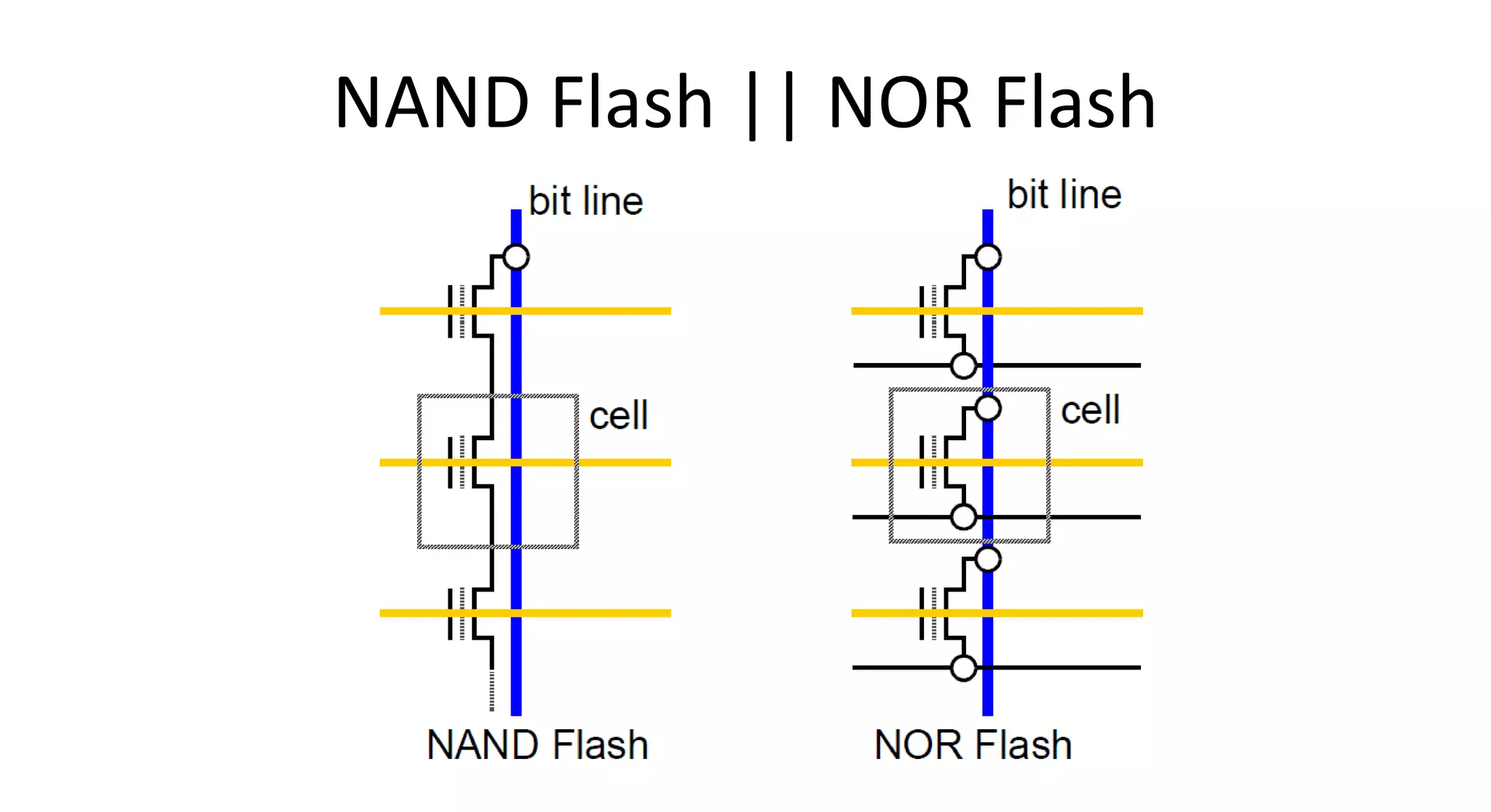
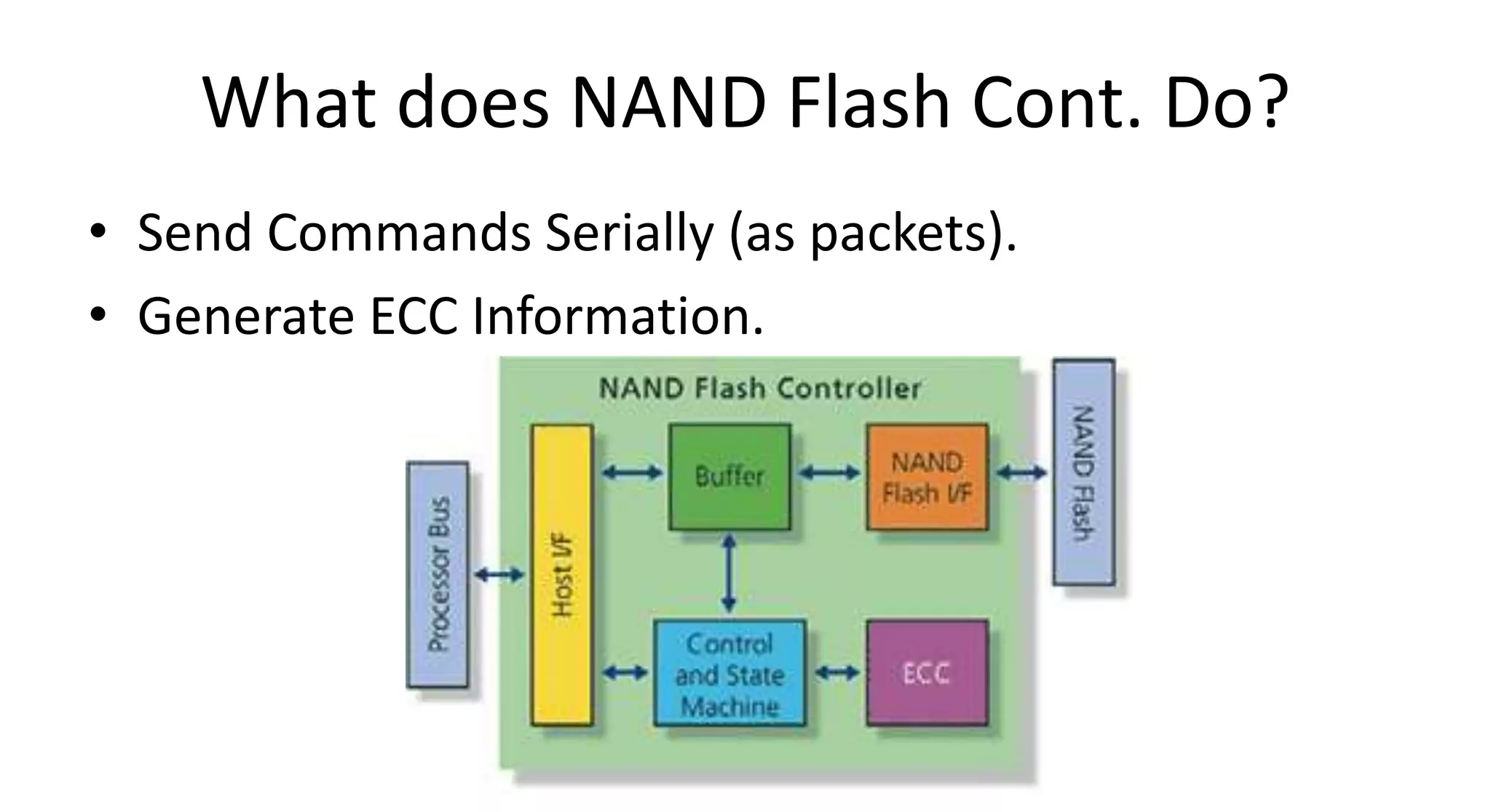
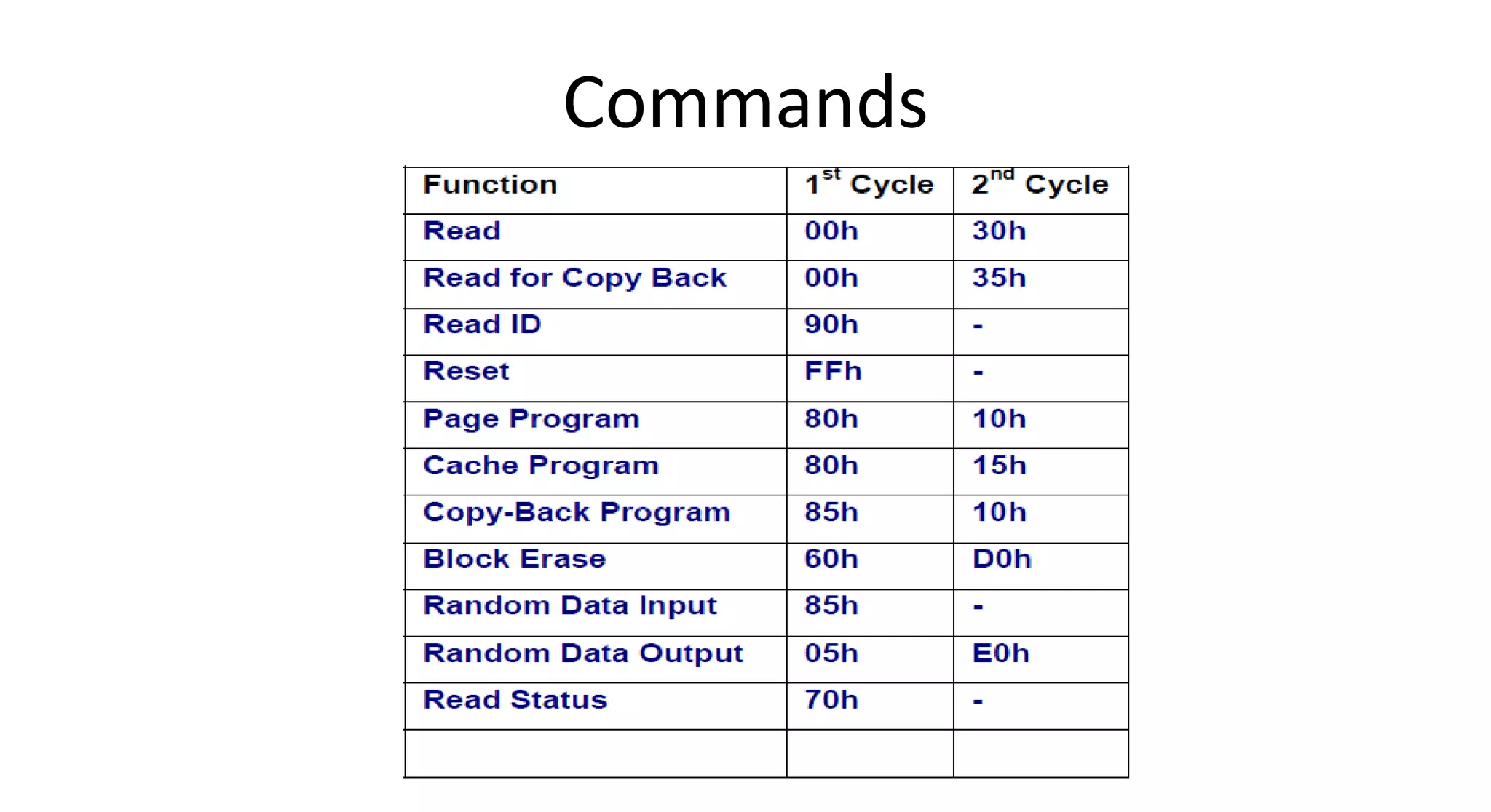
