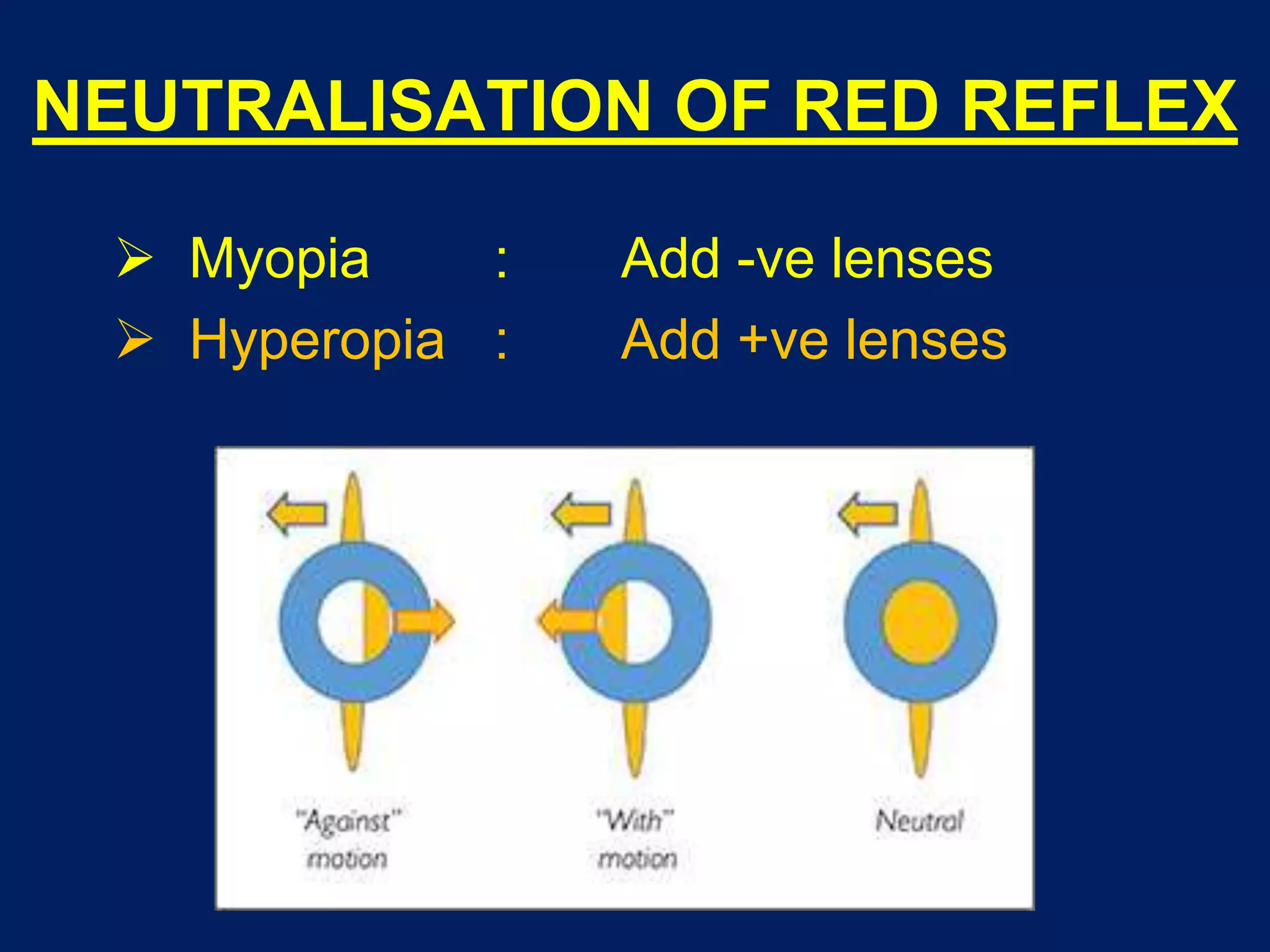
This document provides an overview of clinical refraction. It discusses the scope and various components of refraction, including history, objective tests like retinoscopy and autorefraction, and subjective refinement of refraction. Retinoscopy is described in detail, including the types of retinoscopes, procedures, inferences from the red reflex, and problems that can occur. Autorefraction, monocular and binocular subjective refraction techniques are also outlined. The document provides guidance on determining corrections for both distance and near vision.