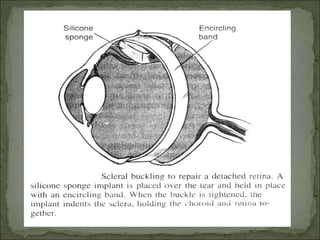
Retinal detachment occurs when the neurosensory retina separates from the underlying pigment epithelium, cutting it off from its blood supply and causing vision loss. It is usually caused by tears in the retina from posterior vitreous detachment. Symptoms include floaters, flashes of light, and blurred or lost vision. Diagnosis is made through examination with an ophthalmoscope. Treatment involves sealing retinal tears with laser or cryotherapy and reattaching the retina surgically using scleral buckling or vitrectomy. Patients require positioning and eye drops post-operatively to prevent further detachment.