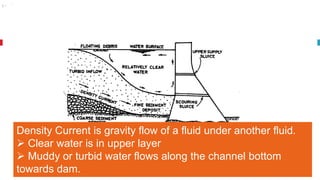
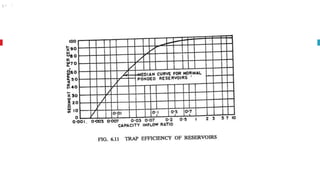
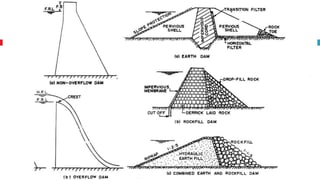
The document outlines key concepts in reservoir water resources engineering, including classification of reservoirs, site selection criteria, and methods for calculating storage capacity and yields. It details the impacts of sedimentation, the types of dams, and essential investigations required for reservoir planning. Additionally, it discusses mass inflow and demand curves used in capacity calculations and the factors influencing the longevity and effectiveness of reservoirs.