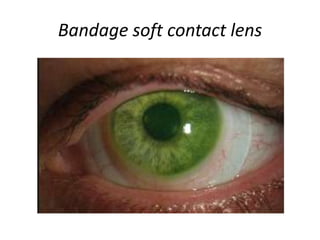
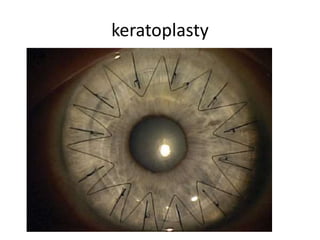
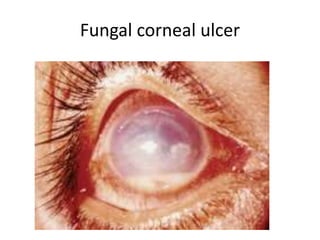
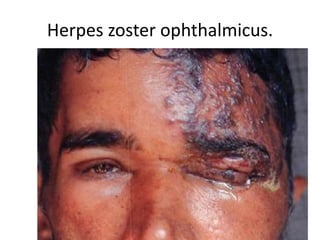
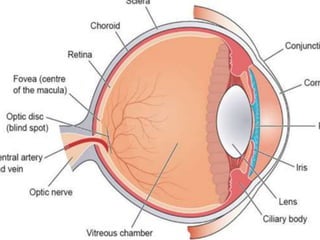
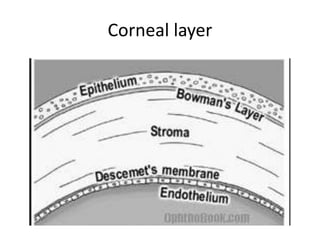
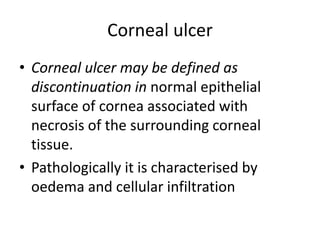
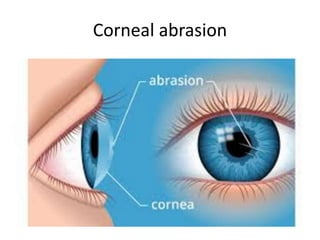
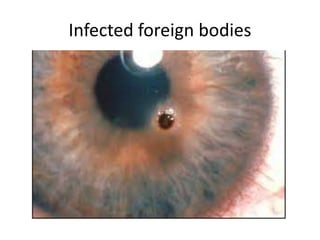
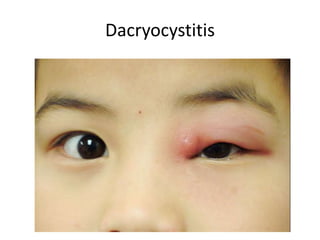
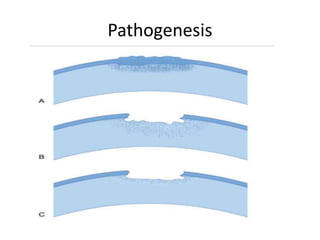
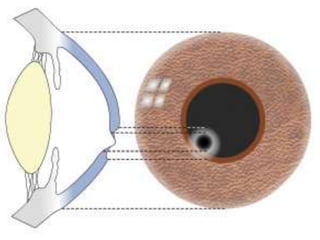
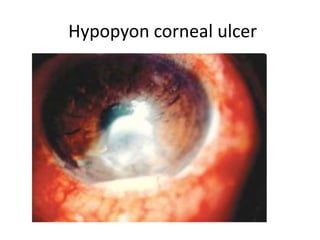
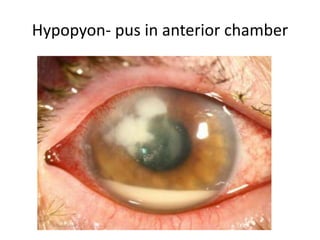
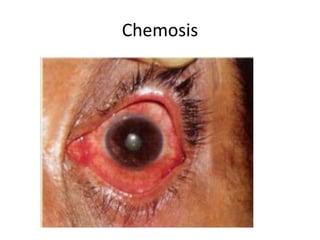
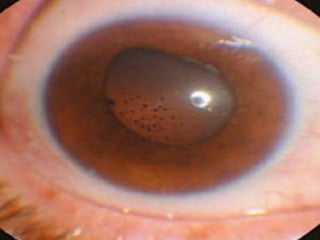
This document summarizes information about corneal ulcers. It discusses the anatomy of the cornea and common causes of corneal infections like bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. Corneal ulcers occur when there is damage to the corneal epithelium allowing infection to set in. Symptoms include pain, watering, photophobia and blurred vision. Signs include swelling, hypopyon in the anterior chamber. Management involves identifying the causative organism, using topical antibiotics and cycloplegics for uncomplicated cases. More severe cases may require debridement, bandage contact lenses or keratoplasty. Complications can include glaucoma, perforation and scarring.
























![Management of a case of corneal
ulcer
• [A] Clinical evaluation
• [B] Laboratory investigations
• [C] Treatment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealulcer-190206171443/85/Corneal-ulcer-38-320.jpg)
![[A] Clinical evaluation
• 1. Thorough history taking to elicit mode of
onset,
• 2. General physical examination
• Nourishment
• Anaemia
• Immunocompromising disease.
• 3. Ocular examination
• i. Diffuse light examination
• ii. Regurgitation test and syringing
• iii. Biomicroscopic examination](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealulcer-190206171443/85/Corneal-ulcer-39-320.jpg)
![[B] Laboratory investigations
• (a) Routine laboratory investigations
• (b) Microbiological investigations.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealulcer-190206171443/85/Corneal-ulcer-40-320.jpg)


![[C] Treatment
• I. Treatment of uncomplicated corneal ulcer
• II. Treatment of non-healing corneal ulcerof
uncomplicated corneal ulcer
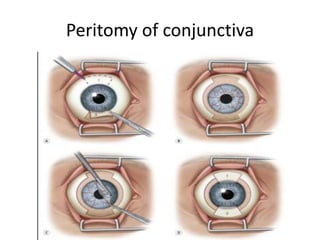
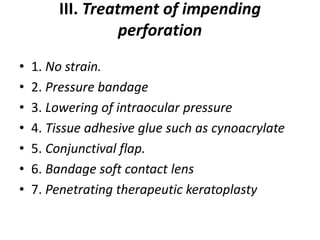
• III. Treatment of impending perforation
• IV. Treatment of perforated corneal ulcer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealulcer-190206171443/85/Corneal-ulcer-43-320.jpg)