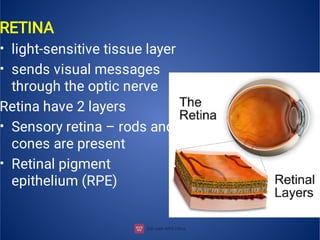
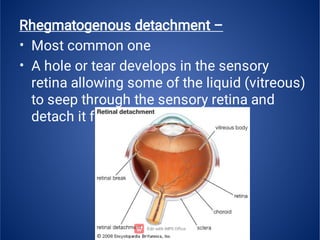
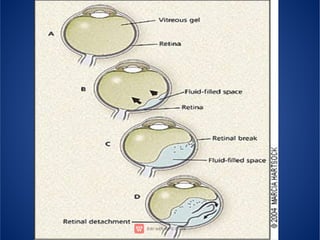
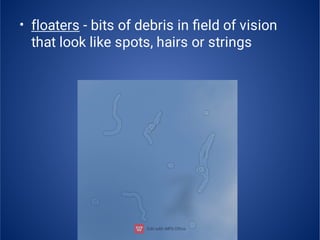
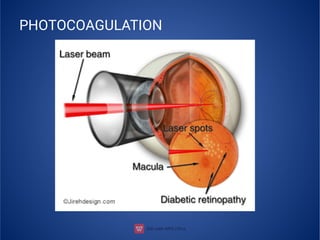
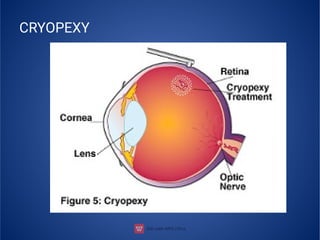
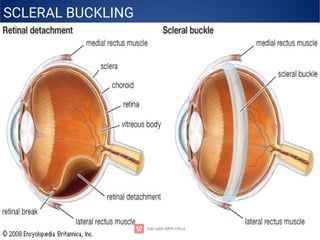
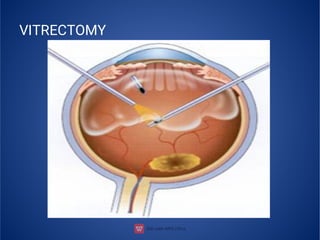
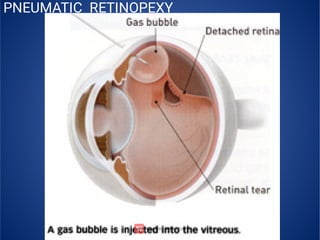
The document provides an extensive overview of retinal detachment, including its types, pathophysiology, symptoms, etiology, diagnosis, and various management strategies. It highlights surgical options like laser surgery, pneumatic retinopexy, and scleral buckling, along with preoperative and postoperative nursing care. The document also addresses risk factors and includes a bibliography for further reference.