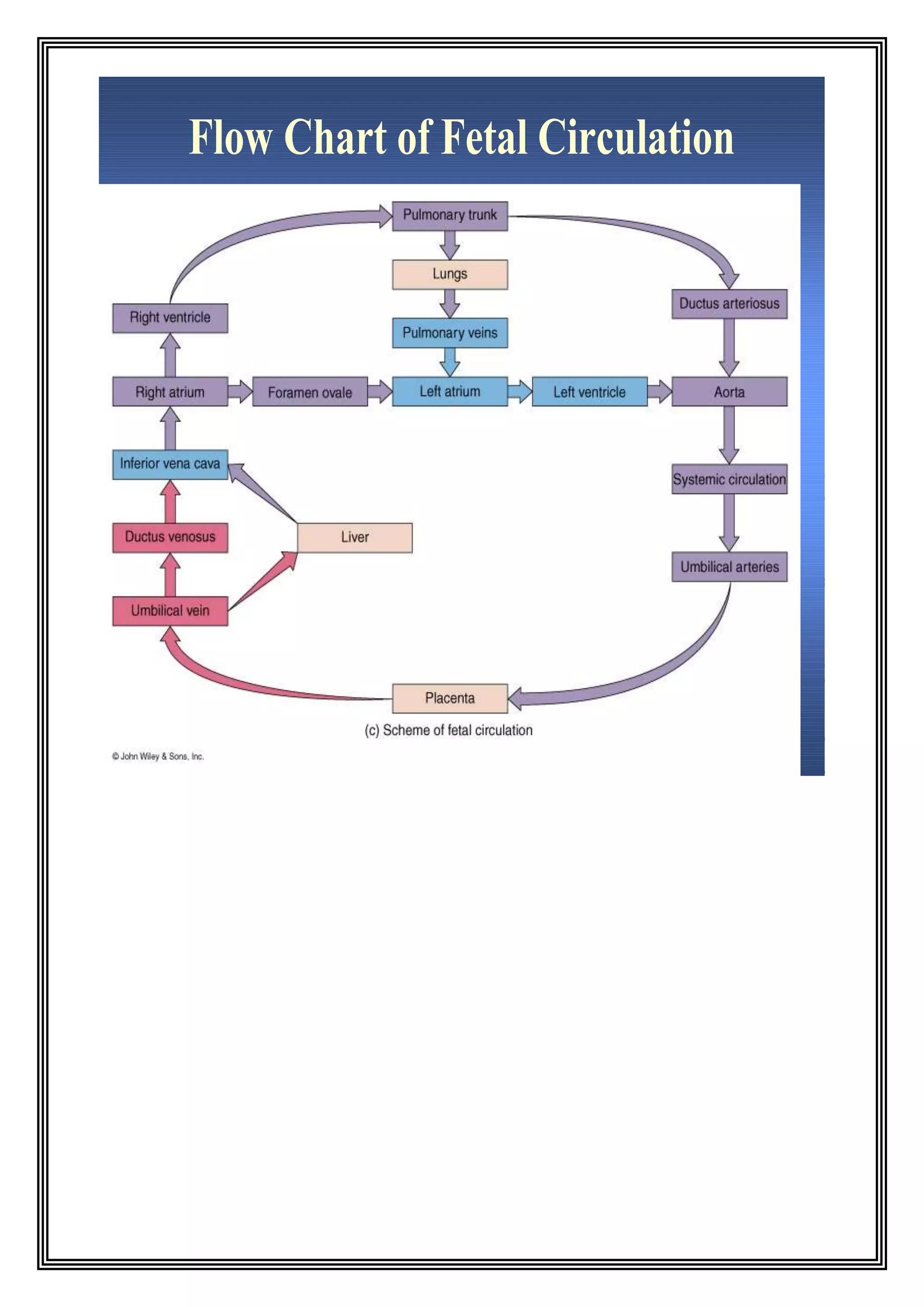
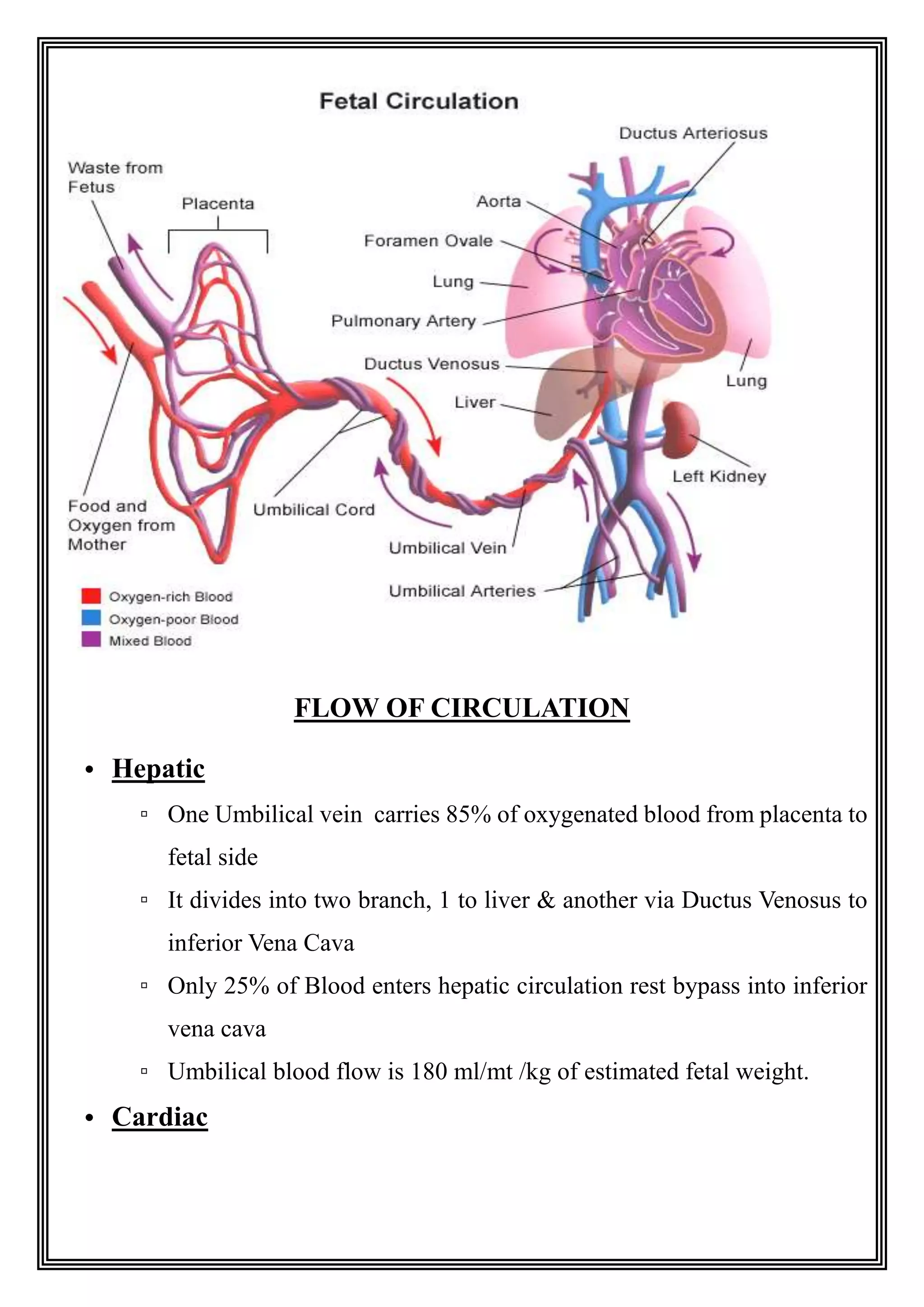
The fetal circulation differs significantly from adult circulation. During development, the placenta provides oxygen to the fetus and the lungs receive very little blood flow. The fetal circulation includes unique structures that allow blood to bypass the lungs, such as the ductus venosus and foramen ovale. At birth, breathing causes changes like closure of the ductus venosus and foramen ovale as well as a drop in pulmonary resistance, transitioning the circulation to its postnatal state where the lungs are the primary site of gas exchange.