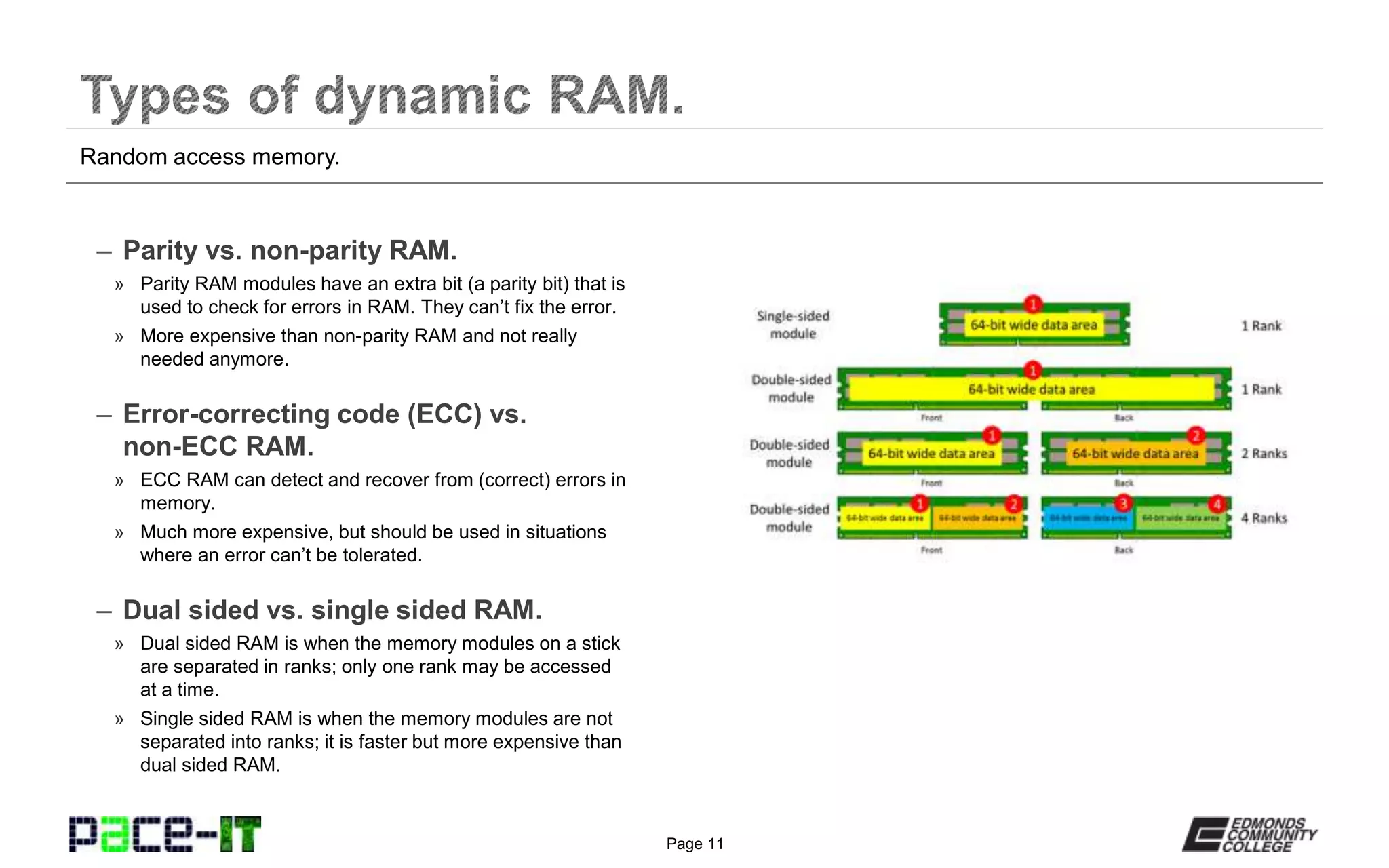
Computer memory usually refers to dynamic random access memory (DRAM). Static RAM (SRAM) is quicker but much more expensive. Modern RAM started with synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) and is currently at double data rate type 3 (DDR3). Special considerations for RAM include parity and error correcting code (ECC) for checking and correcting errors, single or dual sided modules, single or multi-channel configurations, and ensuring RAM types and speeds are compatible with the motherboard.