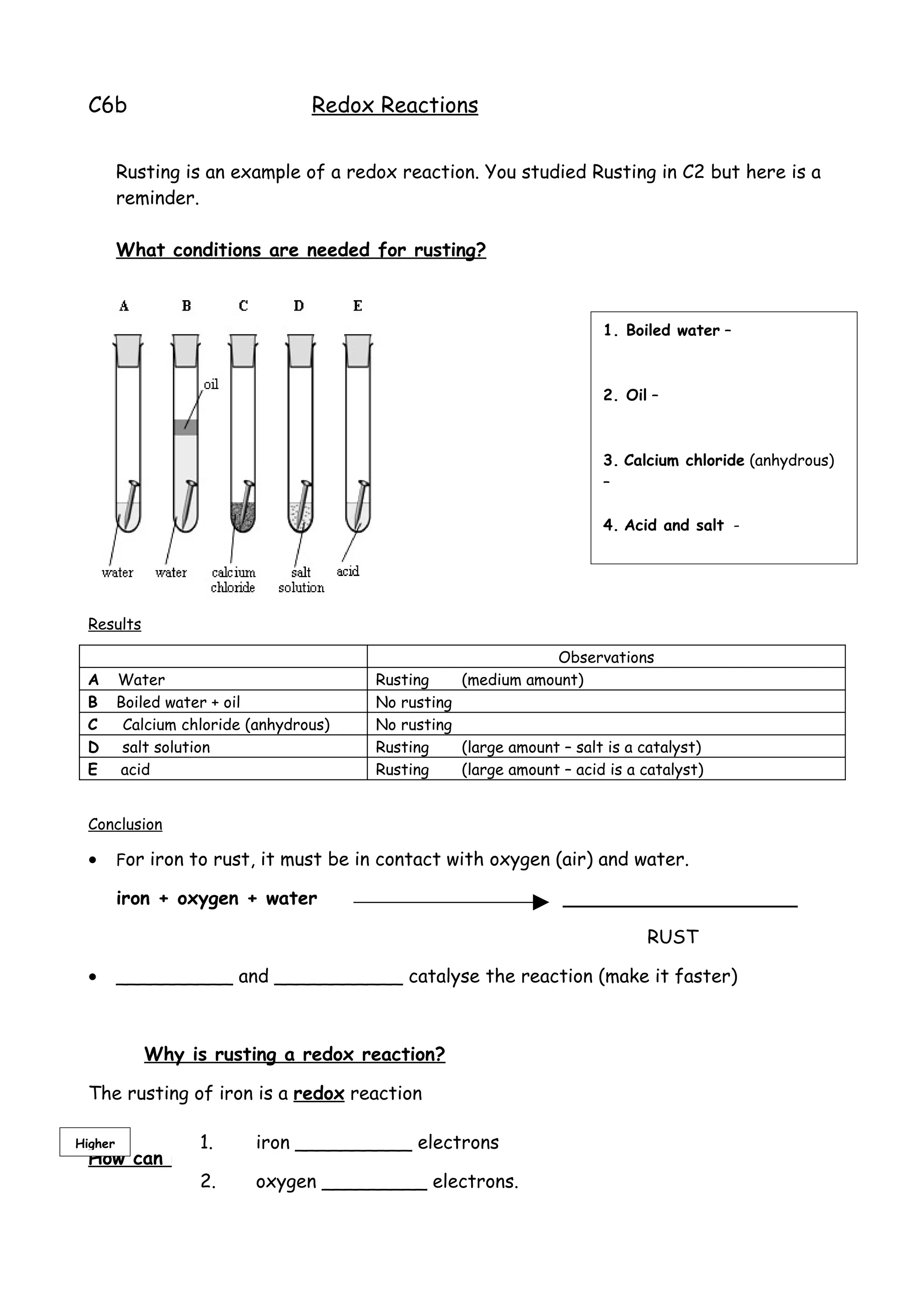
Rusting is an example of a redox reaction where:
1. Iron loses electrons and is oxidized.
2. Oxygen gains electrons and is reduced.
3. For rusting to occur, iron needs to be in contact with both oxygen and water, and acids or salts can catalyze the reaction.