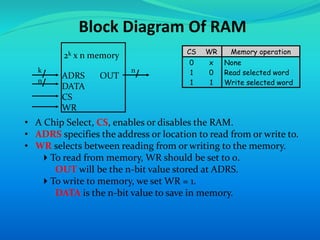
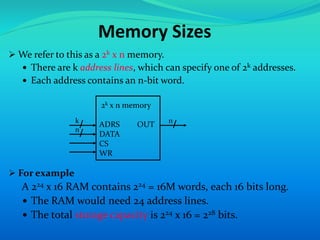
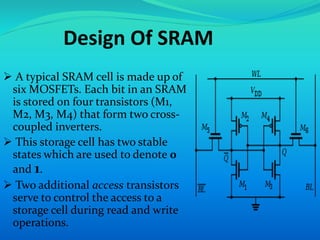
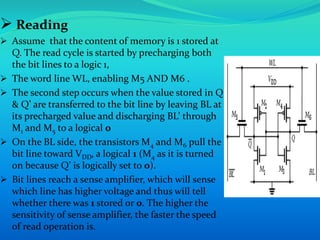
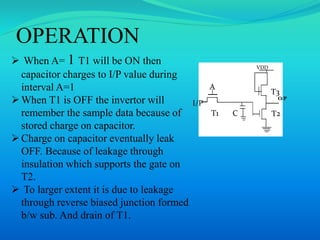
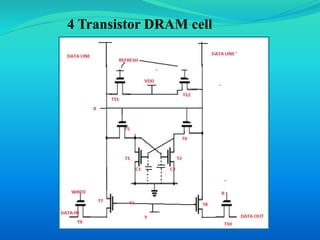
This document provides an overview of RAM (random access memory). It describes RAM as volatile memory that does not retain data when power is turned off. The document then discusses RAM components like SRAM and DRAM. SRAM stores bits using a flip-flop circuit that retains data as long as power is applied, while DRAM uses a capacitor and transistor that must be regularly refreshed to maintain its charge and data. The document concludes with a comparison of SRAM and DRAM, noting key differences in their data volatility, refresh needs, cell structures, speeds and costs.