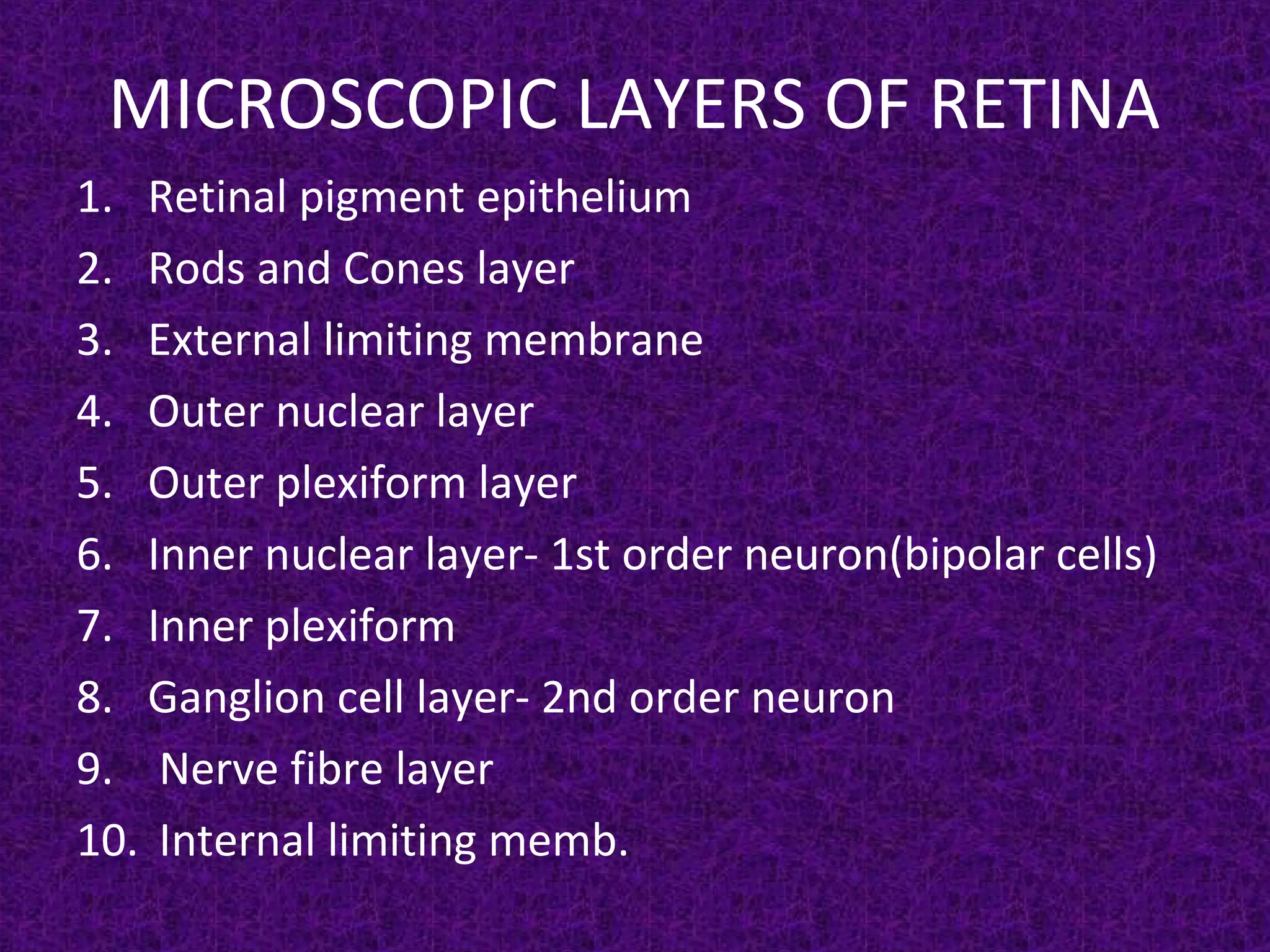
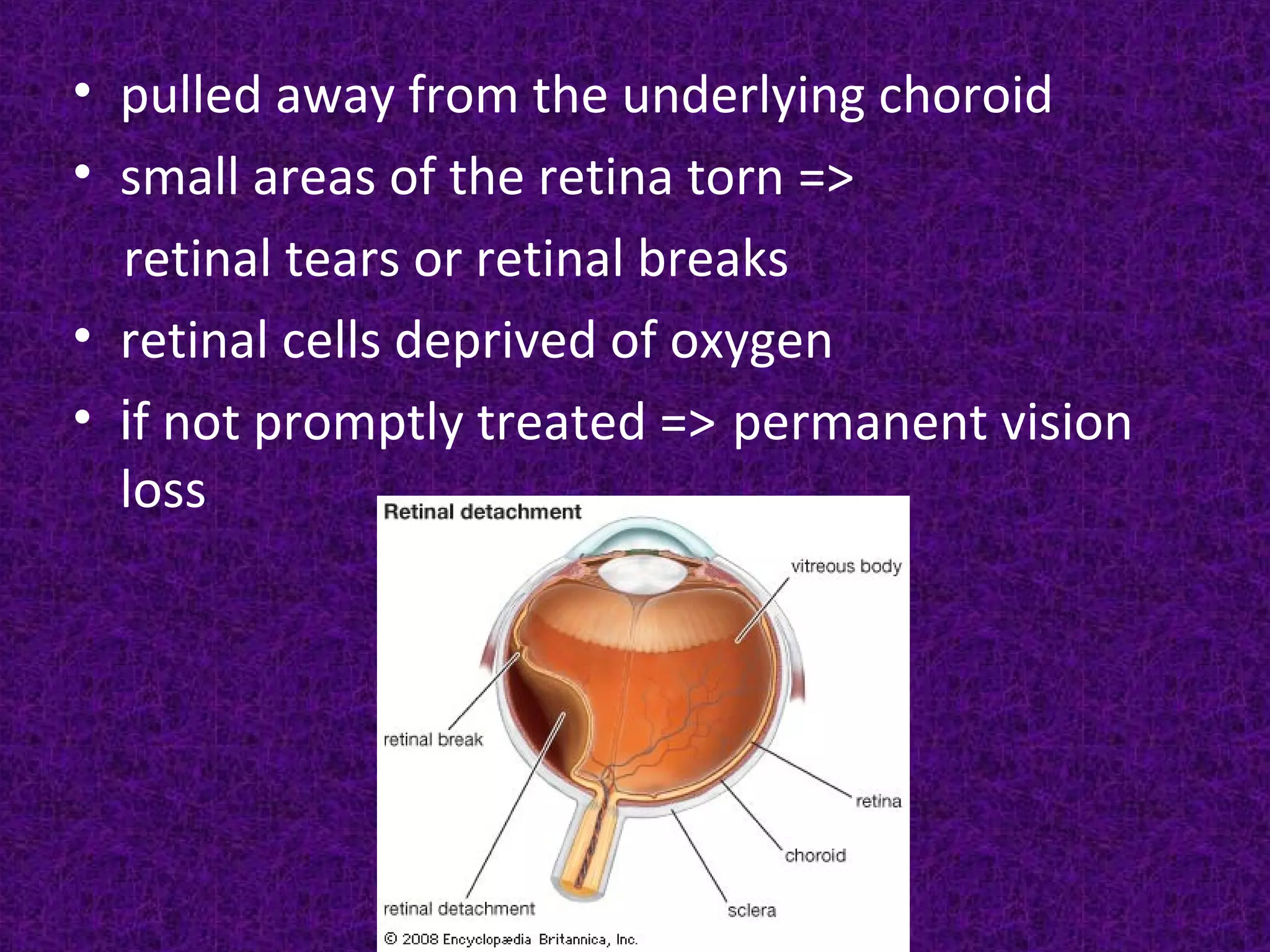
This document discusses retinal detachment, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. The retina is the light-sensitive layer of tissue in the back of the eye. Retinal detachment occurs when the retina separates from its underlying layer, and fluid accumulates underneath. Common causes are trauma, advanced diabetes, high nearsightedness, and vitreous shrinkage. Symptoms include floaters, light flashes, and blurred or lost vision. Treatment options aim to reattach the retina through procedures like laser photocoagulation, cryopexy, pneumatic retinopexy, scleral buckling, or vitrectomy surgery.