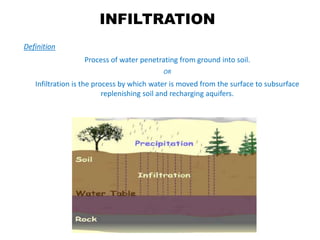
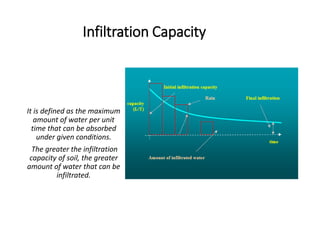
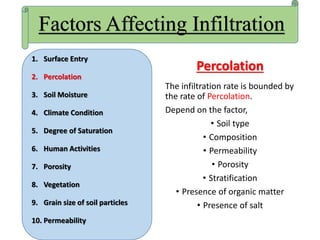
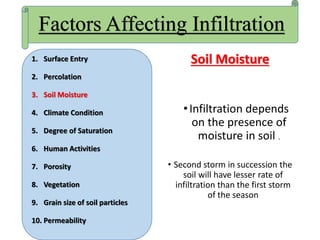
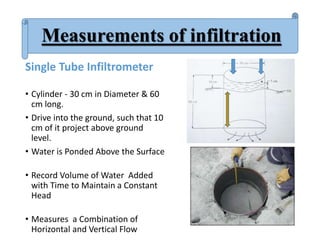
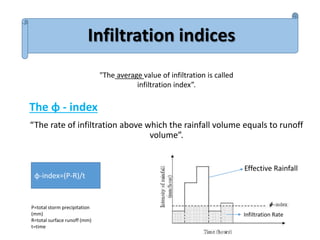
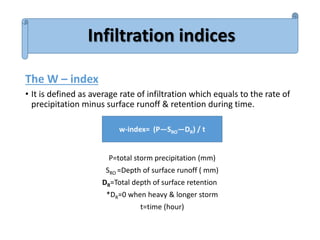
Infiltration is the process by which water enters the soil surface and percolates downward. It is affected by several factors related to the soil, climate, vegetation cover, and human activities. The key factors include surface cover, porosity, permeability, soil moisture, degree of saturation, grain size of soil particles, and climate conditions like temperature. Methods to measure infiltration in the field include single tube and double tube infiltrometers as well as rainfall simulators. Common indices used to represent infiltration rates are the phi index and w index.