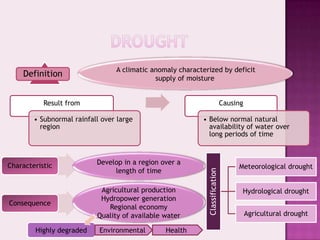
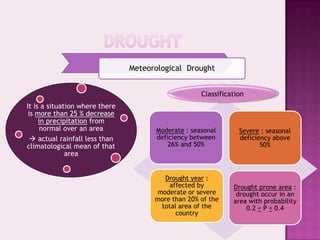
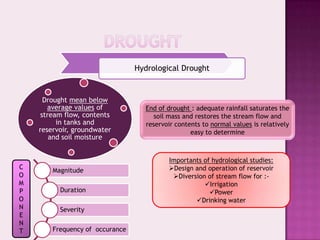
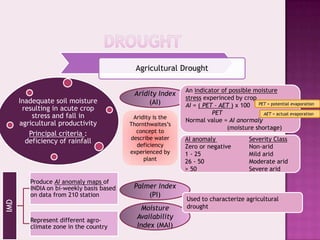
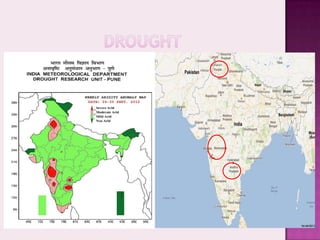
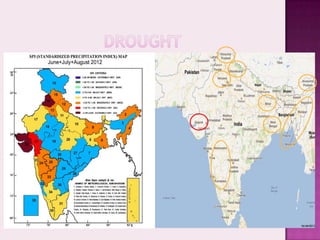
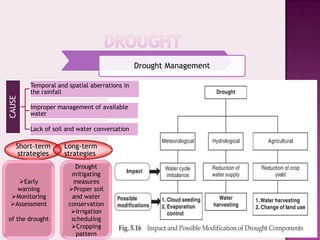
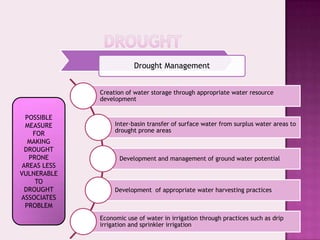
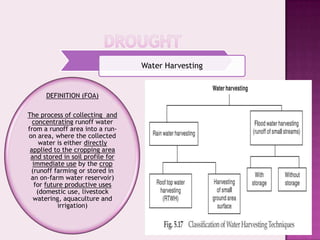
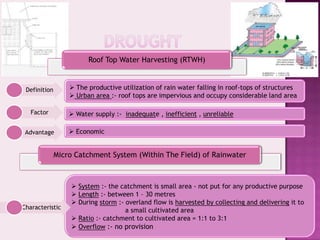
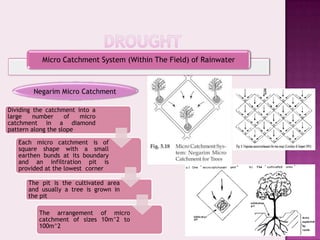
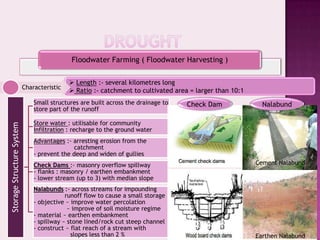
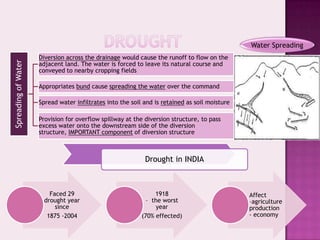
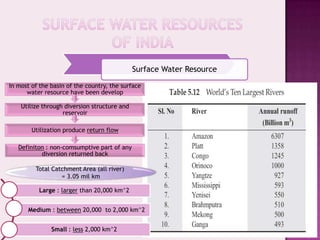
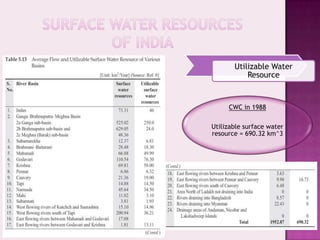
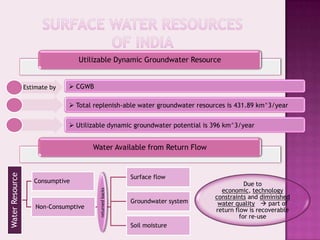
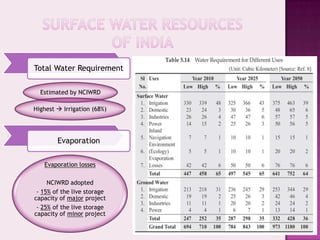
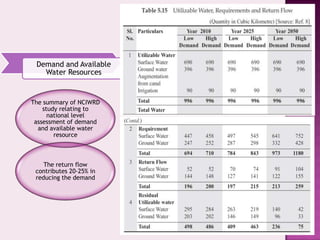
Drought is characterized by a deficit in moisture supply over a period of time, resulting in less than normal availability of water. It can be classified as meteorological, hydrological, or agricultural drought depending on whether it is defined based on rainfall, streamflow and reservoir levels, or soil moisture and crop impacts. Some consequences of drought include reduced agricultural production, impacts on hydropower generation and regional economies, and reduced water quality. Drought management strategies include early warning systems, monitoring, assessment, proper soil and water conservation practices, irrigation scheduling, cropping pattern changes, inter-basin water transfers, groundwater development, and water harvesting techniques.