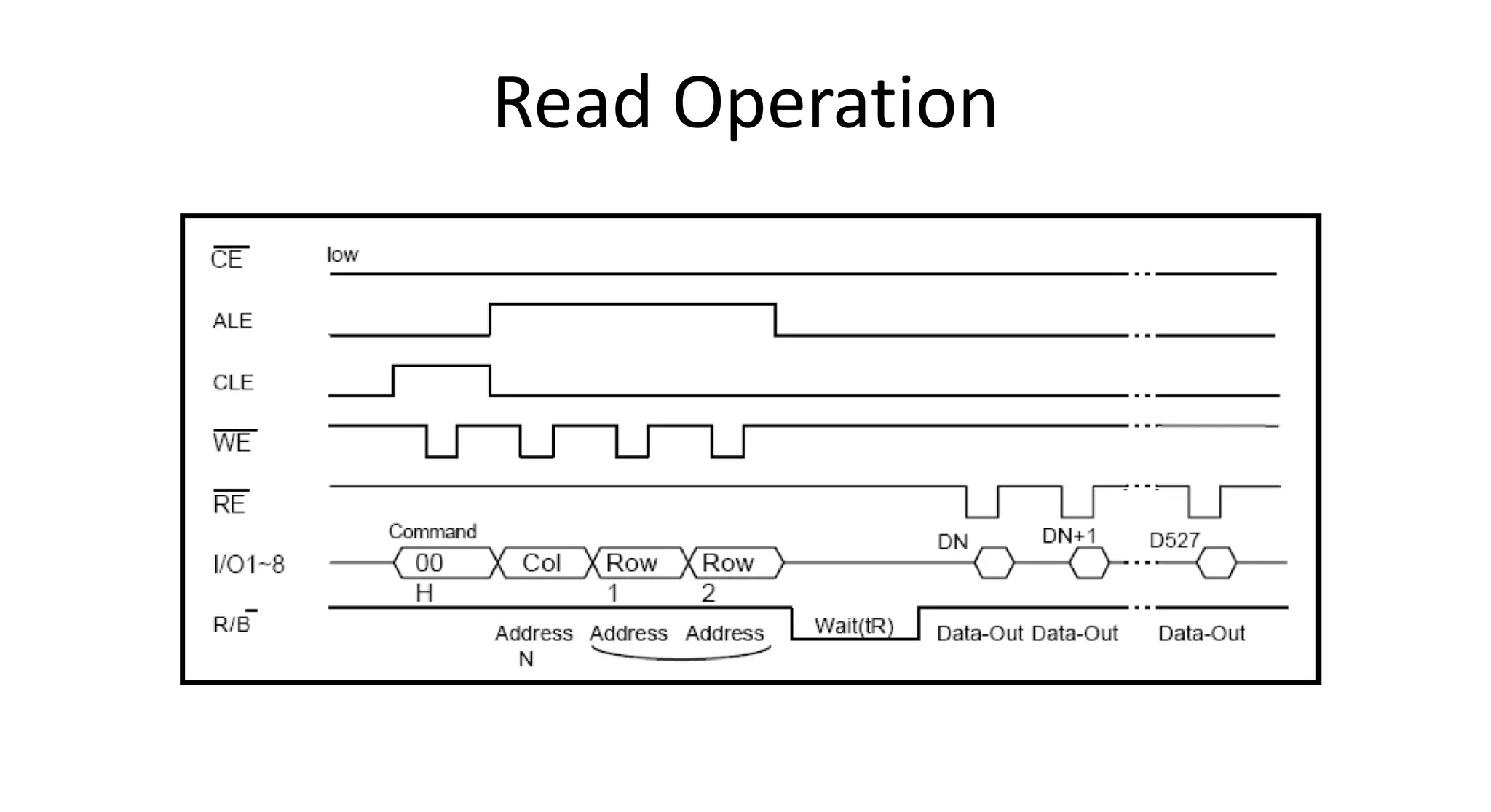
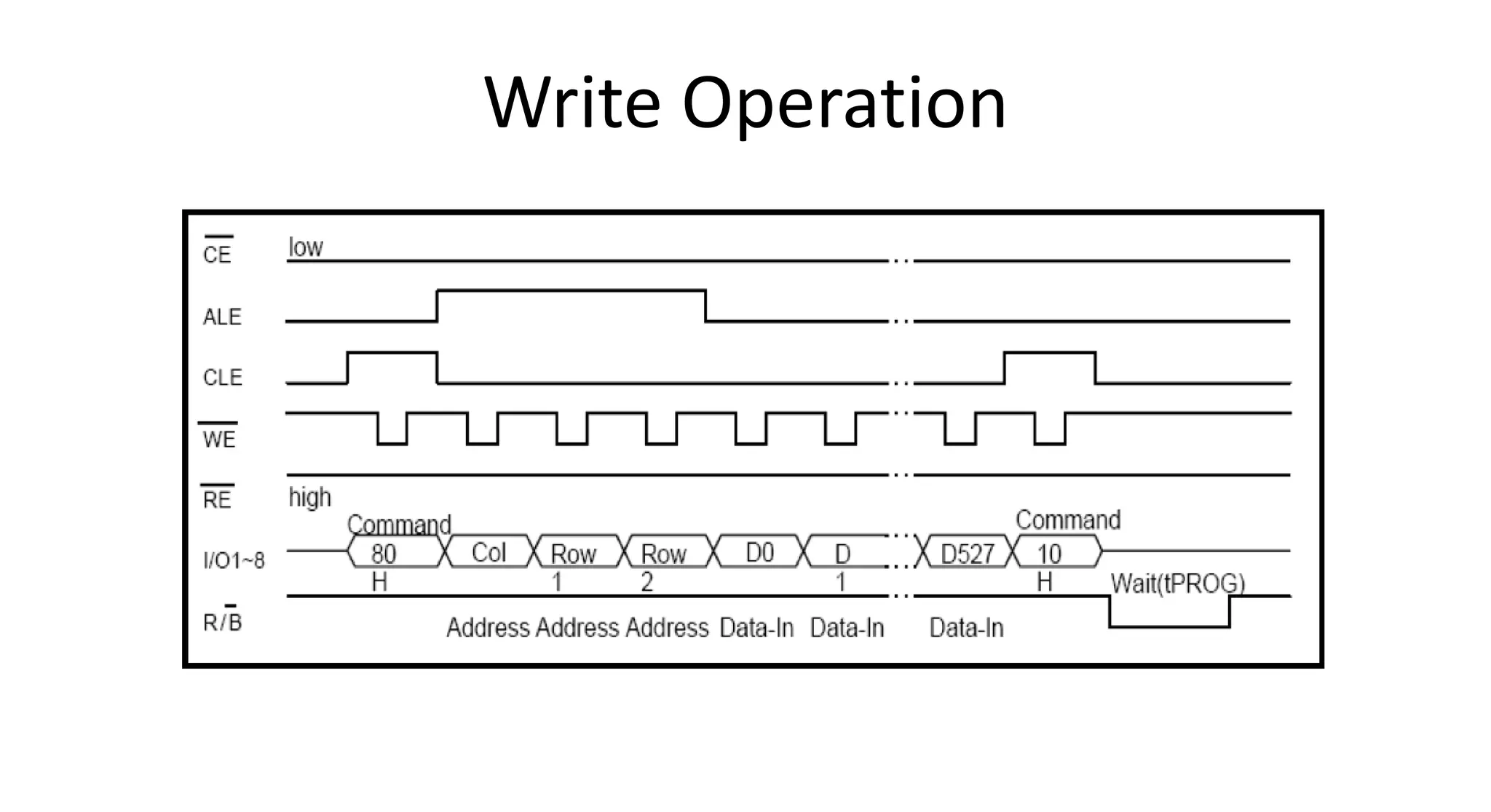
