This document discusses solubility and solubility products. It defines solubility as the amount of a substance that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent. The solubility product (Ksp) is the mathematical product of the dissolved ion concentrations raised to their stoichiometric coefficients. Ksp is a constant for a given ionic compound at a given temperature. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to calculate Ksp from solubility data and vice versa. Factors that affect solubility like temperature, common ions, pH, and complex ion formation are also mentioned. Finally, different types of solutions like unsaturated, saturated, and supersaturated solutions are defined.



![Solubility product
In general, solubility product, Ksp, is the mathematical
product of its dissolved ion concentrations raised to the
power of their stoichiometric coefficients. This
statement is called the solubility product principle
MyXz (s) yMZ+
(aq) + zXY-
(aq)
[ ] [ ]zyyz
sp
XMK −+
=
Solubility product constant Molar solubility of the ions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solubilityandsolubilityproduct-150407063648-conversion-gate01/85/Solubility-and-solubility-product-4-320.jpg)
![Solubility product
Solubility product constant (Ksp)
Most salts dissociate into ions when they dissolve.
For example:
BaSO4(s) ⇌ Ba2+
(aq) + SO4
2-
(aq)
This equilibrium system may be described by the
mass-action expression
Ksp = [Ba2+
][SO4
2-
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solubilityandsolubilityproduct-150407063648-conversion-gate01/85/Solubility-and-solubility-product-5-320.jpg)
![BaSO4(s) ⇌ Ba2+
(aq)+ SO4
2-
(aq)
• The Ba2+
concentration and the SO4
2–
concentration
are equal since for each BaSO4 unit that dissolves
one Ba2+
and one SO4
2–
ion form.
Solubility = s = [Ba2+
] = [SO4
2–
]
From the above equation we know that
Ksp = [Ba2+
] [SO4
2–
]
Ksp = s × s = s2
Ksp = [Ba2+
] [SO4
2-
]
solubilityproduct](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solubilityandsolubilityproduct-150407063648-conversion-gate01/85/Solubility-and-solubility-product-6-320.jpg)
![Problems on solubility product
• Calculate the Ksp value of BaSO4 which has a
solubility of 3.9×10 5‒
mol/L at 25°C.
BaSO4(s) ⇌ Ba2+
(aq)+ SO4
2-
(aq)
Ksp = [Ba2+
] [SO4
2–
]
Ksp = s × s = s2
= 3.9×10 5‒
× 3.9×10 5‒
= 1.52×10 9‒](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solubilityandsolubilityproduct-150407063648-conversion-gate01/85/Solubility-and-solubility-product-7-320.jpg)
![Solubility and Solubility Products
(1) What is the solubility of AgCl if the Ksp is 1.6 x 10-10
AgCl(s) ⇌ Ag+
(aq) + Cl-
(aq)
Ksp = [Ag+
][Cl-
]
If s is the solubility of AgCl, then:
[Ag+
] = s and [Cl-
] = s
Ksp = (s)(s) = s2
= 1.6 x 10-10
s =
s = 1.3 x 10-5
mol/L
-10
10x1.6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solubilityandsolubilityproduct-150407063648-conversion-gate01/85/Solubility-and-solubility-product-8-320.jpg)
![• What is the solubility of CuS if the Ksp is 1.27× 10–45
.
CuS ⇌ Cu2+
+ S2–
Ksp = [Cu2+
] [S2–
]
= [s] [s]
= s2
s =
=
= 3.56 × 10–23
M
spK
-45
10x1.27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solubilityandsolubilityproduct-150407063648-conversion-gate01/85/Solubility-and-solubility-product-9-320.jpg)
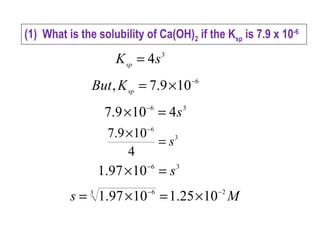
![(1) What is the solubility of Ca(OH)2 if the Ksp is 7.9 x 10-6
Ca(OH)2 (s) Ca2+
(aq) + 2OH-
(aq)
1×s 2×s
[ ] [ ]212
sp OHCaK −+
=
[ ] [ ]21
sp 21K ss ××=
)2()2()1(Ksp sss ××=
)()221(Ksp sss ×××××=
3
sp 4K s=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solubilityandsolubilityproduct-150407063648-conversion-gate01/85/Solubility-and-solubility-product-10-320.jpg)
![Solubility and Solubility Products
What is the solubility of Mg(OH)2 if the Ksp is 1.6 x 10-10
Mg(OH)2(s) ⇌ Mg2+
(aq) + 2 OH-
(aq)
Ksp = [Mg2+
][OH-
]2
= 8.9 x 10-12
If the solubility of Mg(OH)2 is s mol/L, then:
[Mg2+
] = s mol/L and [OH-
] = 2s mol/L,
Ksp = (s)(2s)2
= 4s3
= 8.9 x 10-12
s = 1.3 x 10-4
mol/L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solubilityandsolubilityproduct-150407063648-conversion-gate01/85/Solubility-and-solubility-product-12-320.jpg)

