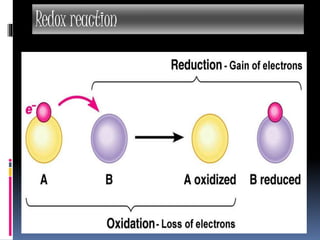
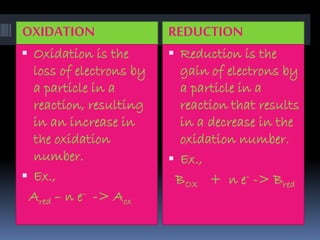
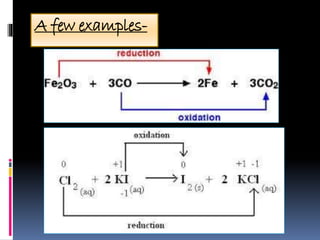
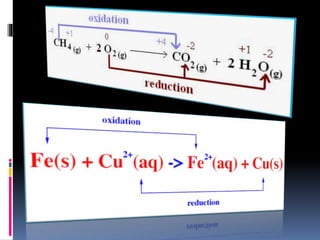
The document discusses redox reactions, which are electron transfer processes where oxidation involves the loss of electrons and reduction involves the gain of electrons. It outlines the balancing of these reactions in aqueous solutions and provides examples to illustrate the concepts of oxidizing and reducing agents. Additionally, it includes exercises for understanding the identification of oxidized and reduced substances in given reactions.