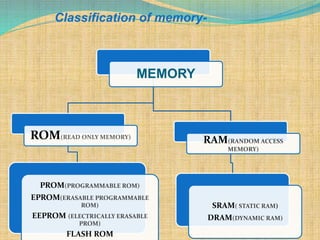
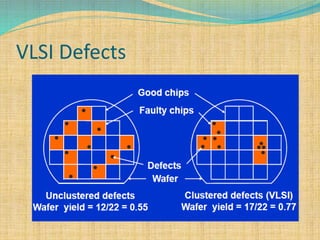
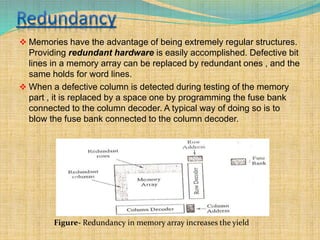
There are two key requirements for VLSI memory to be useful: yield and reliability. Yield refers to the percentage of good chips produced, which impacts costs. Reliability means the memory performs as intended for a given period of time under conditions. As integration density increases, yield decreases due to defects and variations. Memory designers use redundancy and error correction to combat this. Redundancy replaces defective components like columns or rows. Error correction adds redundant data bits to detect and fix errors. This improves yield and addresses soft errors.