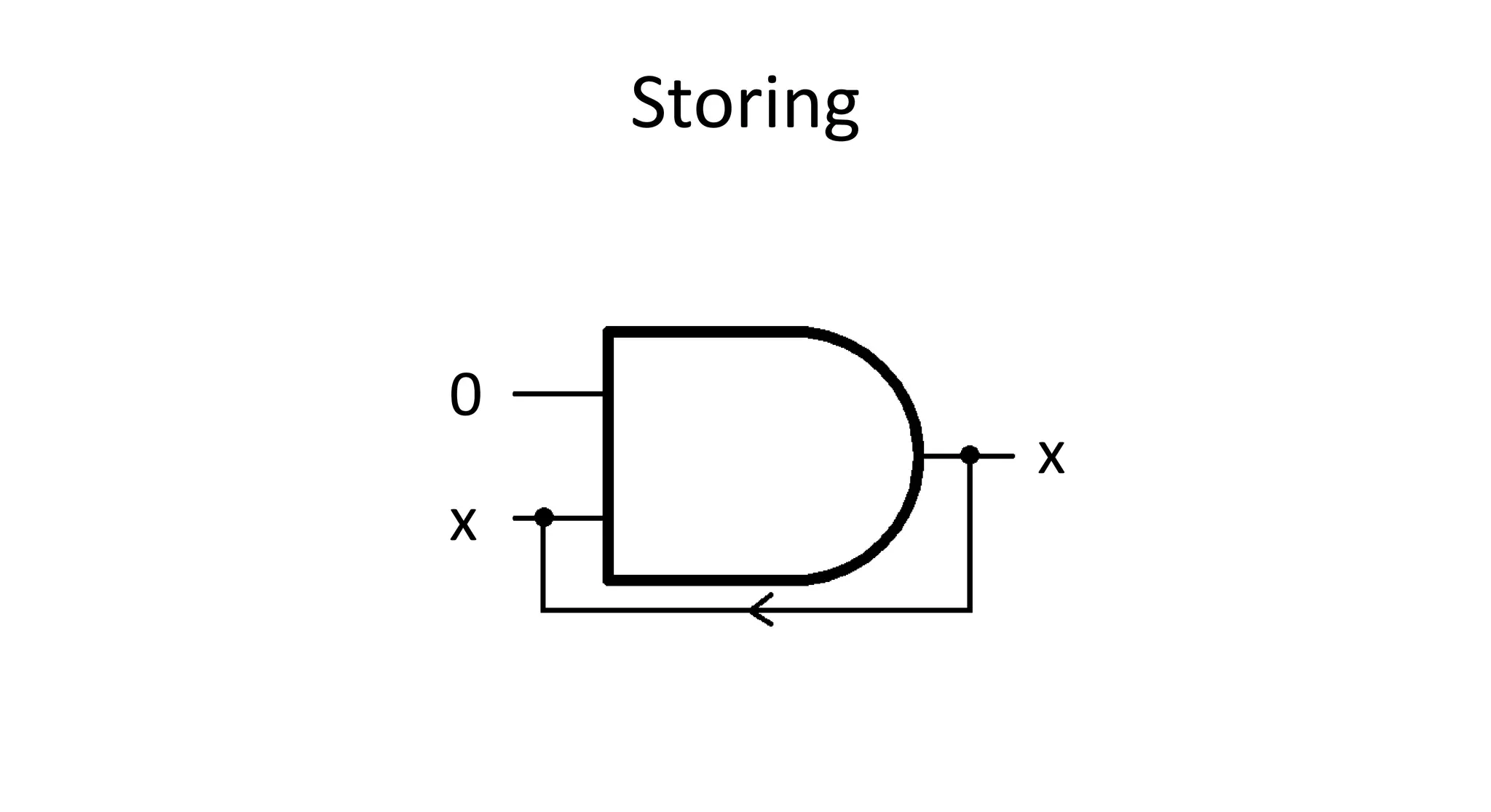
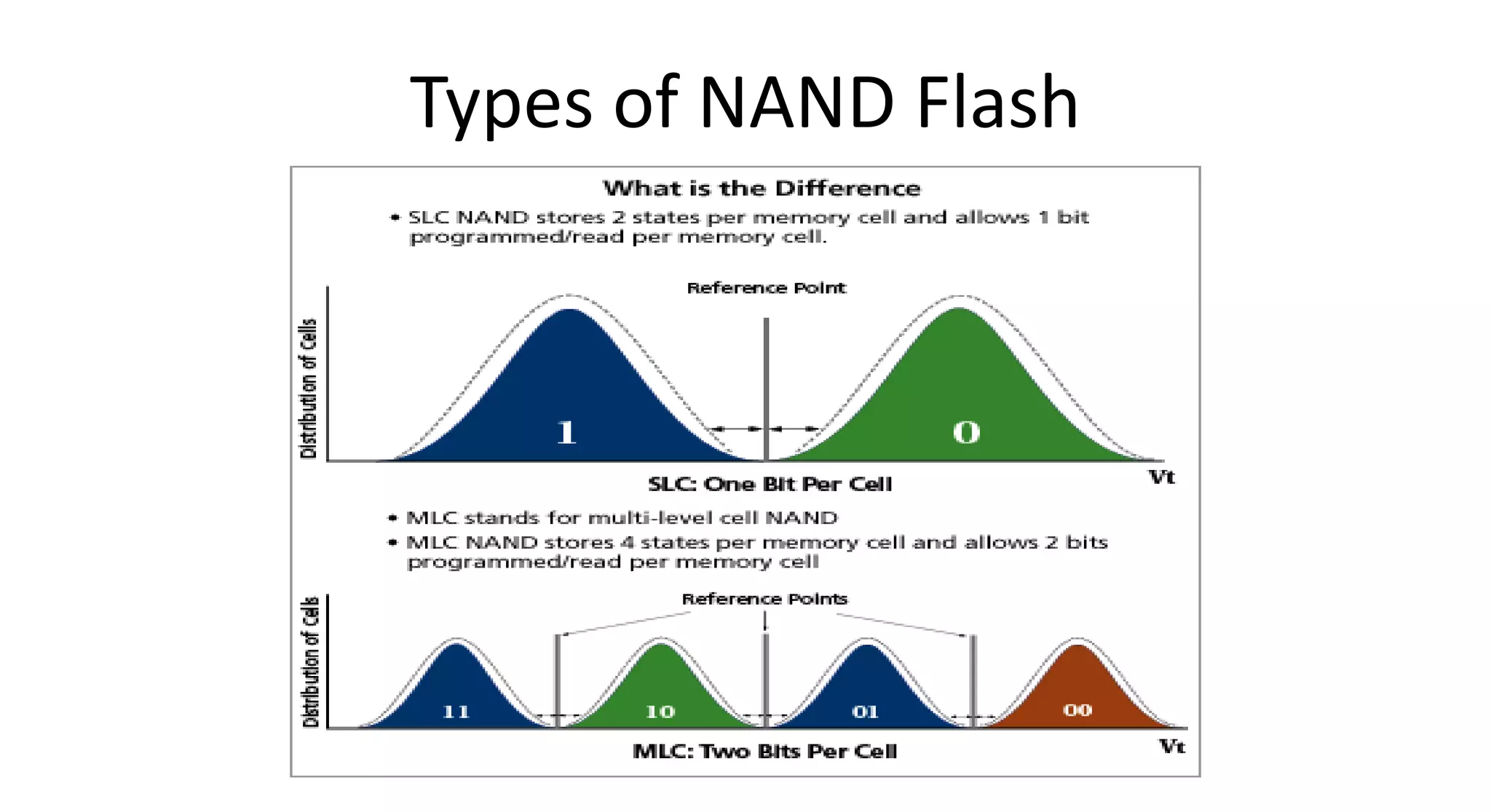
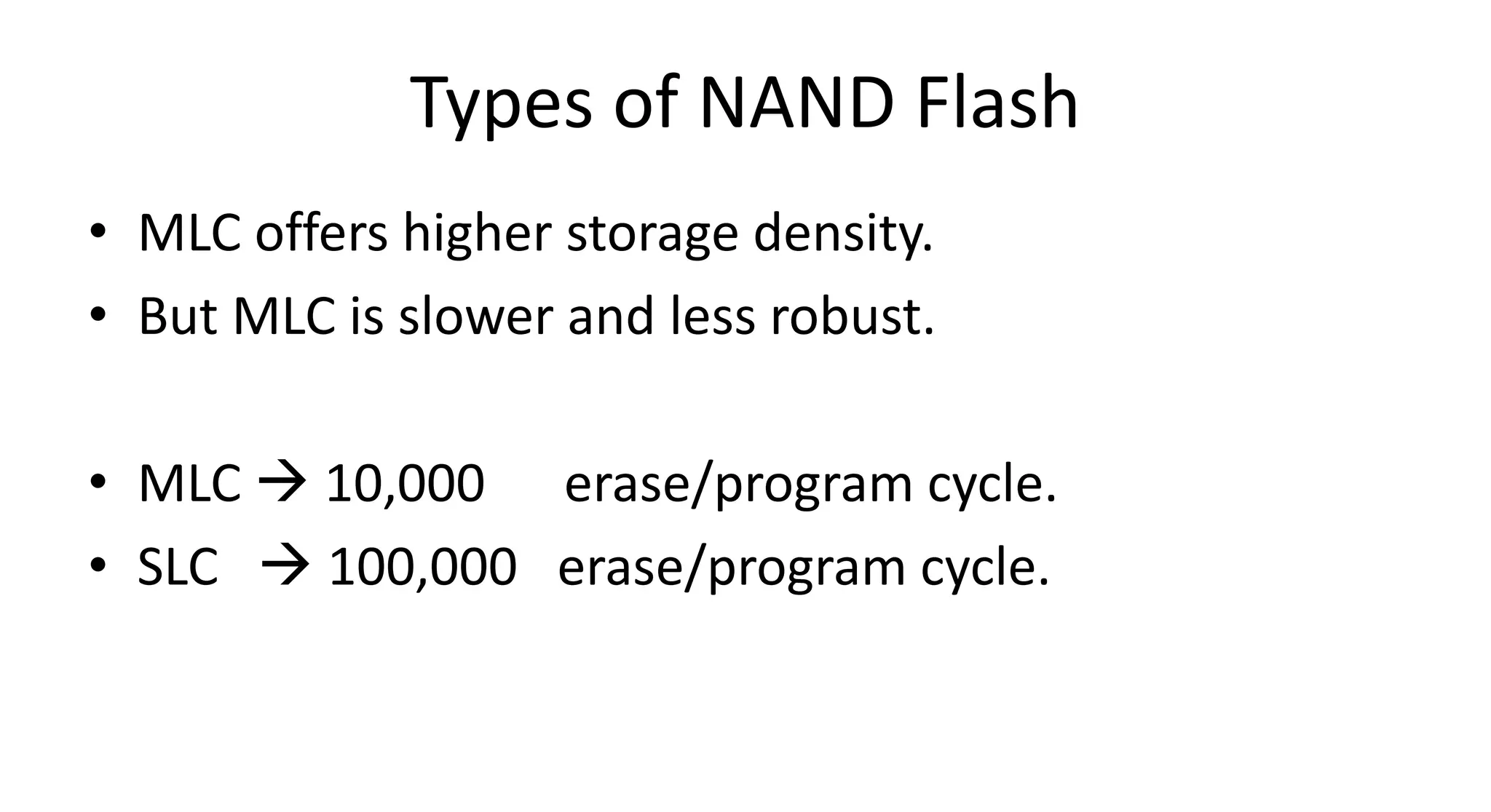
