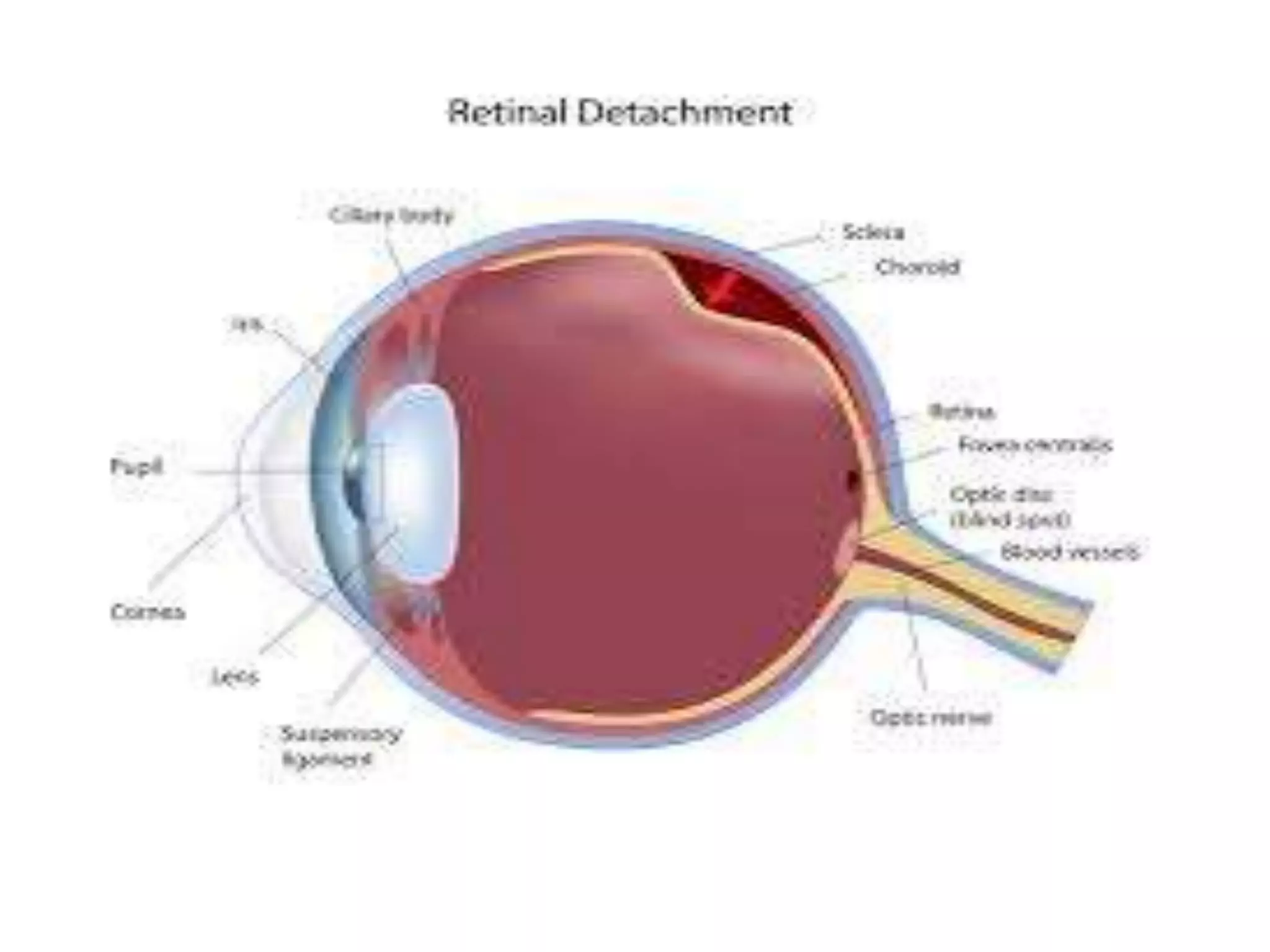
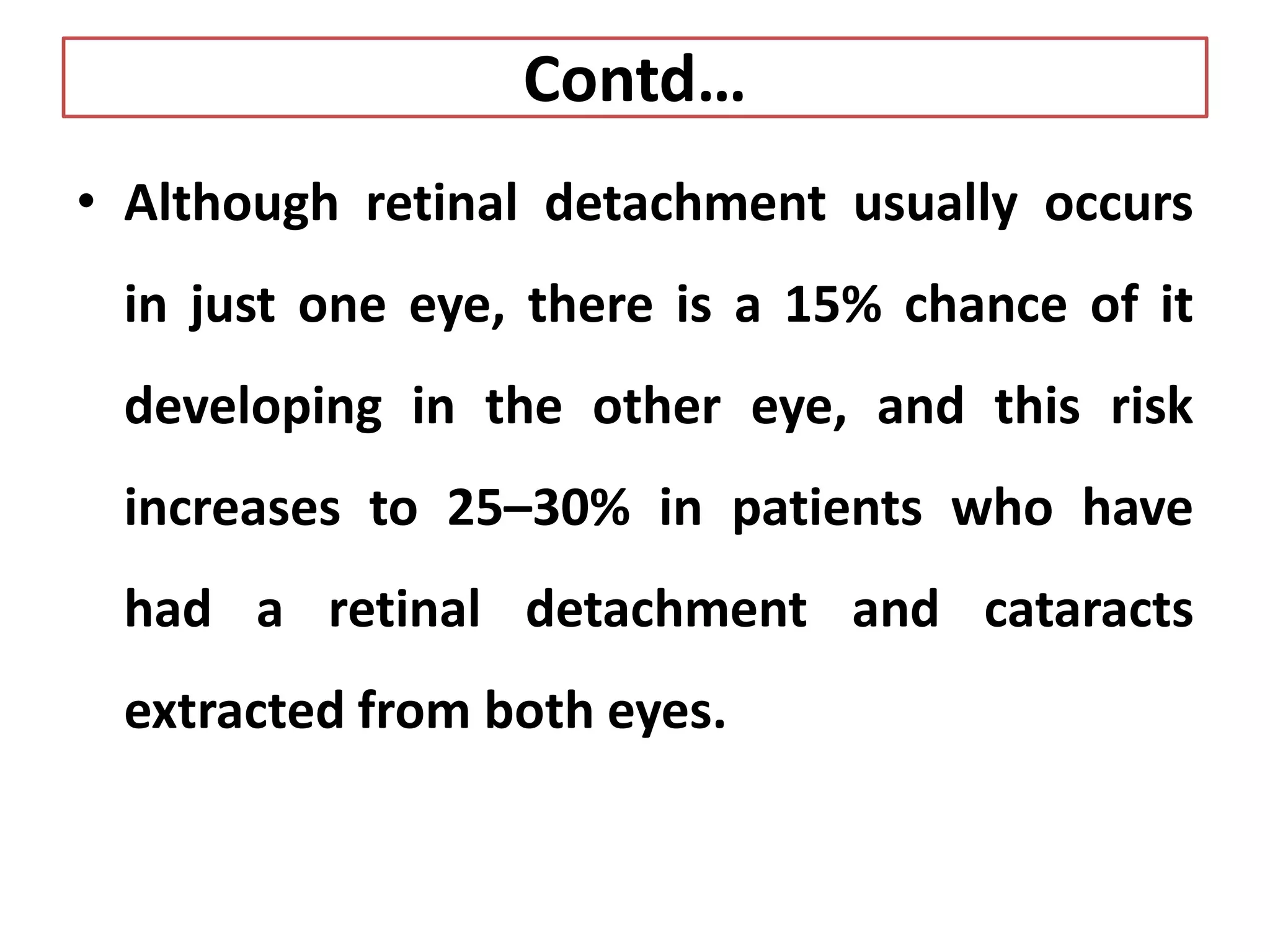
Retinal detachment occurs when the retina separates from the underlying layer of the eye. It can cause vision loss if not treated. Risk factors include severe nearsightedness, prior eye surgery or injury, family history, and activities that increase intraocular pressure. Symptoms include flashes of light, floaters, and blurred or lost vision. Diagnosis involves eye exams like ultrasound or ophthalmoscopy. Treatment depends on the type of detachment but may include cryotherapy, laser photocoagulation, scleral buckling surgery, pneumatic retinopexy, or vitrectomy. With treatment, retinal detachment can be successfully repaired in 85-95% of cases to restore vision.