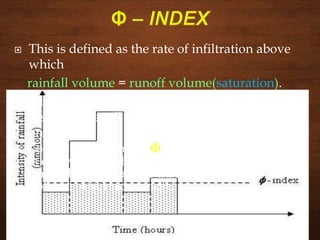
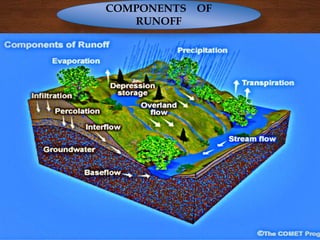
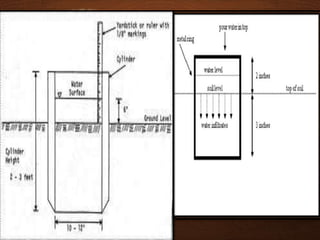
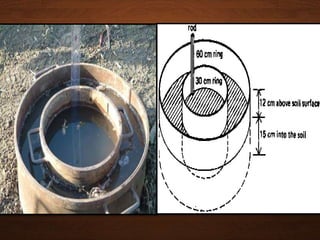
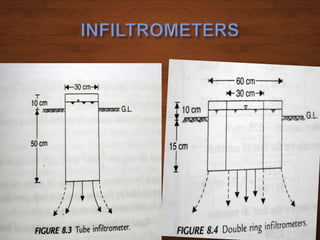
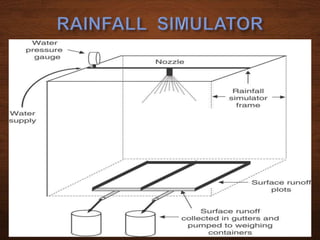
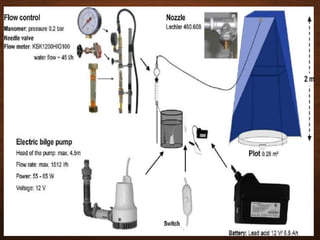
The document discusses infiltration, which is the process of rainwater entering the soil. Infiltrated water first meets any soil moisture deficit and then percolates vertically downward towards the groundwater table. The infiltration capacity of soil is the maximum rate at which it can absorb water and is denoted by f. Actual infiltration (fa) depends on whether the rainfall intensity (i) is greater than or less than the infiltration capacity. Infiltration is measured using infiltrometers and is affected by soil properties and antecedent moisture conditions.























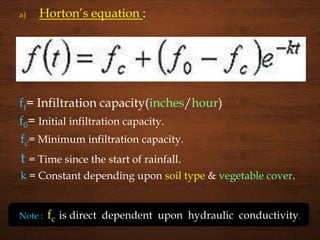
![b) Phillips equation :
Here a = Minimum infiltration capacity.
s = Initial infiltration capacity.
c) kostiakov equation:
c) holtans equation :
Here in above methods a & n are constants
depends on soil moisture & vegetable cover
F=[ A+(s/2) x t-0.5
]
F= (a x t n)
F = ( afn
p + fc )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit3-161116172943/85/Unit-3-INFILTRATION-31-320.jpg)