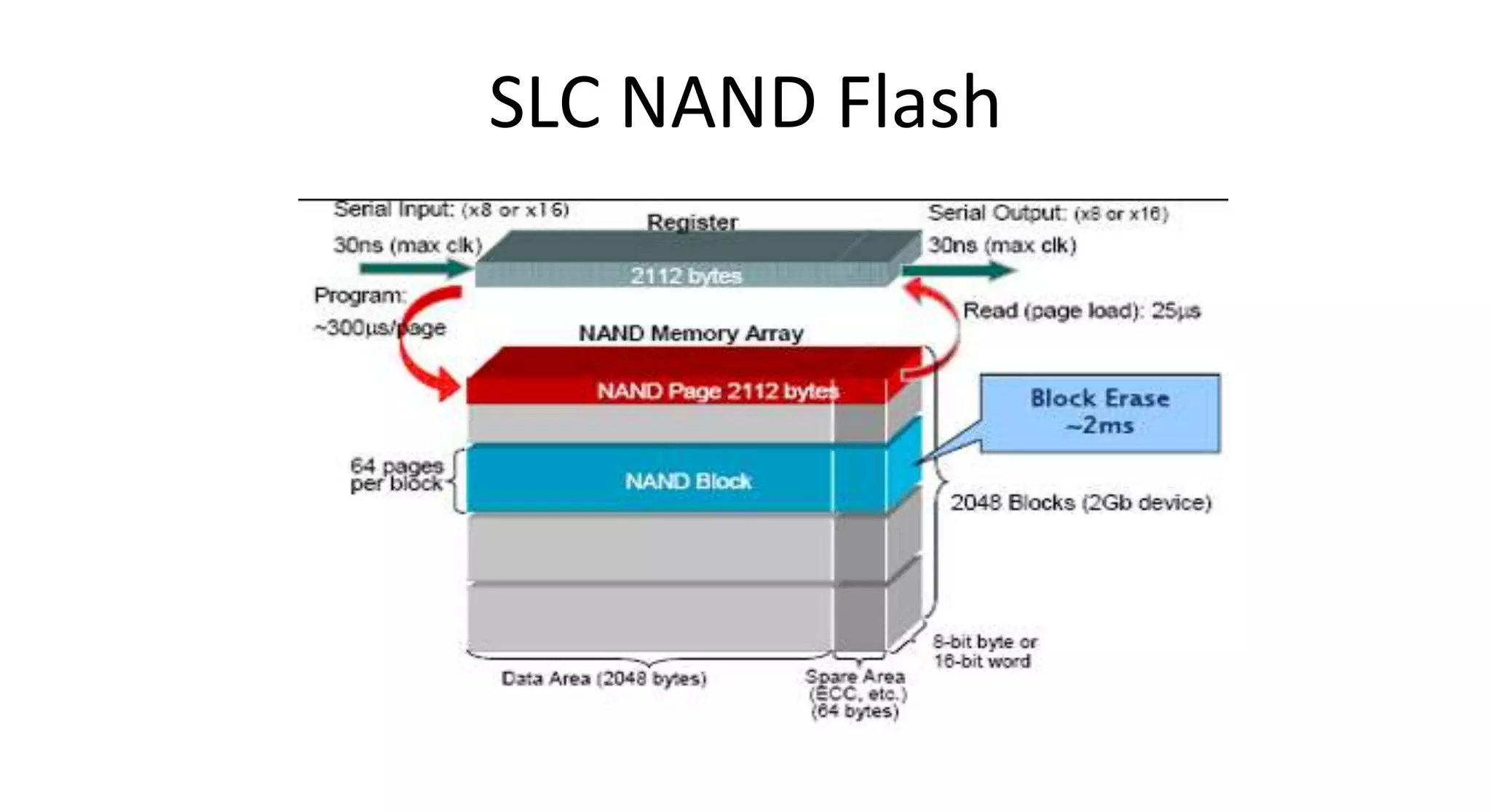
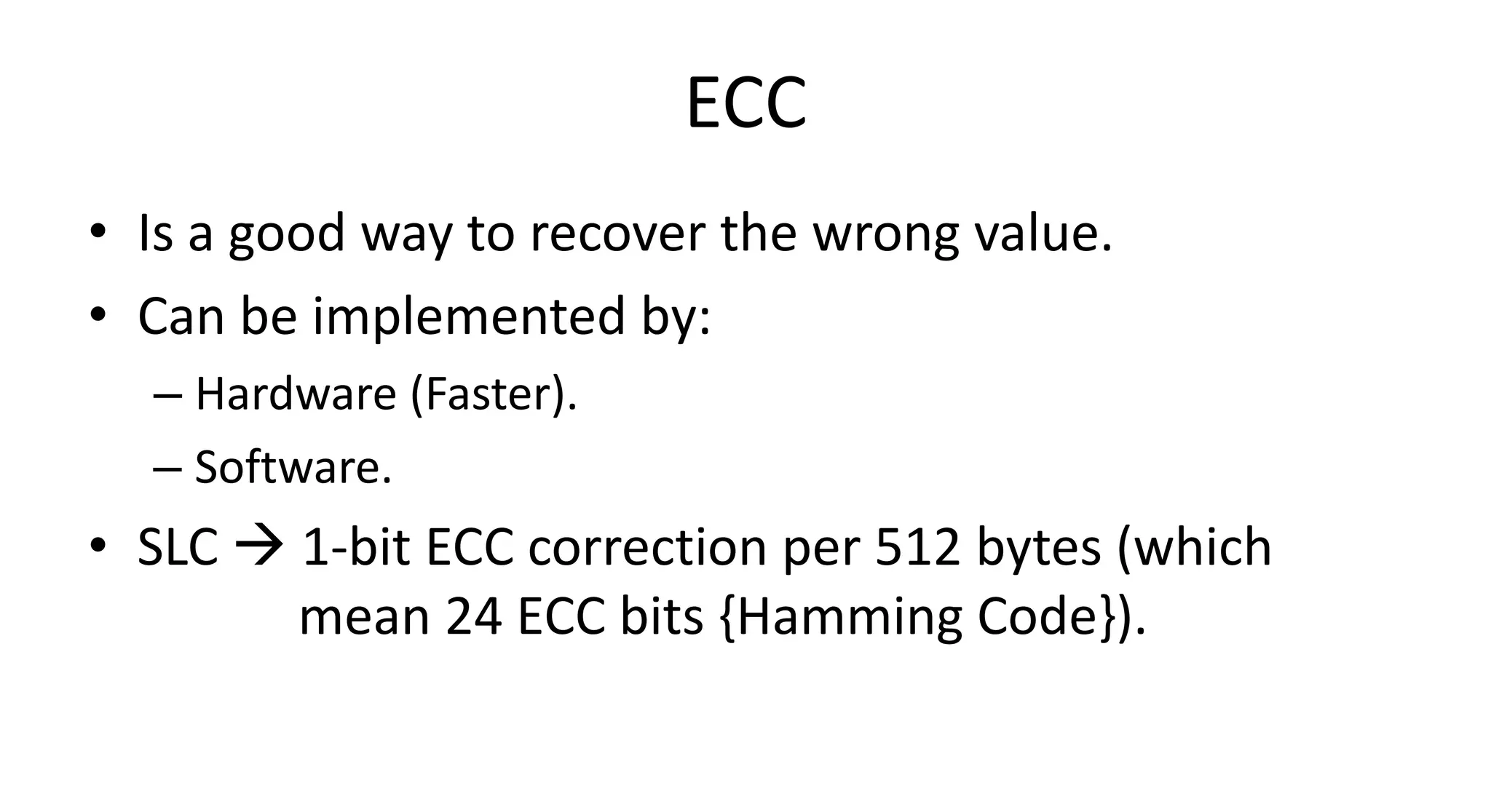
This document discusses NAND flash memory, which is used in USB flash drives for portable storage. It describes how NAND flash works, including that it has a controller that sends commands serially to program and read the flash. Issues with NAND flash include bad blocks, long access times since it is not random access, and short lifetimes due to being programmable. Technologies like wear leveling aim to extend the lifetime by distributing writes across blocks.