Chemical bonds form when atoms share or transfer electrons. There are several main types of bonds:
- Ionic bonds form when metals transfer electrons to nonmetals to form positive and negative ions that are attracted to each other. Ionic compounds are crystalline and dissolve in water.
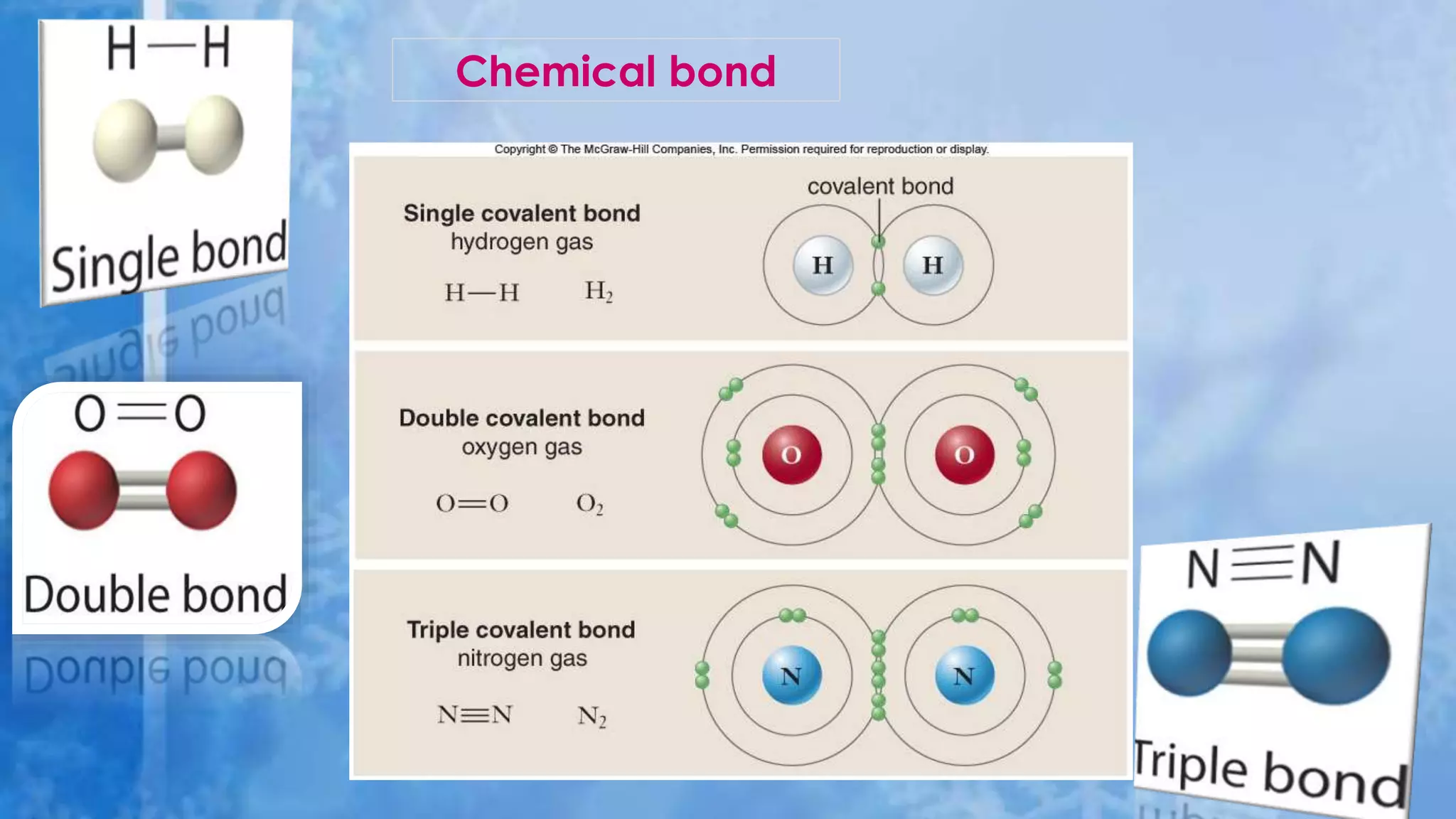
- Covalent bonds form when atoms share two or more valence electrons to achieve stability. Covalent bond strength depends on the number of electron pairs shared. Covalent compounds exist as discrete molecules.
- Metallic bonds result from the attraction between positively charged metal ions and delocalized electrons in the "sea of electrons" in the solid metal. Metallic bonding explains the properties of metals like conductivity.









![› Always formed between metals and non-metals
[METALS ]
+ [NON-METALS ]
-
Lost e-
Gained e-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typesofchemicalbond-150209095906-conversion-gate01/75/Types-of-chemical-bonds-10-2048.jpg)